Google AI can detect breast cancer more effectively than doctors
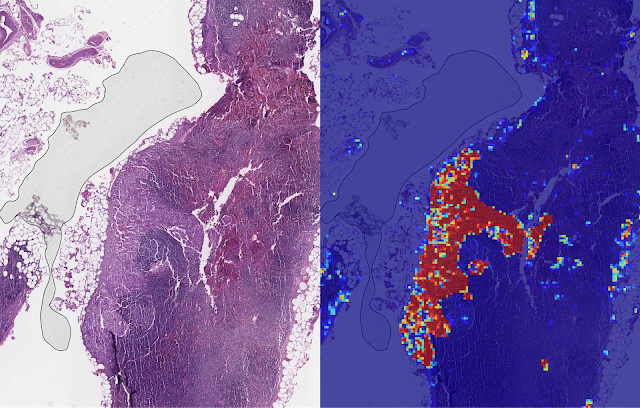
Lyra algorithm can successfully identify cancerous cells 99% of the time
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Google has developed an artificial intelligence (AI) programme that is more effective at identifying signs of breast cancer than doctors.
Created by researchers at Google AI and the Naval Medical Center San Diego, the Lymph Node Assistant (Lyna) has been programmed to recognise the “characteristics” of tumours by analysing scans from real-world cancer patients, Engadget reports.
The process, commonly referred to as machine learning, allows the AI identify cancerous cells 99% of the time, the tech site says.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
It could mean the Lyna is used as a virtual “spell check” for pathologists, says Business Insider, where the AI programme is used as a back-up tool to help medical professionals confirm whether a minute anomaly on a scan is either benign or malign.
The search engine’s researchers found that pathologists who used the tool “performed better” than those who didn’t use the programme, the news site says.
And according to Google, some pathologists claim the Lyra tool makes detecting small growths, an often “laborious task”, notably “easier”.
A member of the search giant’s AI team, Yun Liu, told Business Insider that the Lyna “represents a demonstration that people can work really well with AI algorithms than either one alone.”
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
But Google isn’t the only technology company looking to make inroads into the medical industry.
Last week, Chinese tech firm Tencent revealed that it is developing an algorithm to aid Parkinson’s disease patients record their symptoms. This would help doctors prescribe the correct amount of medication, cutting down the number of hospital visits for patients.
-
 The ‘ravenous’ demand for Cornish minerals
The ‘ravenous’ demand for Cornish mineralsUnder the Radar Growing need for critical minerals to power tech has intensified ‘appetite’ for lithium, which could be a ‘huge boon’ for local economy
-
 Why are election experts taking Trump’s midterm threats seriously?
Why are election experts taking Trump’s midterm threats seriously?IN THE SPOTLIGHT As the president muses about polling place deployments and a centralized electoral system aimed at one-party control, lawmakers are taking this administration at its word
-
 ‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’
‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
 Will AI kill the smartphone?
Will AI kill the smartphone?In The Spotlight OpenAI and Meta want to unseat the ‘Lennon and McCartney’ of the gadget era
-
 Claude Code: Anthropic’s wildly popular AI coding app
Claude Code: Anthropic’s wildly popular AI coding appThe Explainer Engineers and noncoders alike are helping the app go viral
-
 Will regulators put a stop to Grok’s deepfake porn images of real people?
Will regulators put a stop to Grok’s deepfake porn images of real people?Today’s Big Question Users command AI chatbot to undress pictures of women and children
-
 Most data centers are being built in the wrong climate
Most data centers are being built in the wrong climateThe explainer Data centers require substantial water and energy. But certain locations are more strained than others, mainly due to rising temperatures.
-
 The dark side of how kids are using AI
The dark side of how kids are using AIUnder the Radar Chatbots have become places where children ‘talk about violence, explore romantic or sexual roleplay, and seek advice when no adult is watching’
-
 Why 2025 was a pivotal year for AI
Why 2025 was a pivotal year for AITalking Point The ‘hype’ and ‘hopes’ around artificial intelligence are ‘like nothing the world has seen before’
-
 AI griefbots create a computerized afterlife
AI griefbots create a computerized afterlifeUnder the Radar Some say the machines help people mourn; others are skeptical
-
 The robot revolution
The robot revolutionFeature Advances in tech and AI are producing android machine workers. What will that mean for humans?