Is there a savings glut?
To accurately measure the amount of savings in the economy, we have to look beyond the personal savings rate

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Over at Project Syndicate, Barry Eichengreen asks why interest rates have been falling around the Western world for the last 30 years:
Adjusted for inflation, interest rates have been falling for three decades, and their current low level encourages investors, searching for yield, to take on additional risk. Low rates also leave central banks little room for loosening monetary policy in a slowdown, because nominal interest cannot fall below zero. [Project Syndicate]
However, Eichengreen immediately dismisses the obvious culprit — the idea that there is a savings glut. Interest rates are the price of lending money. If more people want to save than lend, then interest rates will tend to trend lower:
Some point to an increase in global saving, attributable mainly to high-saving emerging markets. Readers will detect here echoes of the "savings glut" argument popularized nearly a decade ago by the likes of former U.S. Federal Reserve Board Chairmen Alan Greenspan and Ben Bernanke.
There is only one problem: the data show little evidence of a savings glut. Since 1980, global savings have fluctuated between 22 percent and 24 percent of world GDP, with little tendency to trend up or down. [Project Syndicate]
But I think Eichengreen is wrong to dismiss the possibility of a savings glut based on personal savings rates.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Personal savings rates are the difference between personal income after tax and spending. For example, if the equivalent of 95 percent of household income is spent on goods and services, then the personal savings rate is 5 percent.
While this may be good at measuring changes in household saving from year to year, what this doesn’t cover — as Brad DeLong points out — is corporate and business income and saving, as well as money coming into the U.S. from abroad.
And the savings rate doesn’t consider the weight of past savings still sitting in banks, just the level of saving relative to spending in the economy in the last year.
If we want to determine the level of savings in the economy, we should compare the total level of savings with the level of activity in the economy. If we do that — total savings deposits as a percentage of GDP — we see that saving has climbed and climbed. This has been true even though personal saving rates have trended lower and interest rates have remained at zero, which discourages saving:
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
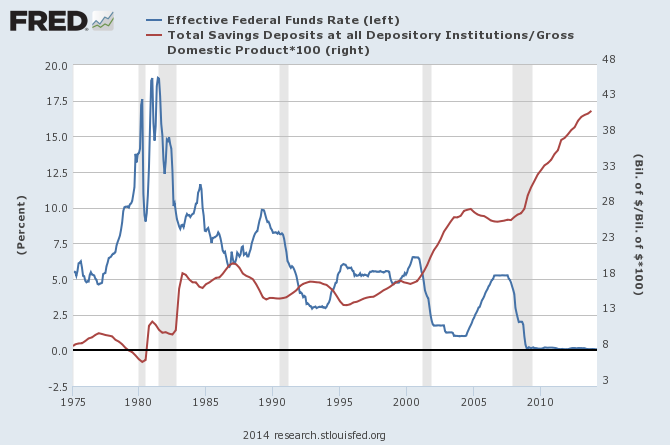
[Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis]
In other words, savers — which include large corporations sitting on an estimated $2.8 trillion — are not finding spending and investment opportunities for their savings, and the economy is not adjusting very quickly to open up new opportunities for all of that idle cash.
As Brad DeLong says, "[I]f that isn't a "savings glut," what would a savings glut be?
This doesn’t mean that the other things Eichengreen suggests as causes for low interest rates — the damage done to the economy and the labor force during the Great Recession, for example — are not legitimate.
But we should definitely not ignore the reality of the huge and growing quantity of savings in the system.
John Aziz is the economics and business correspondent at TheWeek.com. He is also an associate editor at Pieria.co.uk. Previously his work has appeared on Business Insider, Zero Hedge, and Noahpinion.
-
 6 of the world’s most accessible destinations
6 of the world’s most accessible destinationsThe Week Recommends Experience all of Berlin, Singapore and Sydney
-
 How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule works
How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule worksIn the Spotlight The law is at the heart of the Colbert-CBS conflict
-
 What is the endgame in the DHS shutdown?
What is the endgame in the DHS shutdown?Today’s Big Question Democrats want to rein in ICE’s immigration crackdown