Thousands of cattle deaths reported in Kansas due to heat wave


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
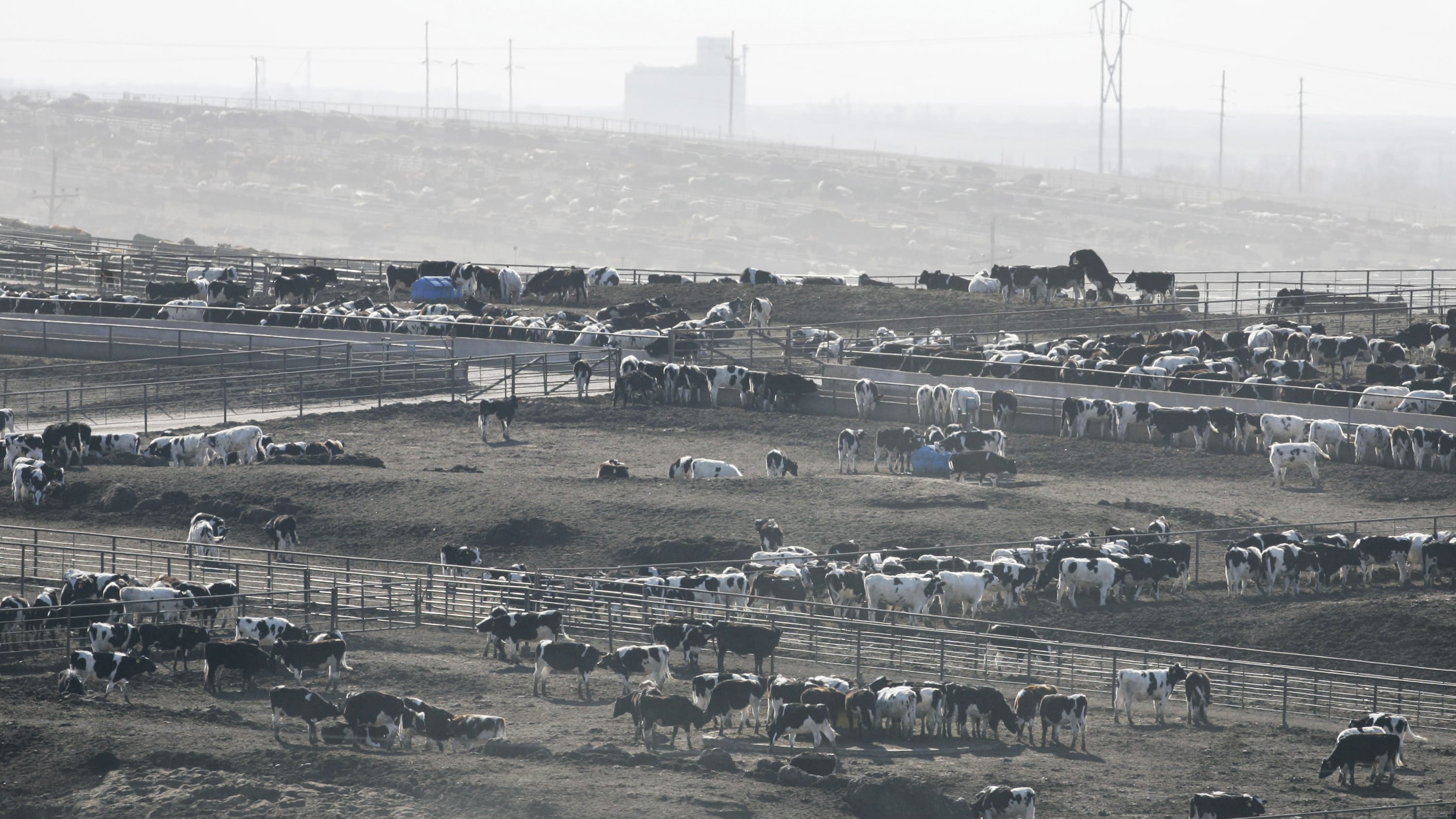
In southwestern Kansas, thousands of cattle have died of heat stress, amid a brutal heat wave.
There have been at least 2,000 heat-related deaths at feedlots in the last week, the Kansas Department of Health and Environment said, and agency spokesman Matt Lara told The Associated Press he expects that number to go up even higher.
Some people have speculated on social media that the cattle didn't die just because of high temperatures and high humidity, but those rumors are false, A.J. Tarpoff, a cattle veterinarian at Kansas State University, told AP. "This was a true weather event," Tarpoff said. "It was isolated to a specific region in southwestern Kansas. Yes, temperatures rose, but the more important reason why it was injurious was that we had a huge spike in humidity ... and at the same time wind speeds actually dropped substantially, which is rare for western Kansas."
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Temperatures shot up from the 70s and 80s to more than 100 degrees, and "it was that sudden change that didn't allow the cattle to acclimate that caused the heat stress issues in them," Scarlett Hagins, spokeswoman for the Kansas Livestock Association, said. The animals are worth about $2,000 each, and Hagins said federal disaster programs will help some of the cattle producers who lost livestock.
There are precautions that ranchers usually take to avoid cattle deaths due to high temperatures, including putting out extra drinking water and turning on sprinkler systems, but "we don't have any control over that pesky Mother Nature," Oklahoma City National Stockyards President Kelli Payne told AP.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Catherine Garcia has worked as a senior writer at The Week since 2014. Her writing and reporting have appeared in Entertainment Weekly, The New York Times, Wirecutter, NBC News and "The Book of Jezebel," among others. She's a graduate of the University of Redlands and the Columbia University Graduate School of Journalism.
-
 How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule works
How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule worksIn the Spotlight The law is at the heart of the Colbert-CBS conflict
-
 What is the endgame in the DHS shutdown?
What is the endgame in the DHS shutdown?Today’s Big Question Democrats want to rein in ICE’s immigration crackdown
-
 ‘Poor time management isn’t just an inconvenience’
‘Poor time management isn’t just an inconvenience’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
 The plan to wall off the ‘Doomsday’ glacier
The plan to wall off the ‘Doomsday’ glacierUnder the Radar Massive barrier could ‘slow the rate of ice loss’ from Thwaites Glacier, whose total collapse would have devastating consequences
-
 Can the UK take any more rain?
Can the UK take any more rain?Today’s Big Question An Atlantic jet stream is ‘stuck’ over British skies, leading to ‘biblical’ downpours and more than 40 consecutive days of rain in some areas
-
 As temperatures rise, US incomes fall
As temperatures rise, US incomes fallUnder the radar Elevated temperatures are capable of affecting the entire economy
-
 The world is entering an ‘era of water bankruptcy’
The world is entering an ‘era of water bankruptcy’The explainer Water might soon be more valuable than gold
-
 Climate change could lead to a reptile ‘sexpocalypse’
Climate change could lead to a reptile ‘sexpocalypse’Under the radar The gender gap has hit the animal kingdom
-
 The former largest iceberg is turning blue. It’s a bad sign.
The former largest iceberg is turning blue. It’s a bad sign.Under the radar It is quickly melting away
-
 How drones detected a deadly threat to Arctic whales
How drones detected a deadly threat to Arctic whalesUnder the radar Monitoring the sea in the air
-
 ‘Jumping genes’: how polar bears are rewiring their DNA to survive the warming Arctic
‘Jumping genes’: how polar bears are rewiring their DNA to survive the warming ArcticUnder the radar The species is adapting to warmer temperatures
