Honeybees help gather data about a city's health


Analyzing honeybees could provide key insight into a city's microbiome as well as the health of its people, according to a study published in the journal Environmental Microbiome. It explains that "honeybees may be effective collaborators in gathering samples of urban microbiota," due to their foraging habits.
"Honeybees will gather a vast number of microbes day to day, far beyond things they are seeking out," said Kevin Slavin, who worked on the report. "They've been optimized by evolution to do everything that the swabs do." The research team collected samples from hives and hove debris in New York City, Melbourne, Venice, and Tokyo. They found that each city had its own "unique genetic signature," per The Independent. "It didn't feel like a disjointed metric from all of the other things that we know about these cities," said Elizabeth Hénaff, lead author of the report. "It actually kind of felt like a puzzle piece that we didn't even know existed."
A microbiome is "the unseen communities of microbes, fungi, viruses, and bacteria that live inside and around us," as defined by Bloomberg. Research has shown that exposure to a diverse microbiome generally leads to better health outcomes. "For those of us who live in cities – which is more than half of the global population at this point – it is important to be able to characterize the microbiomes of the cities that we live in, and work in, and sleep in," commented Hénaff.
Subscribe to The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
This analysis could be used in the future to quantify differences in health among various groups as a result of environmental inequality. "We tie that, currently, to things like pollution or even shade, [but] the idea is in part just to collect as much data as we can ... to better understand what produces healthier neighborhoods, and can it be measured," explained Slavin.
