Surging global ice melt suggests sea level rise predictions are far too conservative


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
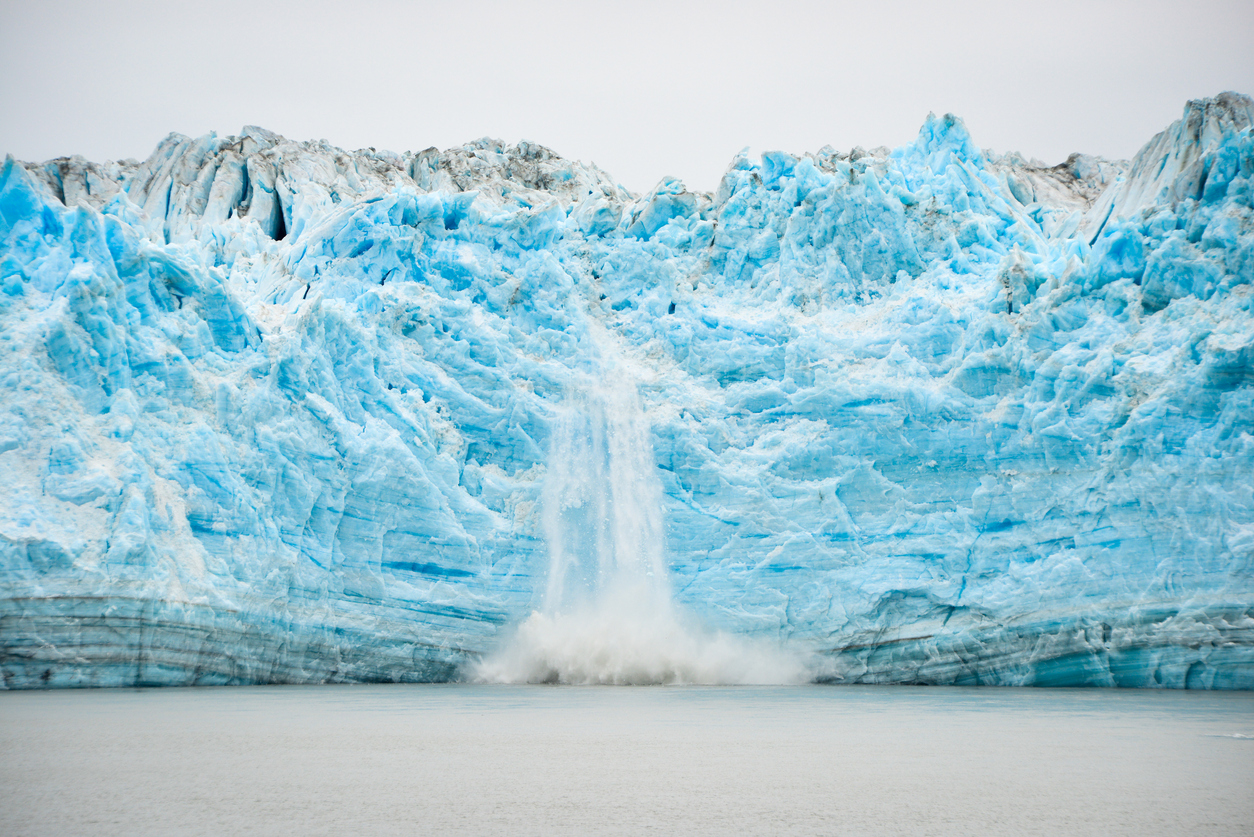
The world's ice is melting so fast that sea level rise predictions can't keep up.
In the 1990s, the Earth's ice was melting at a rate of about 760 billion tons per year. That has surged 60 percent to an average of 1.2 trillion tons per year in the 2010s, a study published Monday in the journal The Cryosphere estimates. And as another study published earlier this month in Science Advances makes clear, the problem is feeding into itself.
Climate change is largely responsible for the huge ice melt surge, the Cryosphere study reports. In fact, about three percent of all the energy trapped within the Earth's systems because of climate change has gone toward that ice melt, the study estimates. "That’s like more than 10,000 'Back to the Future' lightning strikes per second of energy melting ice around-the-clock since 1994," William Colgan, an ice-sheet expert at the Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland, told The Washington Post. "That is just a bonkers amount of energy."
