Sweltering heat wave hits much of the United States
An excessive heat warning was in effect for 10% of the country's population


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
What happened
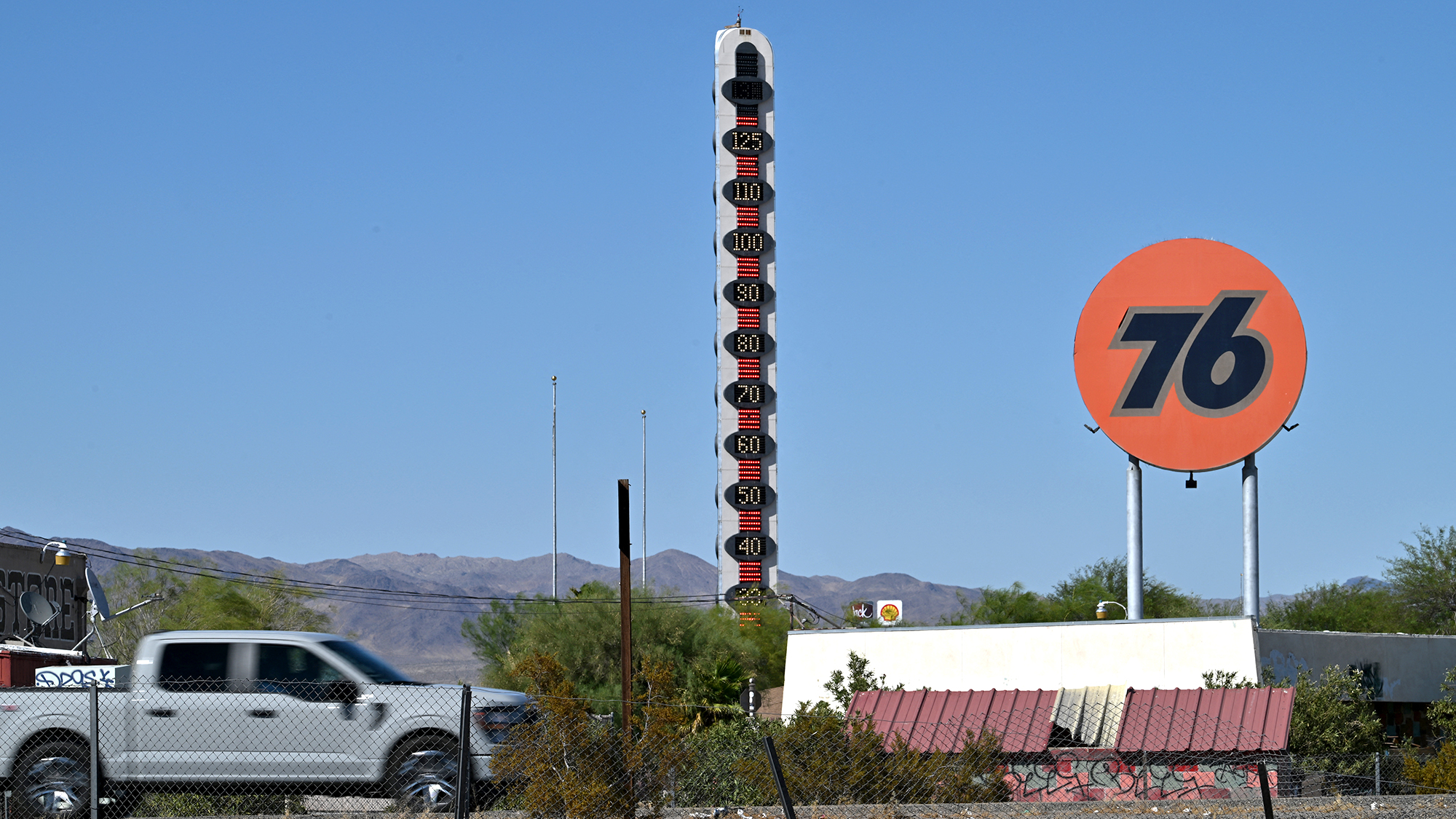
Large portions of the West and East coasts were enveloped by extreme heat over the weekend, with deadly temperatures recorded in several cities. California's Death Valley, consistently one of the hottest areas on Earth, set a new record on Saturday, reaching 128 degrees Fahrenheit, while Las Vegas and Arizona saw similar highs. On the other side of the country, heat indexes reached 110 degrees in Maryland and Washington D.C., and in areas throughout the South, including Florida, Georgia and Alabama.
An excessive heat warning — the National Weather Service's highest alert — was in effect on Sunday for about 36 million people, or about 10% of the population.
Who said what
Climate change caused by humans is "fueling longer and more intensive heat waves, and making dangerously high temperatures more common," NPR said. These types of conditions are "potentially deadly if not taken seriously," said the National Weather Service.
What next?
The "persistent" heat wave is expected to "shatter new records" as temperatures keep climbing in the coming days, NBC News said. In parts of the Pacific Northwest, including Oregon, temperatures "are forecast to stay between 100 to 105 degrees through Tuesday night," said NPR. Nationwide, a total of 40 million people are expected to swelter in temperatures of more than 100 degrees over the next week.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Justin Klawans has worked as a staff writer at The Week since 2022. He began his career covering local news before joining Newsweek as a breaking news reporter, where he wrote about politics, national and global affairs, business, crime, sports, film, television and other news. Justin has also freelanced for outlets including Collider and United Press International.
-
 Properties of the week: pretty thatched cottages
Properties of the week: pretty thatched cottagesThe Week Recommends Featuring homes in West Sussex, Dorset and Suffolk
-
 The week’s best photos
The week’s best photosIn Pictures An explosive meal, a carnival of joy, and more
-
 The ‘ravenous’ demand for Cornish minerals
The ‘ravenous’ demand for Cornish mineralsUnder the Radar Growing need for critical minerals to power tech has intensified ‘appetite’ for lithium, which could be a ‘huge boon’ for local economy
-
 Earth is rapidly approaching a ‘hothouse’ trajectory of warming
Earth is rapidly approaching a ‘hothouse’ trajectory of warmingThe explainer It may become impossible to fix
-
 The plan to wall off the ‘Doomsday’ glacier
The plan to wall off the ‘Doomsday’ glacierUnder the Radar Massive barrier could ‘slow the rate of ice loss’ from Thwaites Glacier, whose total collapse would have devastating consequences
-
 Can the UK take any more rain?
Can the UK take any more rain?Today’s Big Question An Atlantic jet stream is ‘stuck’ over British skies, leading to ‘biblical’ downpours and more than 40 consecutive days of rain in some areas
-
 As temperatures rise, US incomes fall
As temperatures rise, US incomes fallUnder the radar Elevated temperatures are capable of affecting the entire economy
-
 The world is entering an ‘era of water bankruptcy’
The world is entering an ‘era of water bankruptcy’The explainer Water might soon be more valuable than gold
-
 Climate change could lead to a reptile ‘sexpocalypse’
Climate change could lead to a reptile ‘sexpocalypse’Under the radar The gender gap has hit the animal kingdom
-
 The former largest iceberg is turning blue. It’s a bad sign.
The former largest iceberg is turning blue. It’s a bad sign.Under the radar It is quickly melting away
-
 How drones detected a deadly threat to Arctic whales
How drones detected a deadly threat to Arctic whalesUnder the radar Monitoring the sea in the air
