Bluetoothing: the phenomenon driving HIV spike in Fiji
‘Blood-swapping’ between drug users fuelling growing health crisis on Pacific island

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
A new way of getting high is “tearing the roof off” Fiji’s HIV infection rate, said The Fiji Times. “Bluetoothing” sees intravenous drug users “plunging a syringe” of methamphetamine into a vein, then withdrawing some of their drug-rich blood and injecting it into a second person, who does the same for a third – and so on.
Multiple people sharing a “hit” and a syringe like this saves money but, by sharing blood, users are greatly increasing their risk of HIV infection. And, in the past 10 years, Fiji has seen “an elevenfold leap” in the number of people living with HIV – from 500 people to 5,900. An assistant health minister last week warned that the tiny Pacific island may record more than 3,000 new cases by the end of 2025.
‘Surge in addiction’
Bluetoothing is particularly common among Fiji’s teenagers and young adults, with meth-filled syringes selling on the streets for “as little as 10 Fijian dollars” (£3.30), said ABC News. The “surge in addiction is overwhelming” the island’s health services and children “as young as 13” have been contracting HIV due to intravenous drug use.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
“The intersection of meth use and HIV is particularly troubling” because meth users already tend to have weakened immune systems, said Massey University research associate Apisalome Movono on The Conversation. And “the stigma and discrimination associated with both meth use and HIV mean many are reluctant to seek help”.
With nearly 50% of people diagnosed with HIV in Fiji avoiding further treatment, bluetoothing is only going to get riskier, said the Fiji Sun – not to mention that the island nation is also grappling with “simultaneous outbreaks” of illness caused by two other bloodborne viruses, hepatitis B and hepatitis C.
‘A perfect storm’
The government has taken some action, said The Telegraph, designating the spread of HIV infection a “national outbreak” in January, and authorising $10 million Fijian dollars (£3.3 million) in new funding for treatment, testing and an awareness campaign. But health experts say there is much more to be done. Many are pushing for a “needle exchange programme” and an official public health response to tackle meth addiction.
Grassroots activists are using Pacific cultural practices to work with those affected by HIV. Jokapeci Tuberi Cati, the first person in Fiji to “live openly” with HIV, promotes “talanoa”, the principle of “exchanging open conversation”, to share knowledge and offer support for those living with the disease, said SBS News.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
There is “no quick fix” to this “perfect storm” of addiction, HIV and a struggling health system, said Movono on The Conversation. But “empowering local communities” will engender “more sustainable and culturally appropriate solutions”, particularly when it comes to “reducing the stigma and discrimination”. Other Pacific nations “will be looking to Fiji to tackle the issue head on and prevent the crisis spreading”.
