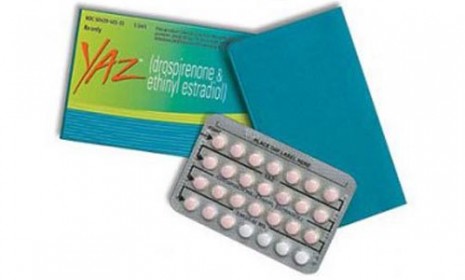
Does Yaz birth control cause deadly blood clots?
An FDA panel urges new warning labels on the popular oral contraceptives, saying there's a small but real health risk associated with the drug
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
One of the most widely used oral contraceptives in the U.S. may be getting a new warning label — a label that would describe the risks of potentially fatal blood clots. Here's what you should know:
Is birth control really so dangerous?
Blood clots have actually been "a known side effect" of birth control pills ever since these contraceptives "hit the market 50 years ago," says Bloomberg Businessweek. However, a new generation of pills may be raising the risk. According to several recent studies, about 10 in 10,000 women on Yasmin, Yaz, or their generic versions may experience a clot, compared to seven in 10,000 women on older pills. It's still a relatively small risk — but higher than it once was.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
How dangerous are blood clots?
They can sometimes, though rarely, be fatal. "Blood clots can trigger heart attacks, strokes, and blockages in lungs or blood vessels," reports the Associated Press.
And there may be new warning labels?
Possibly. An FDA panel voted 21-5 last week that "labeling on Yaz, Yasmin, Beyaz, Safyral, and its generic versions is inadequate and should be revised," says Meredith Melnick at TIME. The panelists recommended that the labels "should make clearer the potential risk of blood clots in the legs and lungs."
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
How popular are these pills?
Yaz used to be the best-selling birth control pill in the country. After being released in 2006, Yaz's manufacturer, Bayer, poured "hundreds of millions of dollars in TV and magazine advertising that emphasized its ability to clear up acne and other hormonal side effects," says the Associated Press. But since studies pointing to the risk of blood clots began to surface, prescriptions have fallen "more than 80 percent."
What now?
The FDA will decide whether to approve or reject the panel's recommendation. The FDA has yet to set a timetable for changing Yaz's labeling, says the Associated Press, and "many doctors say they don't expect to stop prescribing the drugs anytime soon."
Sources: Associated Press, Bloomberg Businessweek, TIME
-
 Switzerland could vote to cap its population
Switzerland could vote to cap its populationUnder the Radar Swiss People’s Party proposes referendum on radical anti-immigration measure to limit residents to 10 million
-
 Political cartoons for February 15
Political cartoons for February 15Cartoons Sunday's political cartoons include political ventriloquism, Europe in the middle, and more
-
 The broken water companies failing England and Wales
The broken water companies failing England and WalesExplainer With rising bills, deteriorating river health and a lack of investment, regulators face an uphill battle to stabilise the industry