If a robot takes your job, should it pay your taxes too?
Or do robots need a tax cut, too?

Bill Gates wants to tax robots.
Now, Gates is a fantastically successful businessman. The Microsoft co-founder is worth $85 billion, after all. He's also a major philanthropist with a keen interest in public policy. But he should be careful about his musings to the media. The world's richest person can't just leave live ammo like "Maybe there should be a robot tax" lying around for some opportunistic politician to pick up. Certainly not with Donald Trump as president.
Look, all that has to happen is for America's cable-news-addict-in-chief to hear someone on Fox & Friends talking about how "Bill Gates said we should tax robots," and the idea might end up in Trump's address to Congress later this month. Since Trump wants to protect American jobs from being eliminated by foreign trade, it's hardly a huge leap to wanting to protect them from the rise of the machines. Indeed, the vast preponderance of manufacturing job loss since peak factory employment in 1979 has been due to automation, not trade. Make America great again: Ban the 'bots!
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
But Gates wasn't expressing some sort of neo-luddism when he recently floated this idea to Quartz:
Certainly there will be taxes that relate to automation. Right now, the human worker who does, say, $50,000 worth of work in a factory, that income is taxed and you get income tax, Social Security tax, all those things. If a robot comes in to do the same thing, you'd think that we'd tax the robot at a similar level. [Quartz]
Gates' real point was that policymakers need to pay close attention to how broadly the fruits of automation are distributed. He specifically mentioned using robot tax revenue for improved worker training, but one could also imagine directing the dough toward subsidizing wages or other ways to modernize the social safety net in the automation age.
How would a robot tax work? Gates mentions taxing both the robot owners — likely corporations — as well as some other sort of direct tax. One could imagine a sales tax, perhaps, or not allowing businesses to fully deduct the cost of certain advanced machines or software. European lawmakers just rejected taxing robots to pay for social insurance programs. But as Gates' comments suggest, the idea seems likely to keep popping up, especially as technology penetrates ever deeper into our working lives.
Opponents argue that such levies would kill progress. But the end result of robot taxes might be less the end of automation than, as Gates said, to "slow down the speed of that adoption somewhat to figure out, okay, what about the communities where this has a particularly big impact?" It's an idea that has a counterpart in the debate about trade. Economist David Autor, who has extensively researched the 21st century's "China trade shock" on American blue-collar workers, recently told The Washington Post that if "we knew how disruptive this would be, we would have wanted to do it more slowly."
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Of course one could argue we actually want the robots to rise even faster. U.S. productivity growth, at least as officially measured, has pretty much flatlined since the Great Recession. That means living standards are also rising at a snail's pace. Weak business investment is a big chunk of that. If machines were getting better faster, one might expect to see companies buy more of them and spur higher productivity growth. Also, there already is a kind of tax on technology, slowing its progress. If the U.S. more richly funded science research and reduced barriers to entrepreneurship, innovation and automation might be happening faster. Doing all that would actually be a de facto tax cut on tech progress.
For their part, many denizens of Silicon Valley think government statisticians are mismeasuring the tech economy. They're worried fast-advancing automation will lead to mass technological unemployment or underemployment, sparking an anti-tech, populist backlash. This is a big reason many techies are so interested in the idea of a universal basic income. Checks for all to soften the blow, perhaps funded by robot taxes.
Some of the biggest names in tech — Microsoft, Amazon, IBM, Google, and Facebook — have formed a group to promote the benefits of artificial intelligence, while avoiding any potential Terminator scenarios. They also want to preempt meddling by the heavy hand of Washington bureaucrats. But as problems go, worrying about how to make sure everyone safely shares in a future of tech-driven abundance is a good one to have.
James Pethokoukis is the DeWitt Wallace Fellow at the American Enterprise Institute where he runs the AEIdeas blog. He has also written for The New York Times, National Review, Commentary, The Weekly Standard, and other places.
