COP26: will China play ball on climate change?
Fears grow that the world’s biggest greenhouse gas emitter will not co-operate at forthcoming climate talks

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
There are growing concerns about China’s attitude towards the upcoming COP26 climate summit in Glasgow after Beijing was angered by the new security and defence pact between Australia, the UK and the US.
Following the announcement of the Aukus deal, COP26 chair Alok Sharma admitted last night that he was unable to say whether President Xi Jinping would attend the gathering, The Guardian reported.
With November’s talks fast approaching, Boris Johnson heaped praise on Beijing’s role in tackling climate change, saying: “The Chinese actually have stepped up. They’ve gone a long way already and I congratulate President Xi on his vision.”
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Speaking to journalists on his way to New York for a three-day visit to the US, in which he hopes to “galvanise” progress towards a new climate deal, the prime minister added that Sharma had “some great conversations already with his Chinese counterparts about the things they want to do” and that these talks show “real signs of making progress”.
However, there are widespread doubts over whether China, the world’s biggest greenhouse gas emitter, will play ball at the forthcoming climate talks.
The nation’s role is crucial to efforts on climate change because China produces 28% of global emissions, compared with the UK’s 1%. Thanks to its “turbo-charged economy”, said the BBC, China is now emitting more CO2 than all rich nations put together, according to some estimates.
Although President Xi has offered to freeze emissions growth by 2030, scientists say that’s not enough to evade deadly climate change. The BBC’s environmental analyst, Roger Harrabin, said that if China doesn’t slash emissions, the planet is in “even more serious trouble” environmentally.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Last week, Reuters reported that China’s refusal to accept requests for deeper carbon emissions cuts during recent visits from the top climate envoys of the US and Britain could undermine progress in Glasgow.
It added that Beijing “no longer feels obliged to consider requests for deeper carbon cuts” because former President Donald Trump “rejected US climate change commitments, most notably by withdrawing from the Paris accord”.
Xi has previously promised to “increase the strength” of emissions goals, to reflect his commitment to reach the 2060 “net zero” target.
Last month, China’s top climate envoy Xie Zhenhua said China had already strengthened other pledges, including a new renewable energy target and a commitment to bring emissions to a peak “before” 2030 instead of “around” 2030.
Beijing has also said it will cut coal consumption starting in 2026 and produce 25% of its energy from non-fossil fuel sources by 2030.
However, Sharma told Sky News, UK ministers “want to see the detail of that” and “that is what we are pressing them”.
