Experts believe Mexico's coronavirus cases could be 17 times higher than official tally


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
The Mexican government has said it assumes the true number of coronavirus cases in the country is eight times higher than what is officially reported, but experts believe the actual number of cases could be 17 times higher, Vox reports.
As of Wednesday, Mexico has reported 38,000 coronavirus infections and close to 4,000 deaths. Funeral home directors, mayors, doctors, and former officials have said they reported deaths that haven't been reflected in the government's tally; the mayor of Chimalhuacán told Al Jazeera the town had 87 coronavirus deaths, but the government "counted us as having 24 dead."
It's unclear if the discrepancy is due to inefficiency or if the numbers are deliberately being undercounted, Vox notes. "If Mexico is good at anything, it's hiding numbers," said Dr. Laurie Ann Ximénez-Fyvie of the National Autonomous University of Mexico. El País reports that Mexico, which has a low testing rate, likely has between 620,000 and 730,000 COVID-19 cases. "We don't even know who the sick people are, and we don't know where they are," Ximénez-Fyvie said.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Mexican President Andrés Manuel López Obrador has been criticized for his response to the coronavirus and accused of not taking it seriously. In late March, he traveled to several cities and met supporters, even shaking hands with the mother of convicted drug lord Joaquin "El Chapo" Guzman in Badiraguato. Read more about how the Mexican government is handling the coronavirus pandemic and the state of its health care system at Vox.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Catherine Garcia has worked as a senior writer at The Week since 2014. Her writing and reporting have appeared in Entertainment Weekly, The New York Times, Wirecutter, NBC News and "The Book of Jezebel," among others. She's a graduate of the University of Redlands and the Columbia University Graduate School of Journalism.
-
 Tourangelle-style pork with prunes recipe
Tourangelle-style pork with prunes recipeThe Week Recommends This traditional, rustic dish is a French classic
-