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Climate change not only melts ice sheets on land, but also warms ocean waters to melt glaciers from the bottom up as well. Past sea level rise projections have failed to account for this glacial undercutting by "at least a factor of 2" the Science Advances study found.
"Together, the two studies present a worrying picture," the Post writes. The first study found "the ice sheets are now following the worst-case climate warming scenarios set out by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change," study author Thomas Slater said in a statement. But the second reveals that the panel's sea level projections, which were already criticized as too conservative, may have underestimated the role of glacial undercutting in accelerating ice melt even more. Read more at The Washington Post.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Kathryn is a graduate of Syracuse University, with degrees in magazine journalism and information technology, along with hours to earn another degree after working at SU's independent paper The Daily Orange. She's currently recovering from a horse addiction while living in New York City, and likes to share her extremely dry sense of humor on Twitter.
-
 Political cartoons for February 21
Political cartoons for February 21Cartoons Saturday’s political cartoons include consequences, secrets, and more
-
 Crisis in Cuba: a ‘golden opportunity’ for Washington?
Crisis in Cuba: a ‘golden opportunity’ for Washington?Talking Point The Trump administration is applying the pressure, and with Latin America swinging to the right, Havana is becoming more ‘politically isolated’
-
 5 thoroughly redacted cartoons about Pam Bondi protecting predators
5 thoroughly redacted cartoons about Pam Bondi protecting predatorsCartoons Artists take on the real victim, types of protection, and more
-
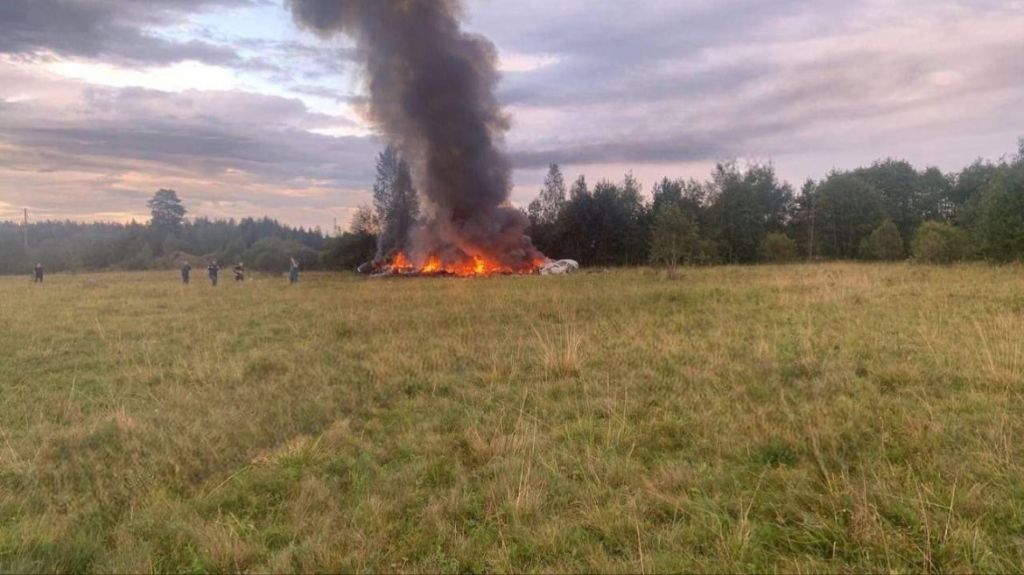 Nobody seems surprised Wagner's Prigozhin died under suspicious circumstances
Nobody seems surprised Wagner's Prigozhin died under suspicious circumstancesSpeed Read
-
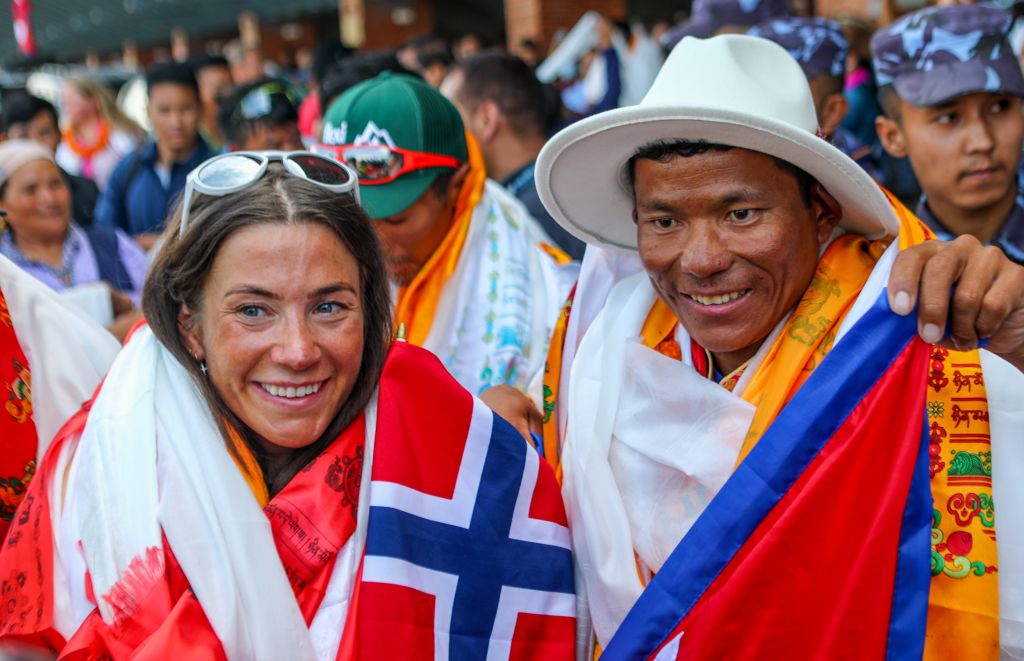 Western mountain climbers allegedly left Pakistani porter to die on K2
