Is evaporating water the future of renewable energy?
It just might be ...

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
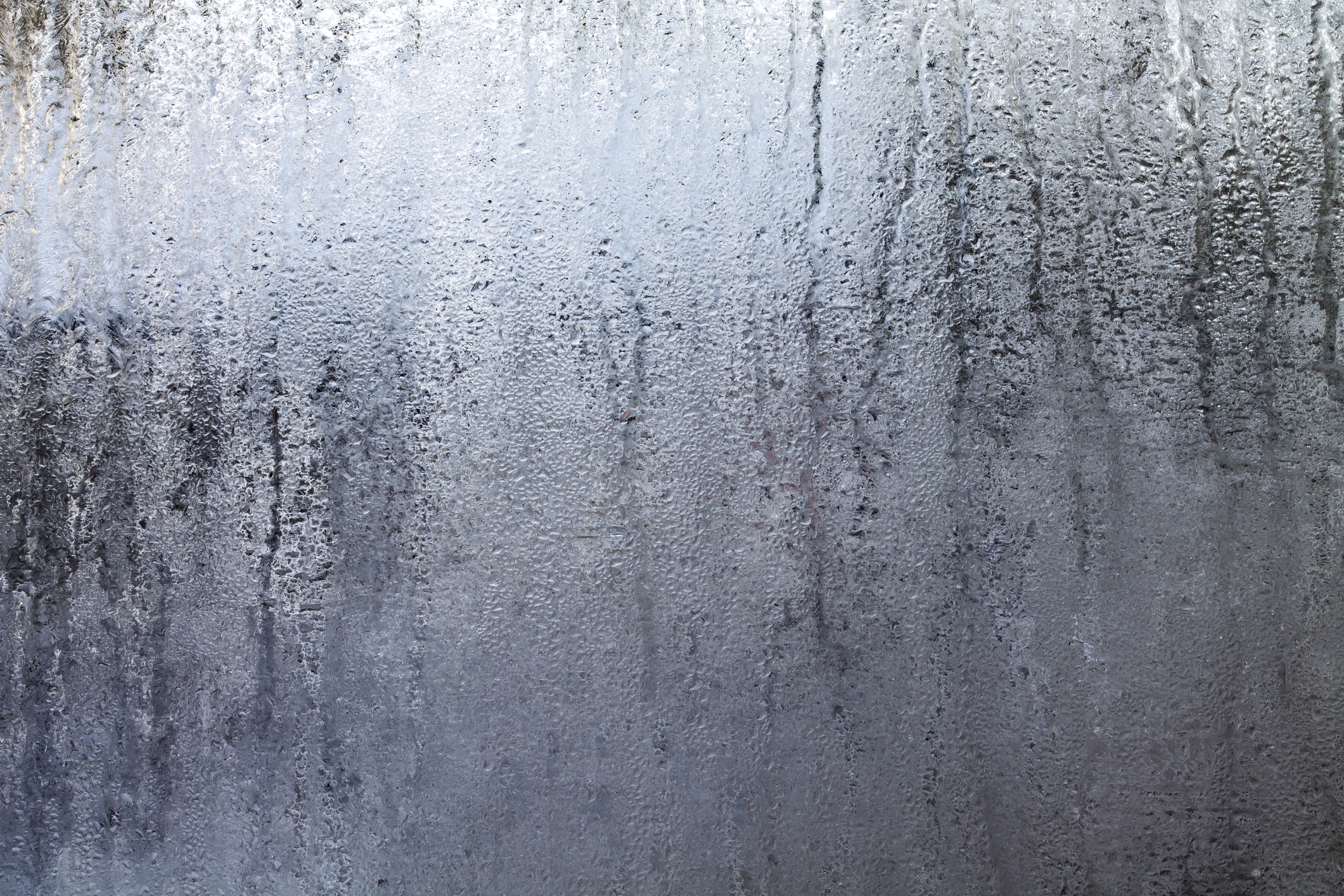
Forget the sun and wind — evaporating water could be the next big source of renewable energy, said James Temple at Technology Review. So-called evaporation-driven engines "generate power from the motion of bacterial spores that expand and contract as they absorb and release air moisture." Evaporation continues 24/7, so the engines, which sit on the water's surface, could provide power nonstop — unlike solar panels.
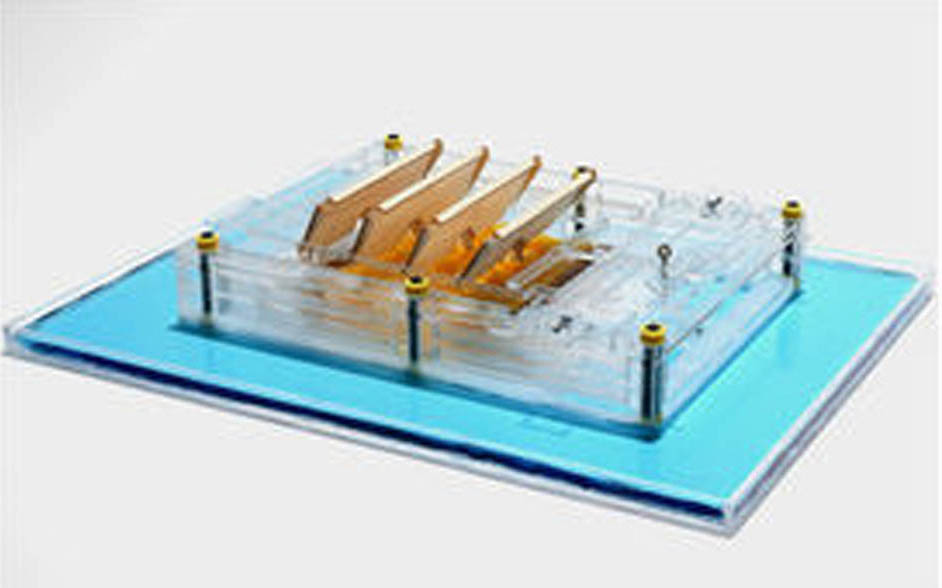
The technology is still in a prototype phase, but a new study in the journal Nature Communications notes that the power available from natural evaporation in lakes and reservoirs in the continental U.S. could meet 70 percent of the nation's needs. If even a small amount of that energy were tapped, says study co-author Ozgur Sahin of Columbia University, evaporation-driven engines "could make a significant contribution to clean-energy and climate goals."
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
-
 How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule works
How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule worksIn the Spotlight The law is at the heart of the Colbert-CBS conflict
-
 What is the endgame in the DHS shutdown?
What is the endgame in the DHS shutdown?Today’s Big Question Democrats want to rein in ICE’s immigration crackdown
-
 ‘Poor time management isn’t just an inconvenience’
‘Poor time management isn’t just an inconvenience’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day