-
 The battle over the Irish language in Northern Ireland
The battle over the Irish language in Northern IrelandUnder the Radar Popularity is soaring across Northern Ireland, but dual-language sign policies agitate division as unionists accuse nationalists of cultural erosion
-
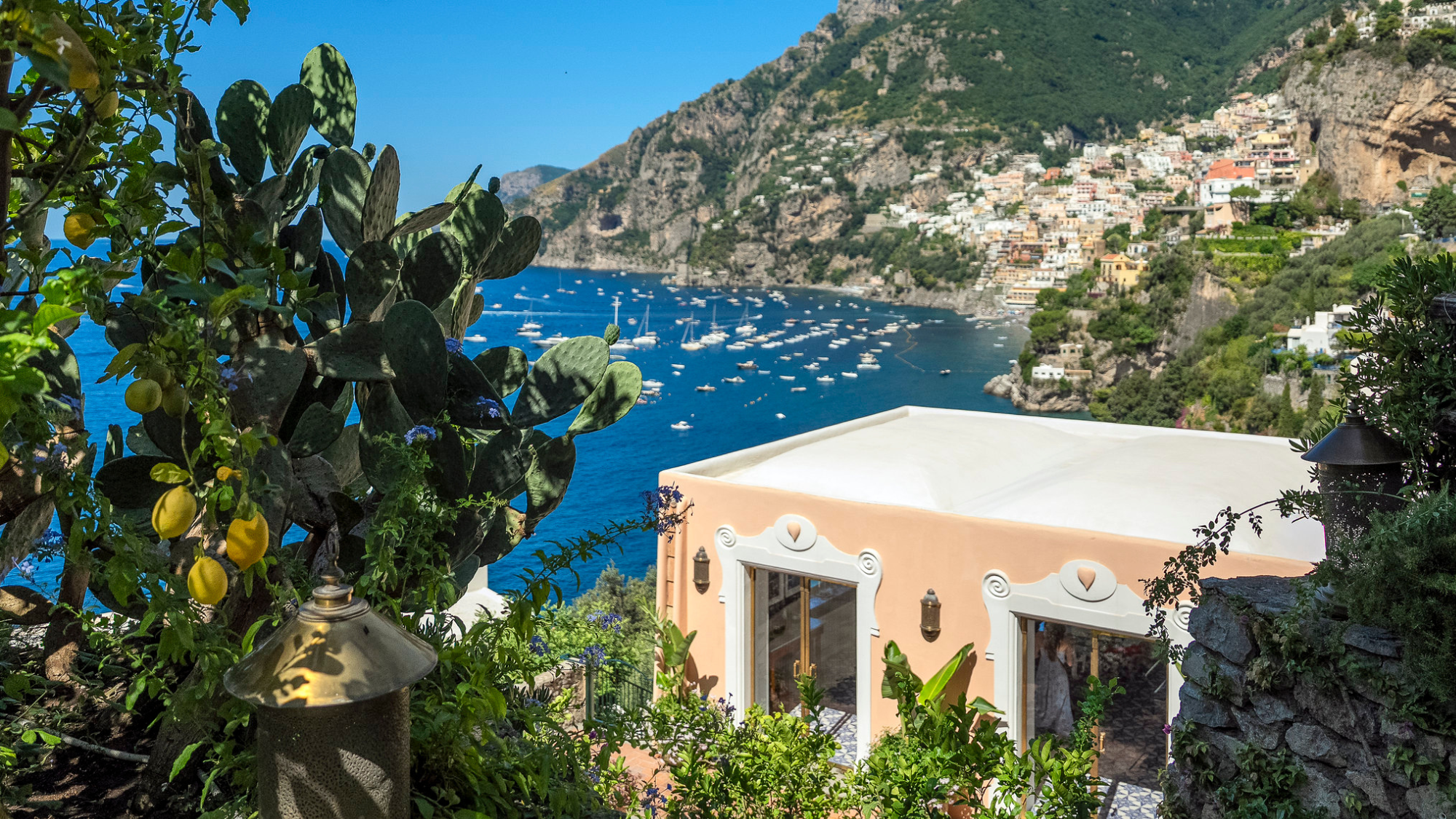 Villa Treville Positano: a glamorous sanctuary on the Amalfi Coast
Villa Treville Positano: a glamorous sanctuary on the Amalfi CoastThe Week Recommends Franco Zeffirelli’s former private estate is now one of Italy’s most exclusive hotels
-
 How roadkill is a surprising boon to scientific research
How roadkill is a surprising boon to scientific researchUnder the radar We can learn from animals without trapping and capturing them
