CHARTS: How the rich won the Great Recession
The top 1 percent of U.S. earners now have the biggest share of the American pie since the Roaring Twenties


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
When the economy crashed in the fall of 2008, the wealthiest Americans lost the most money.
From the time the Great Recession started in late 2007 until it officially ended in 2009, the richest 1 percent of America saw its income drop 36.3 percent, according to a new report by economists Emmanuel Saez and Thomas Piketty [PDF]. Collectively, the top 1 percent lost 49 percent of the billions in wealth that vanished like so much Lehman Brothers stock.
But before you start writing that sympathy card to your favorite hedge fund manager, remember that the U.S. is now in its sixth-longest economic expansion in history — 51 months and counting — and most of the benefits are trickling up to the wealthy.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
According to Saez, the top 1 percent (earning at least $394,000 a year) saw its income rise 31.4 percent between 2009 and 2012. And because the income of the bottom 99 percent of earners rose an anemic 0.4 percent in that same period, the top 1 percent captured 95 percent of the total growth in American wealth during the economic recovery.
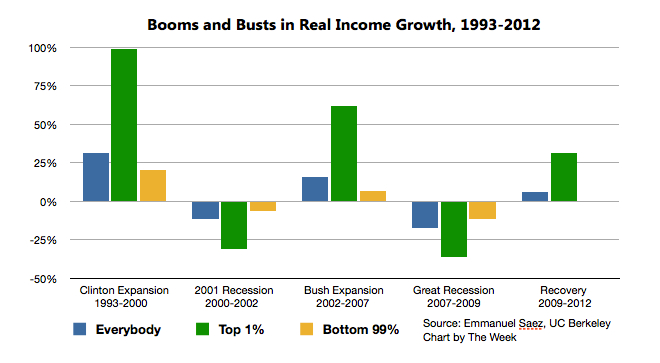
As the chart shows, it's nothing new for the super-rich to reap the lion's share of the growth in income (before then losing a small amount of their gains). But 95 percent is a pretty eye-popping number. Even when the top 1 percent saw its income skyrocket 98.7 percent during the Clinton administration, Saez notes, they only accrued 45 percent of the new wealth generated.
Where does that leave us in terms of the haves and have-nots? In a place we haven't been in at least 100 years. For the first time since the government started collecting the relevant data in 1917, the wealthiest 10 percent (earning at least $114,000 a year in 2012 dollars) is earning more than half — 50.4 percent — of U.S. income. The top 1 percent is eating nearly a quarter of the American income pie:
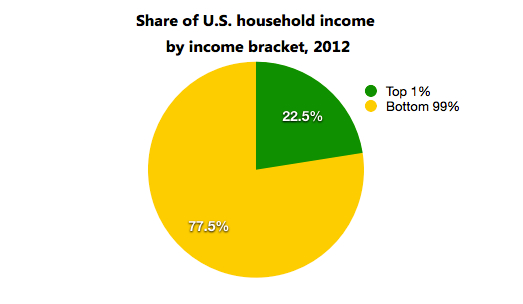
In 2007, before the recession, the top 1 percent brought in 23.5 percent of the money, about the same percentage as in 1928, right before the stock market crash that precipitated the Great Depression. But income disparity flattened out considerably in the post–World War II years, as this chart from The New York Times illustrates:
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
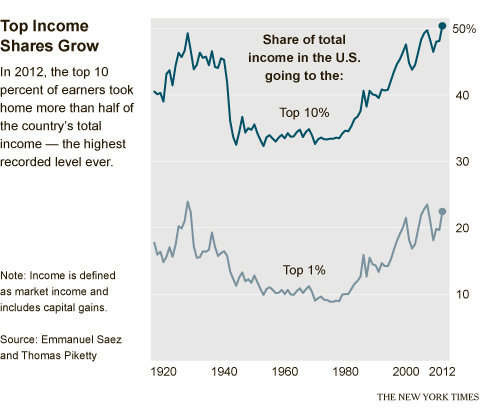
By 1973, the top 1 percent earned only 7.7 percent of U.S. income. But the percentage has been rising in fits and starts since the 1980s, and now it's clear that "even after the recession the country remains in a new Gilded Age," says Annie Lowrey at The New York Times. And like the last Gilded Age, a lot of the explanation can be found in the stock market. Lowrey explains:
Generally, richer households have disproportionately benefited from the boom in the stock market during the recovery, with the Dow Jones industrial average more than doubling in value since it bottomed out early in 2009. About half of households hold stock, directly or through vehicles like pension accounts. But the richest 10 percent of households own about 90 percent of the stock....
The economy remains depressed for most wage-earning families. With sustained, relatively high rates of unemployment, businesses are under no pressure to raise their employees' incomes because both workers and employers know that many people without jobs would be willing to work for less. The share of Americans working or looking for work is at its lowest in 35 years. [New York Times]
As Slate's Matthew Yglesias notes, the Great Recession was egalitarian in that everybody lost some money, but "the catastrophic recession approach to reducing inequality doesn't look so good" right now.
Peter has worked as a news and culture writer and editor at The Week since the site's launch in 2008. He covers politics, world affairs, religion and cultural currents. His journalism career began as a copy editor at a financial newswire and has included editorial positions at The New York Times Magazine, Facts on File, and Oregon State University.
-
 Health insurance: Premiums soar as ACA subsidies end
Health insurance: Premiums soar as ACA subsidies endFeature 1.4 million people have dropped coverage
-
 Anthropic: AI triggers the ‘SaaSpocalypse’
Anthropic: AI triggers the ‘SaaSpocalypse’Feature A grim reaper for software services?
-
 NIH director Bhattacharya tapped as acting CDC head
NIH director Bhattacharya tapped as acting CDC headSpeed Read Jay Bhattacharya, a critic of the CDC’s Covid-19 response, will now lead the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
