Ebola: experimental drug cures monkeys infected with the virus
Scientists developing TKM-Ebola celebrate successful animal trial as the race for a human cure continues
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
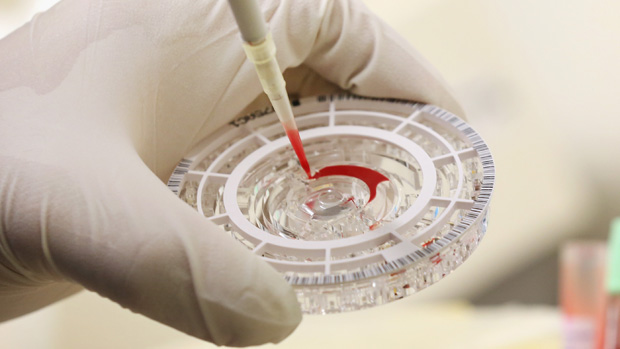
Scientists have used an experimental drug to successfully treat monkeys with Ebola, raising hopes of a human cure.
"This is the first study to show post-exposure protection," senior author Thomas Geisbert told the BBC.
TKM-Ebola-Guinea targets the Makona strain of the virus which is responsible for the ongoing outbreak in West Africa that has left over 10,000 people dead.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Developed by a Canadian pharmaceutical company, the drug works by interfering with the virus's genetic code, stopping it from producing disease-causing proteins.
One of the main advantages of the drug is that it can be easily modified to target different strains of virus. It is also be relatively quickly manufactured, while alternative drugs – such as the experimental ZMapp – take several months to produce.
During the animal trial, six monkeys were given a lethal dose of the virus. Three days later, half were given the drug while the other half were left untreated. All of the animals who received TKM Ebola went on to make a full recovery, while the others three died within nine days.
Geisbert said his team were hopeful that the results could be replicated in humans. "In most cases we would say there is a 90 per cent chance that this would work but not 100 per cent – there's nothing that is that definitive," he told the Daily Telegraph.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
A number of Ebola patients received the experimental drug during the outbreak, but as they were given several other treatments it is impossible to identify which one was responsible for their recovery.
A large-scale human trial of the drug has already begun in Sierra Leone, but its safety and efficacy are still unknown, with results only expected to be released later this year.
The Ebola outbreak in West Africa is waning, but the World Health Organization continues to warn against complacency, and the race to develop a cure is ongoing.