Western mountain climbers allegedly left Pakistani porter to die on K2Speed Read
-
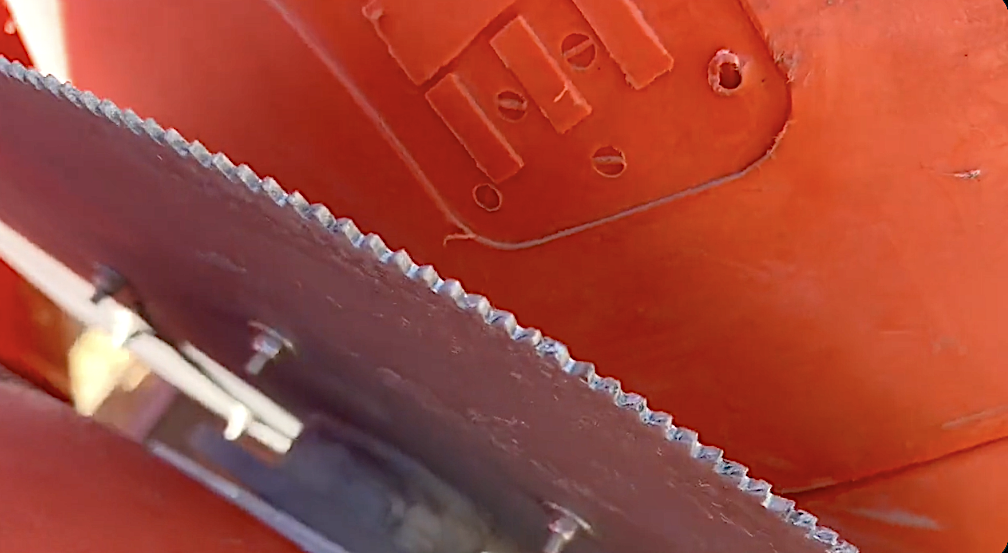 'Circular saw blades' divide controversial Rio Grande buoys installed by Texas governor
'Circular saw blades' divide controversial Rio Grande buoys installed by Texas governorSpeed Read
-
 Los Angeles city workers stage 1-day walkout over labor conditions
Los Angeles city workers stage 1-day walkout over labor conditionsSpeed Read
-
 Mega Millions jackpot climbs to an estimated $1.55 billion
Mega Millions jackpot climbs to an estimated $1.55 billionSpeed Read
-
 Bangladesh dealing with worst dengue fever outbreak on record
Bangladesh dealing with worst dengue fever outbreak on recordSpeed Read
-
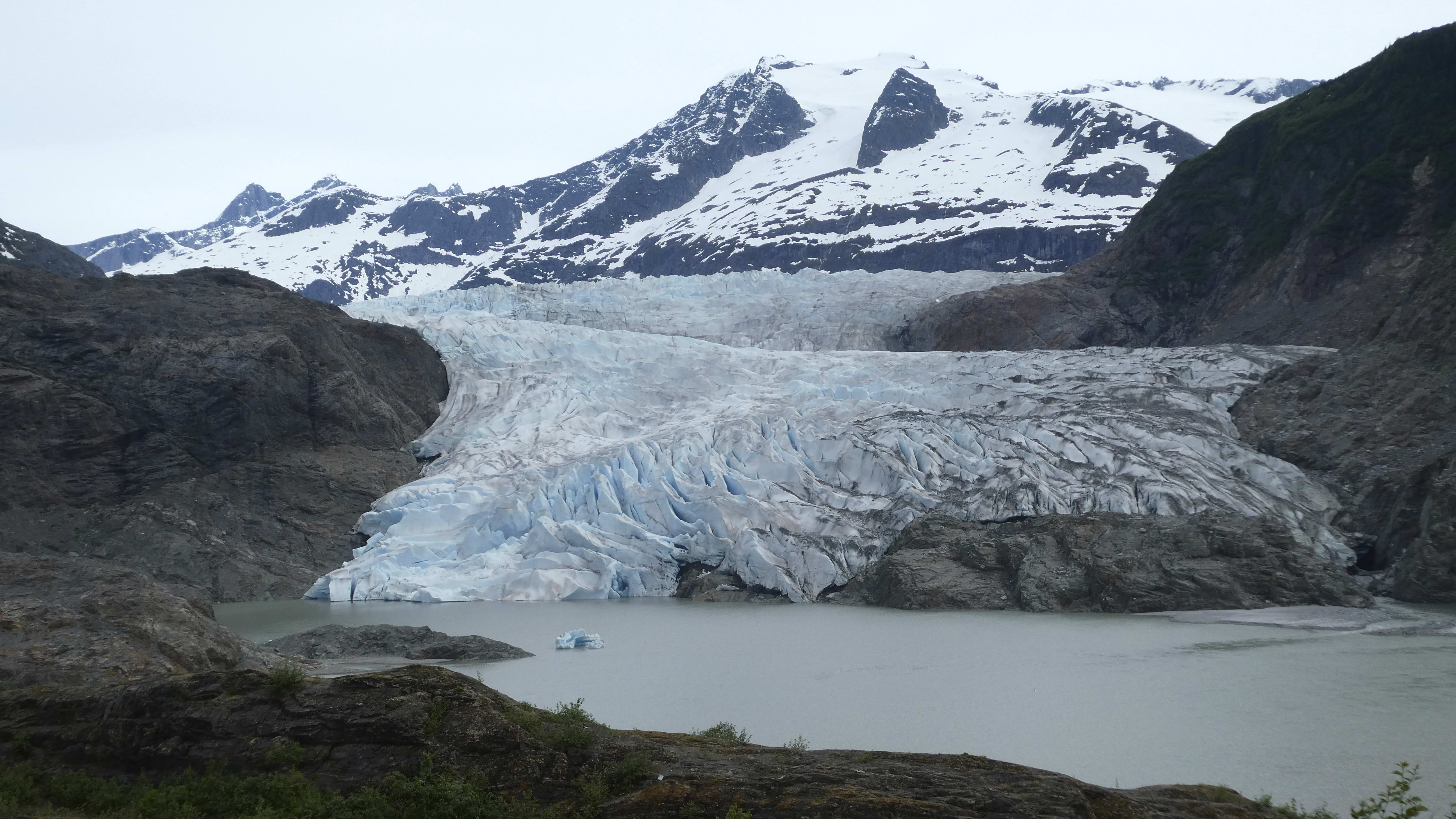 Glacial outburst flooding in Juneau destroys homes
Glacial outburst flooding in Juneau destroys homesSpeed Read
-
 Scotland seeking 'monster hunters' to search for fabled Loch Ness creature
Scotland seeking 'monster hunters' to search for fabled Loch Ness creatureSpeed Read
