How facial software can identify liars
Facial-recognition software could warn immigration officers if someone is lying

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Surveillance cameras at airports could be used to identify passengers who are not telling the truth, helping better identify terrorists and drug-smugglers while minimising instances of racial profiling.
The artificial-intelligence programme was developed by a team of computer scientists at the University of Rochester, New York, using crowdsourcing technology to build the largest public data resource of liars’ facial expressions.
Researchers used a machine-learning algorithm to analyse over 1.3 million frames of one-to-one interactions interactions.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Among the most common traits associated with lying identified by the programme was a high-intensity version of the so-called Duchenne smile, in which people effectively smile with their eyes. Another surprising finding was that honest people would contract their eyes, but not smile with their mouths.
Even highly-trained immigration officers often struggled to assess whether someone is lying, deliberately concealing something or just nervous.
However, existing lie-detector technology is “controversial and a camera-based system that could be more widely used would be even more so”, says The Times, “especially if it found its way into courtrooms, offices and schools”.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
-
 How to Get to Heaven from Belfast: a ‘highly entertaining ride’
How to Get to Heaven from Belfast: a ‘highly entertaining ride’The Week Recommends Mystery-comedy from the creator of Derry Girls should be ‘your new binge-watch’
-
 The 8 best TV shows of the 1960s
The 8 best TV shows of the 1960sThe standout shows of this decade take viewers from outer space to the Wild West
-
 Microdramas are booming
Microdramas are boomingUnder the radar Scroll to watch a whole movie
-
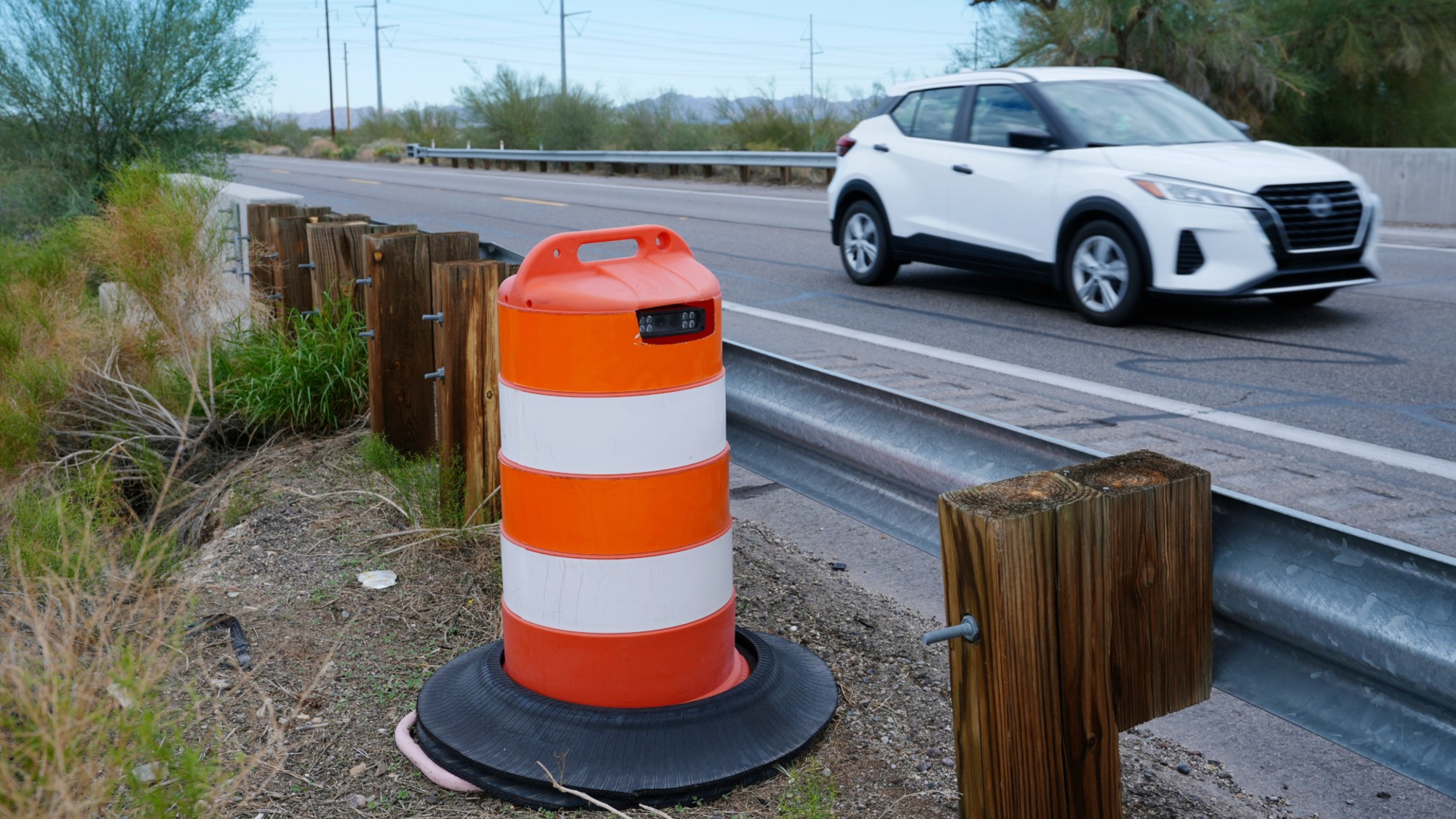 Border Patrol may be tracking drivers with secret cameras
Border Patrol may be tracking drivers with secret camerasIn the Spotlight The cameras are reportedly hidden in objects like traffic safety cones
-
 Pros and cons of the emergency alert
Pros and cons of the emergency alertPros and Cons Already used successfully in US, Greece and Japan, mobile notifications could help save lives, but pose risk to domestic abuse victims and drivers
-
 The UK’s new mobile emergency alert system: what is it and how does it work?
The UK’s new mobile emergency alert system: what is it and how does it work?feature Government will test new scheme this month with warning sound and vibration on nation’s phones
-
 DEA tells TikTok, Snapchat, and Instagram to do more to stop online drug sales
DEA tells TikTok, Snapchat, and Instagram to do more to stop online drug salesSpeed Read
-
 The Biden administration's new facial recognition app for asylum seekers sets off alarm bells
The Biden administration's new facial recognition app for asylum seekers sets off alarm bellsSpeed Read
-
 How cybercriminals are hacking into the heart of the US economy
How cybercriminals are hacking into the heart of the US economySpeed Read Ransomware attacks have become a global epidemic, with more than $18.6bn paid in ransoms in 2020
-
 Language-learning apps speak the right lingo for UK subscribers
Language-learning apps speak the right lingo for UK subscribersSpeed Read Locked-down Brits turn to online lessons as a new hobby and way to upskill
-
 Brexit-hobbled Britain ‘still tech powerhouse of Europe’
Brexit-hobbled Britain ‘still tech powerhouse of Europe’Speed Read New research shows that UK start-ups have won more funding than France and Germany combined over past year