Omicron now dominant coronavirus strain in new U.S. cases


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
The Omicron variant accounted for 73 percent of new coronavirus cases between Dec. 12 and 18, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said on Monday.
The Delta variant has been the driving force in U.S. infections for more than five months, with CDC data showing that at the end of last month, more than 99.5 percent of coronavirus cases were Delta. Omicron was first detected in southern Africa in late November, and has since been found in 90 countries. It's estimated that last week, more than 650,000 Omicron infections were reported in the United States.
In New York, the Pacific Northwest, and the Southeast, it's believed that at least 90 percent of new infections are because of Omicron, The Associated Press reports. The numbers are "stark," CDC Director Dr. Rochelle Walensky said, but "they're not surprising," as they follow the growth seen in other countries. She also anticipates that over time, "Delta will be crowded out by Omicron."
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Researchers are still trying to determine if Omicron causes a more severe illness; both Moderna and Pfizer have said in lab tests, a third dose of their COVID-19 vaccines increased immune response against Omicron. Dr. Amesh Adalja, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, told AP he expects Omicron will further spread during the holidays.
"All of us have a date with Omicron," Adalja said. "If you're going to interact with society, if you're going to have any type of life, Omicron will be something you encounter, and the best way you can encounter this is to be fully vaccinated."
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Catherine Garcia has worked as a senior writer at The Week since 2014. Her writing and reporting have appeared in Entertainment Weekly, The New York Times, Wirecutter, NBC News and "The Book of Jezebel," among others. She's a graduate of the University of Redlands and the Columbia University Graduate School of Journalism.
-
 Why is the Trump administration talking about ‘Western civilization’?
Why is the Trump administration talking about ‘Western civilization’?Talking Points Rubio says Europe, US bonded by religion and ancestry
-
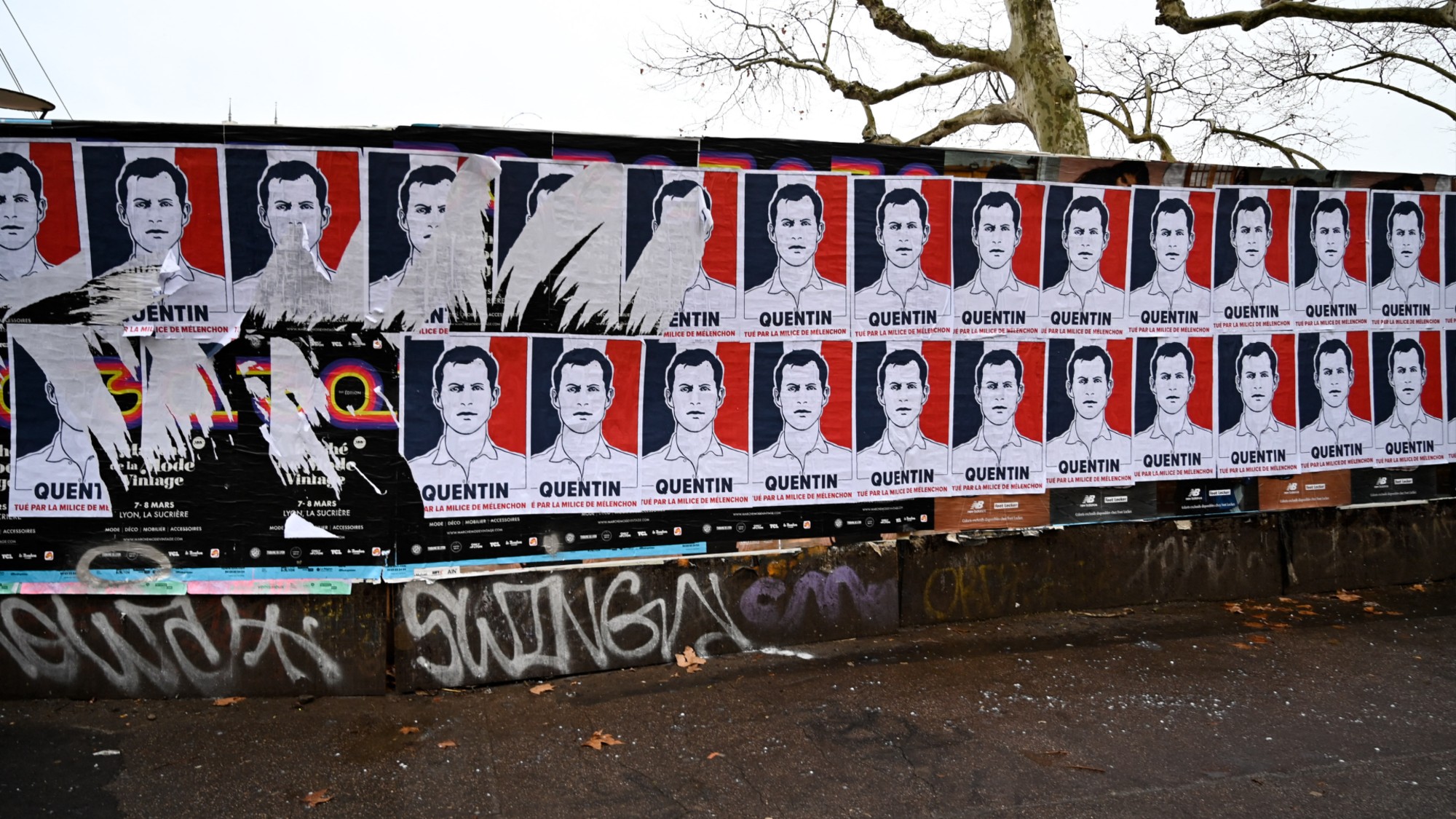 Quentin Deranque: a student’s death energizes the French far right
Quentin Deranque: a student’s death energizes the French far rightIN THE SPOTLIGHT Reactions to the violent killing of an ultraconservative activist offer a glimpse at the culture wars roiling France ahead of next year’s elections
-
 Secured vs. unsecured loans: how do they differ and which is better?