Sign up for Today's Best Articles in your inbox
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Devika Rao has worked as a staff writer at The Week since 2022, covering science, the environment, climate and business. She previously worked as a policy associate for a nonprofit organization advocating for environmental action from a business perspective.
-
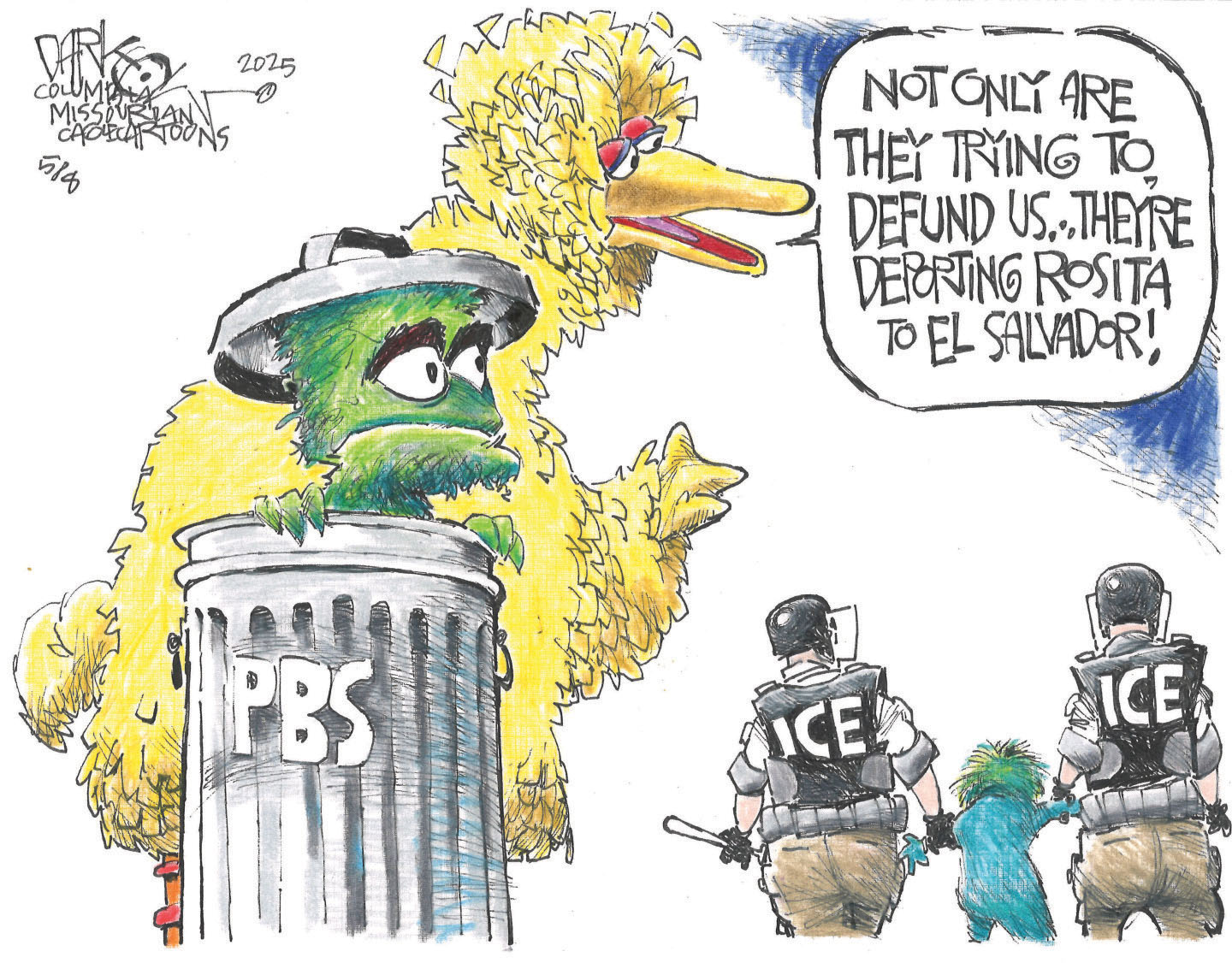 5 streetwise cartoons about defunding PBS
5 streetwise cartoons about defunding PBSCartoons Artists take on immigrant puppets, defense spending, and more
-
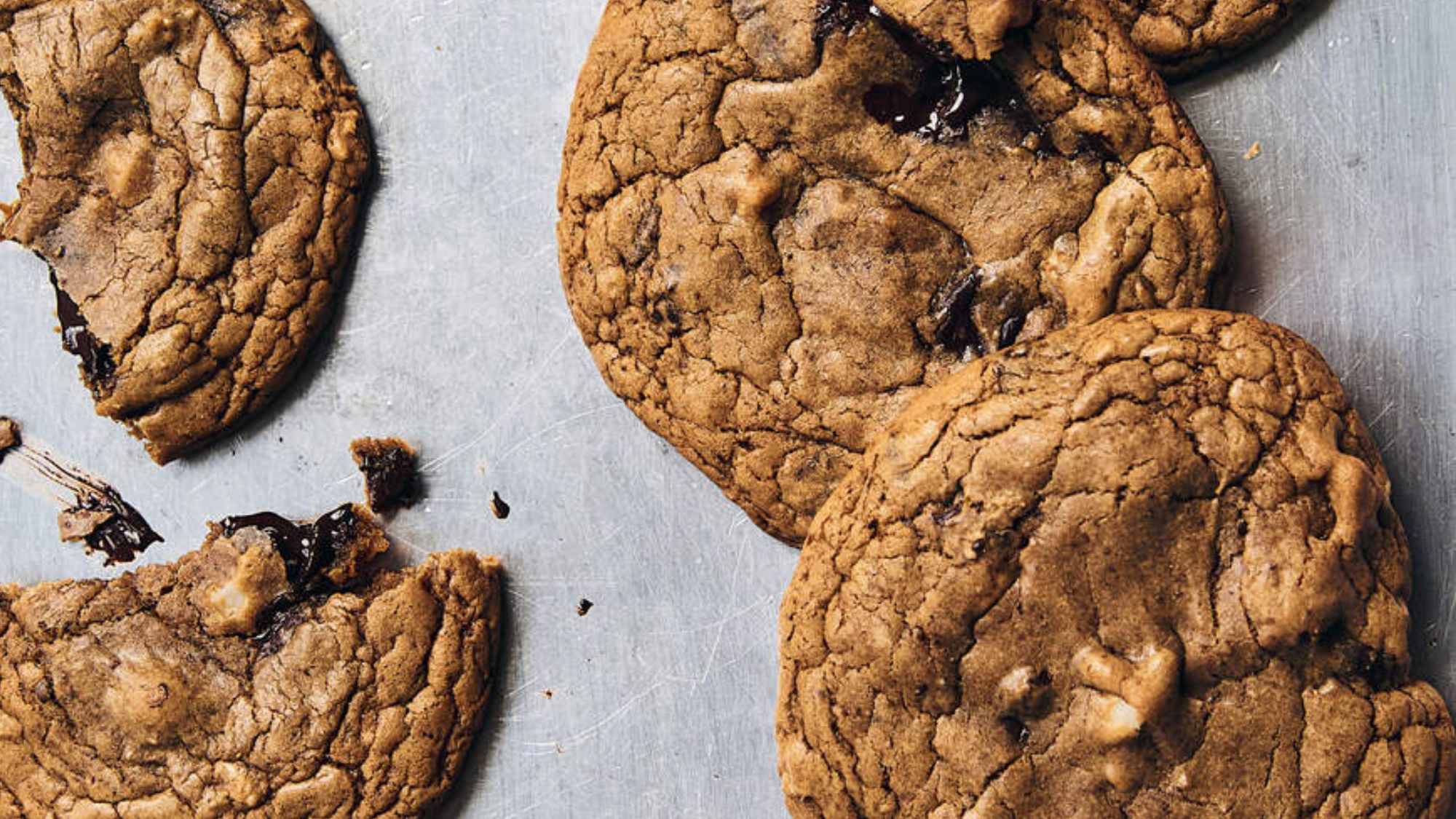 Dark chocolate macadamia cookies recipe
Dark chocolate macadamia cookies recipeThe Week Recommends These one-bowl cookies will melt in your mouth
-
 Israel's plan to occupy Gaza