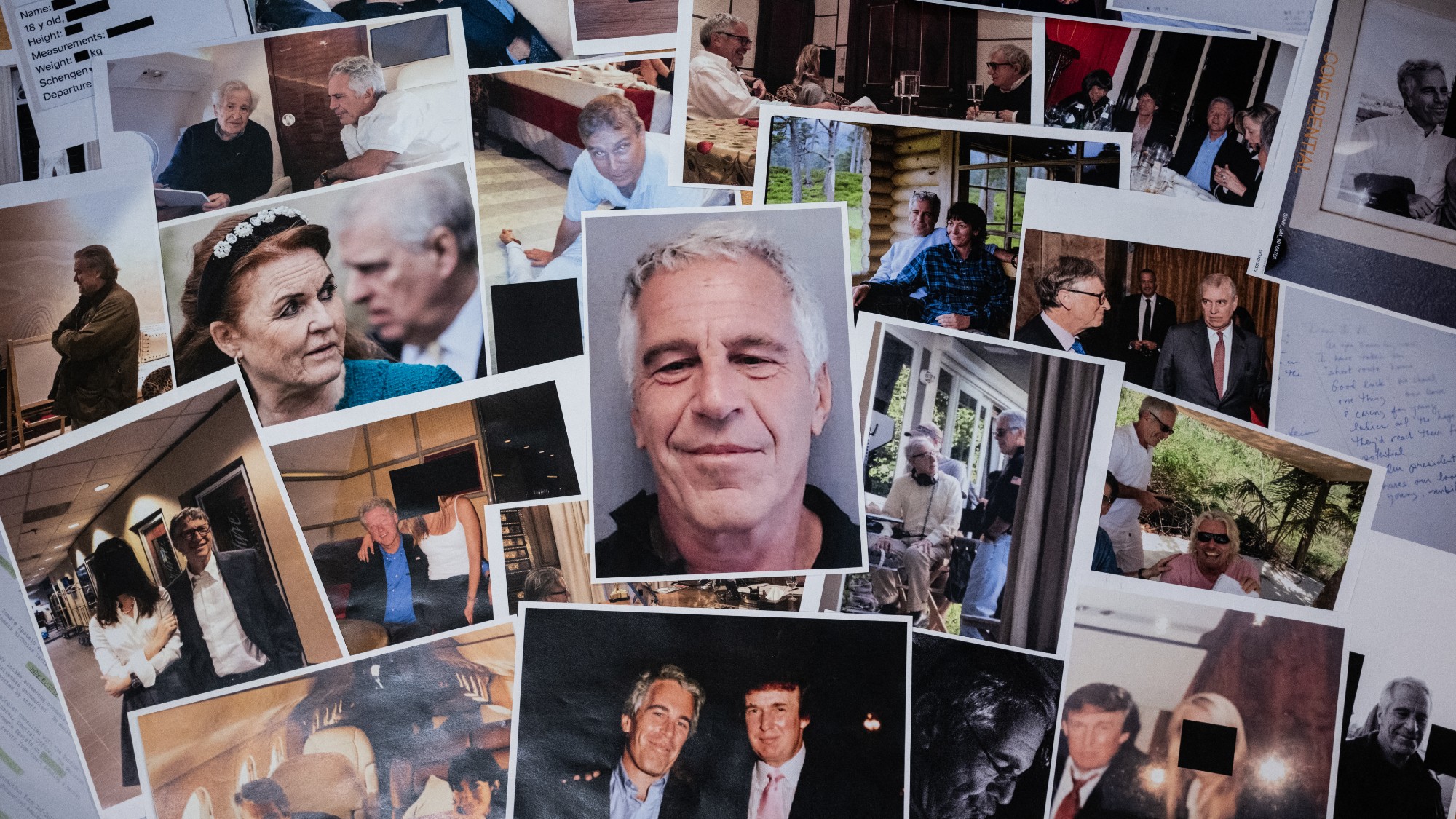 The Epstein files: glimpses of a deeply disturbing world
The Epstein files: glimpses of a deeply disturbing worldIn the Spotlight Trove of released documents paint a picture of depravity and privilege in which men hold the cards, and women are powerless or peripheral
-
 Jeff Bezos: cutting the legs off The Washington Post
Jeff Bezos: cutting the legs off The Washington PostIn the Spotlight A stalwart of American journalism is a shadow of itself after swingeing cuts by its billionaire owner
-
 Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinations
Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinationsSpeed Read In a widely condemned move, the CDC will now recommend that children get vaccinated against 11 communicable diseases, not 17
-
 FDA OKs generic abortion pill, riling the right
FDA OKs generic abortion pill, riling the rightSpeed Read The drug in question is a generic version of mifepristone, used to carry out two-thirds of US abortions
-
 RFK Jr. vaccine panel advises restricting MMRV shot
RFK Jr. vaccine panel advises restricting MMRV shotSpeed Read The committee voted to restrict access to a childhood vaccine against chickenpox
-
 Texas declares end to measles outbreak
Texas declares end to measles outbreakSpeed Read The vaccine-preventable disease is still spreading in neighboring states, Mexico and Canada
-
 RFK Jr. shuts down mRNA vaccine funding at agency
RFK Jr. shuts down mRNA vaccine funding at agencySpeed Read The decision canceled or modified 22 projects, primarily for work on vaccines and therapeutics for respiratory viruses
-
 Measles cases surge to 33-year high
Measles cases surge to 33-year highSpeed Read The infection was declared eliminated from the US in 2000 but has seen a resurgence amid vaccine hesitancy
-
 Kennedy's vaccine panel signals skepticism, change
Kennedy's vaccine panel signals skepticism, changeSpeed Read RFK Jr.'s new vaccine advisory board intends to make changes to the decades-old US immunization system
-
 Kennedy ousts entire CDC vaccine advisory panel
Kennedy ousts entire CDC vaccine advisory panelspeed read Health Secretary RFK Jr. is a longtime anti-vaccine activist who has criticized the panel of experts