He added: “I said to them we want to see the detailed policy around this and they – along with every other major economy in the G20 – have committed before COP26 they will come forward with ambitious plans to cut emissions.”
US diplomatic sources said the Chinese government is unwilling to be seen buckling to overseas pressure on the coal consumption cuts.
Green Party MP Caroline Lucas said it was “absolutely essential” that China had a presence at the COP26 summit, as she expressed her concern that a new security pact between the US, UK and Australia had “just enraged the Chinese even more”.
Meanwhile, noted the BBC, some activists fear that China’s record is being used as a distraction by other nations. A spokeswoman for Extinction Rebellion UK said: “We mustn’t allow those trying to frustrate action to use China as a scapegoat and further excuse their own responsibility.”
-
 Political cartoons for February 21
Political cartoons for February 21Cartoons Saturday’s political cartoons include consequences, secrets, and more
-
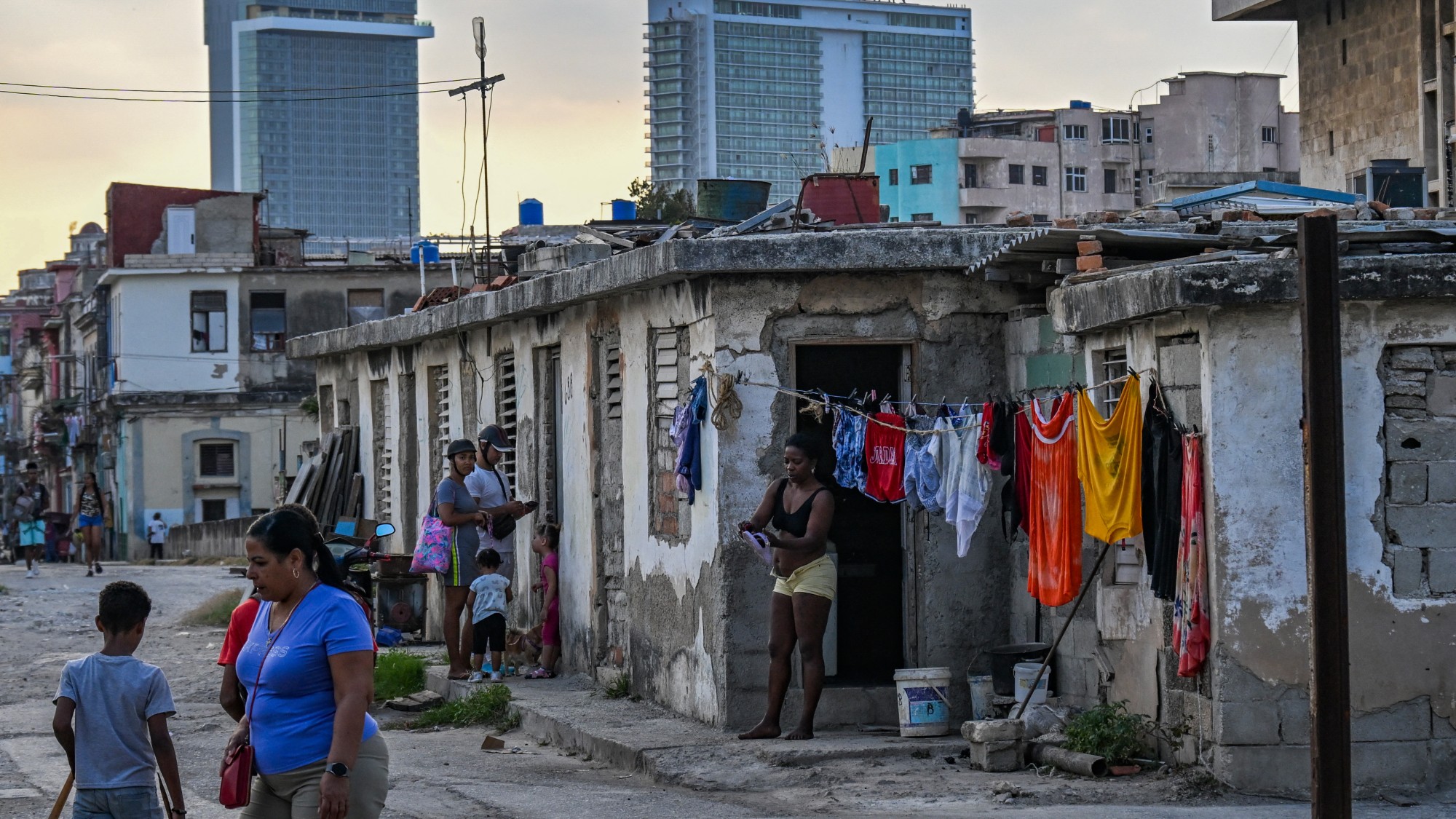 Crisis in Cuba: a ‘golden opportunity’ for Washington?
Crisis in Cuba: a ‘golden opportunity’ for Washington?Talking Point The Trump administration is applying the pressure, and with Latin America swinging to the right, Havana is becoming more ‘politically isolated’
-
 5 thoroughly redacted cartoons about Pam Bondi protecting predators
5 thoroughly redacted cartoons about Pam Bondi protecting predatorsCartoons Artists take on the real victim, types of protection, and more
-
 Earth is rapidly approaching a ‘hothouse’ trajectory of warming
Earth is rapidly approaching a ‘hothouse’ trajectory of warmingThe explainer It may become impossible to fix
-
 The plan to wall off the ‘Doomsday’ glacier
The plan to wall off the ‘Doomsday’ glacierUnder the Radar Massive barrier could ‘slow the rate of ice loss’ from Thwaites Glacier, whose total collapse would have devastating consequences
-
 Can the UK take any more rain?
Can the UK take any more rain?Today’s Big Question An Atlantic jet stream is ‘stuck’ over British skies, leading to ‘biblical’ downpours and more than 40 consecutive days of rain in some areas
-
 As temperatures rise, US incomes fall
As temperatures rise, US incomes fallUnder the radar Elevated temperatures are capable of affecting the entire economy
-
 The world is entering an ‘era of water bankruptcy’
The world is entering an ‘era of water bankruptcy’The explainer Water might soon be more valuable than gold
-
 Fifteen years after Fukushima, is Japan right to restart its reactors?
Fifteen years after Fukushima, is Japan right to restart its reactors?Today’s Big Question Balancing safety fears against energy needs
-
 Climate change could lead to a reptile ‘sexpocalypse’
Climate change could lead to a reptile ‘sexpocalypse’Under the radar The gender gap has hit the animal kingdom
-
 The former largest iceberg is turning blue. It’s a bad sign.
The former largest iceberg is turning blue. It’s a bad sign.Under the radar It is quickly melting away