Israel's plan to occupy GazaIn Depth Operation Gideon's Chariots will see Israel sending thousands of troops into Gaza later this month to seize control of the strip
-
 'Bioelectric bacteria on steroids' could aid in pollutant cleanup and energy renewal
'Bioelectric bacteria on steroids' could aid in pollutant cleanup and energy renewalUnder the radar The new species is sparking hope for environmental efforts
-
 Sea lion proves animals can keep a beat
Sea lion proves animals can keep a beatspeed read A sea lion named Ronan beat a group of college students in a rhythmic dance-off, says new study
-
 Earth's oceans were once green and could one day turn purple
Earth's oceans were once green and could one day turn purpleUnder the radar The current blue may be temporary
-
 Humans heal much slower than other mammals
Humans heal much slower than other mammalsSpeed Read Slower healing may have been an evolutionary trade-off when we shed fur for sweat glands
-
 Novel 'bone collector' caterpillar wears its prey
Novel 'bone collector' caterpillar wears its preySpeed Read Hawaiian scientists discover a carnivorous caterpillar that decorates its shell with the body parts of dead insects
-
 Scientists find hint of alien life on distant world
Scientists find hint of alien life on distant worldSpeed Read NASA's James Webb Space Telescope has detected a possible signature of life on planet K2-18b
-
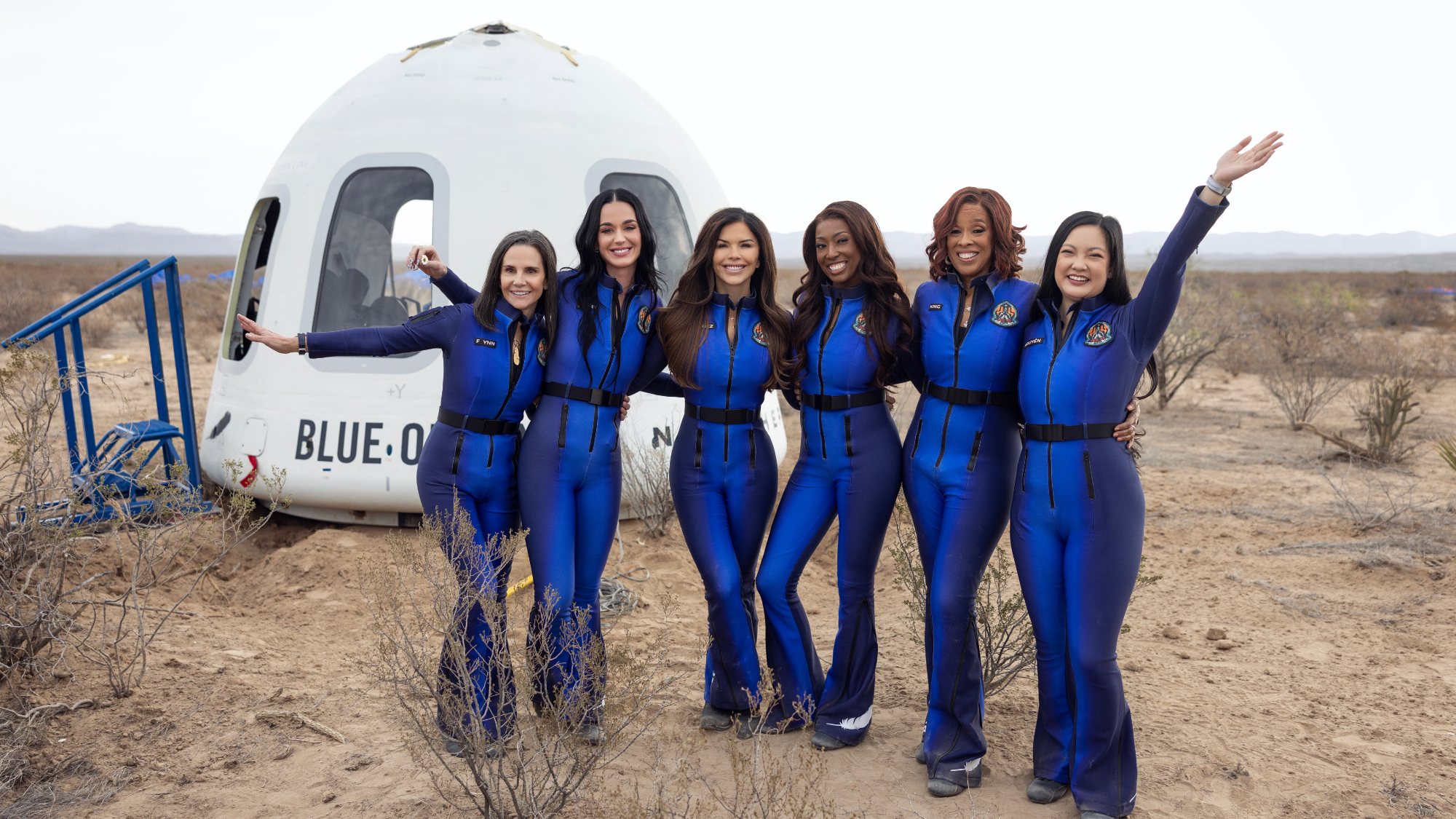 Katy Perry, Gayle King visit space on Bezos rocket
Katy Perry, Gayle King visit space on Bezos rocketSpeed Read Six well-known women went into lower orbit for 11 minutes
-
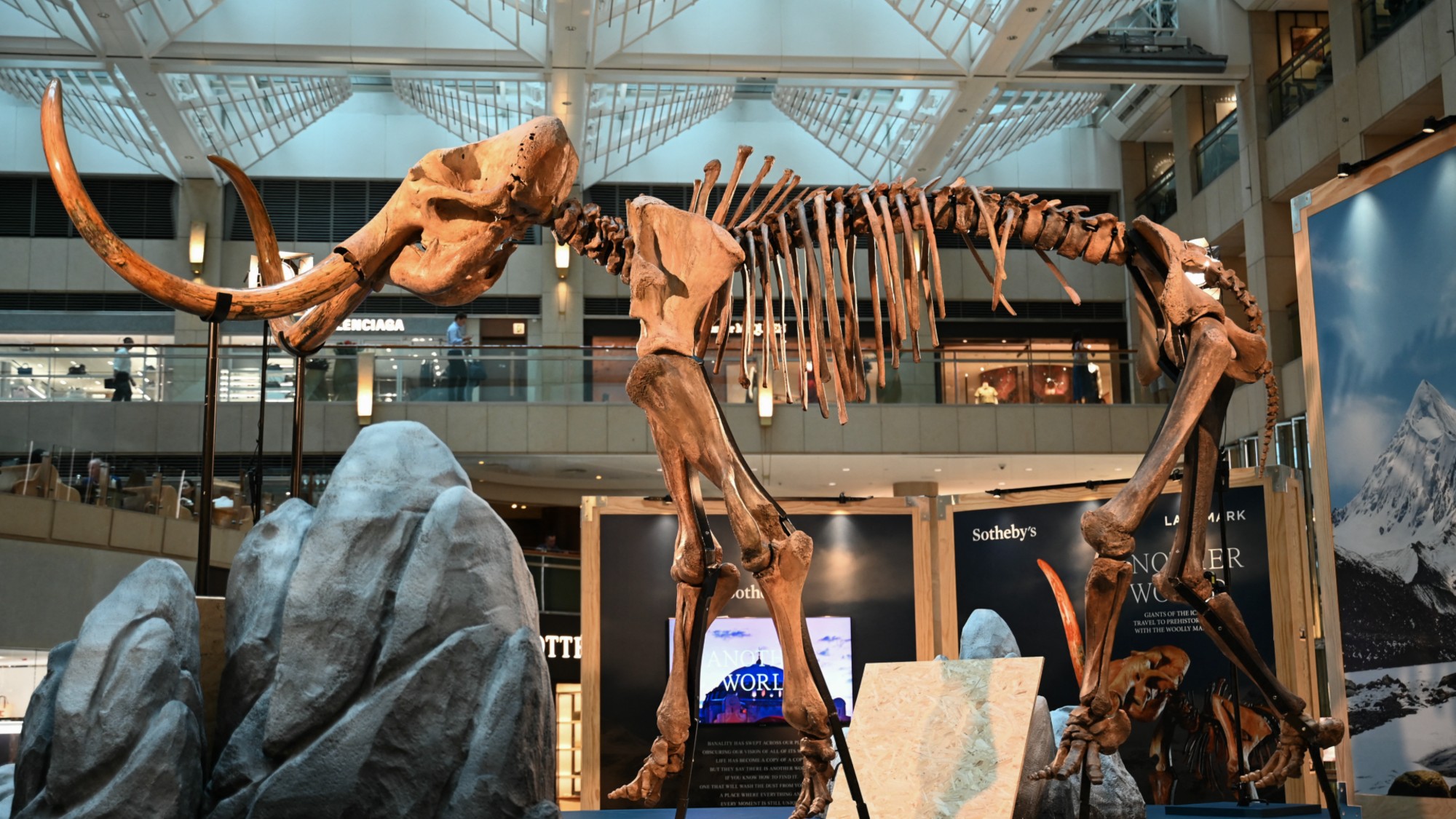 The dubious nature of de-extinction
The dubious nature of de-extinctionThe Explainer Is it a vanity project backed by billions, or the future of animal conservation?