Rebekah Evans joined The Week as newsletter editor in 2023 and has written on subjects ranging from Ukraine and Afghanistan to fast fashion and "brotox". She started her career at Reach plc, where she cut her teeth on news, before pivoting into personal finance at the height of the pandemic and cost-of-living crisis. Social affairs is another of her passions, and she has interviewed people from across the world and from all walks of life. Rebekah completed an NCTJ with the Press Association and has written for publications including The Guardian, The Week magazine, the Press Association and local newspapers.
-
 Gisèle Pelicot’s ‘extraordinarily courageous’ memoir is a ‘compelling’ read
Gisèle Pelicot’s ‘extraordinarily courageous’ memoir is a ‘compelling’ readIn the Spotlight A Hymn to Life is a ‘riveting’ account of Pelicot’s ordeal and a ‘rousing feminist manifesto’
-
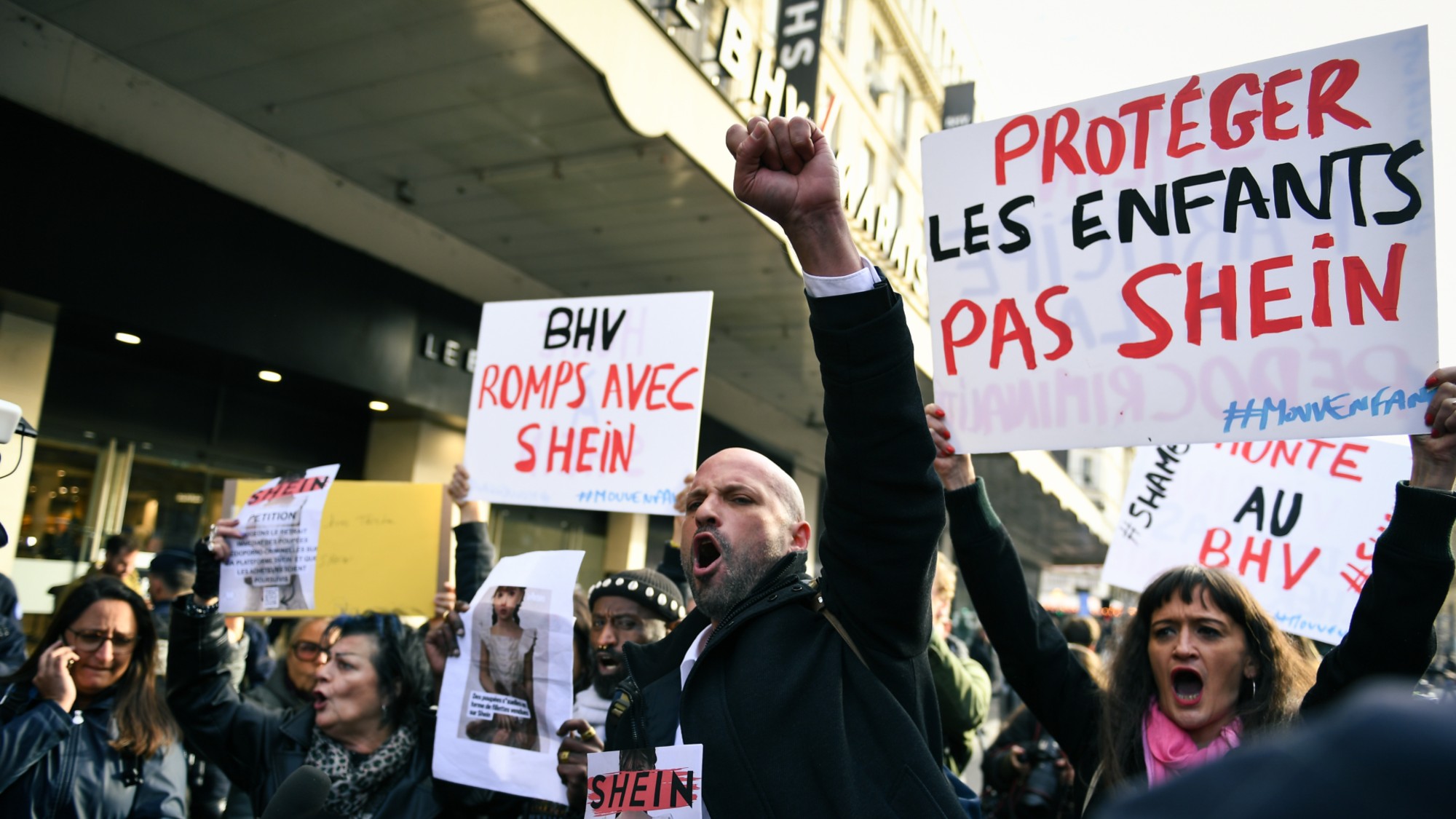 The EU’s war on fast fashion
The EU’s war on fast fashionIn the Spotlight Bloc launches investigation into Shein over sale of weapons and ‘childlike’ sex dolls, alongside efforts to tax e-commerce giants and combat textile waste
-
 How to Get to Heaven from Belfast: a ‘highly entertaining ride’
How to Get to Heaven from Belfast: a ‘highly entertaining ride’The Week Recommends Mystery-comedy from the creator of Derry Girls should be ‘your new binge-watch’
-
 Scientists are worried about amoebas
Scientists are worried about amoebasUnder the radar Small and very mighty
-
 High Court action over Cape Verde tourist deaths
High Court action over Cape Verde tourist deathsThe Explainer Holidaymakers sue Tui after gastric illness outbreaks linked to six British deaths
-
 A Nipah virus outbreak in India has brought back Covid-era surveillance
A Nipah virus outbreak in India has brought back Covid-era surveillanceUnder the radar The disease can spread through animals and humans
-
 Is the US about to lose its measles elimination status?
Is the US about to lose its measles elimination status?Today's Big Question Cases are skyrocketing
-
 A real head scratcher: how scabies returned to the UK
A real head scratcher: how scabies returned to the UKThe Explainer The ‘Victorian-era’ condition is on the rise in the UK, and experts aren’t sure why
-
 Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinations
Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinationsSpeed Read In a widely condemned move, the CDC will now recommend that children get vaccinated against 11 communicable diseases, not 17
-
 Deaths of children under 5 have gone up for the first time this century
Deaths of children under 5 have gone up for the first time this centuryUnder the radar Poor funding is the culprit
-
 A fentanyl vaccine may be on the horizon
A fentanyl vaccine may be on the horizonUnder the radar Taking a serious jab at the opioid epidemic