Secured vs. unsecured loans: how do they differ and which is better?the explainer They are distinguished by the level of risk and the inclusion of collateral
-
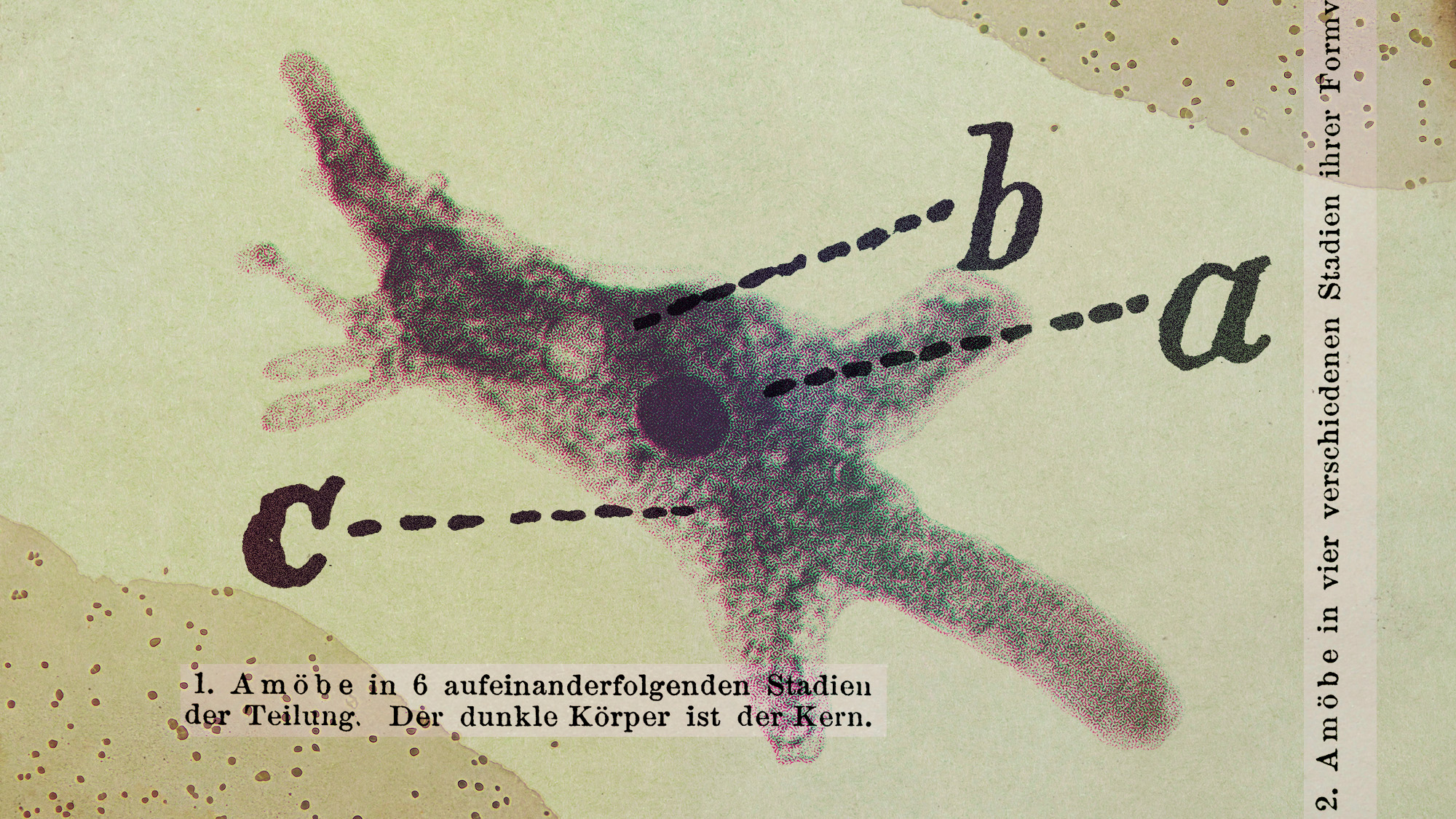 Scientists are worried about amoebas
Scientists are worried about amoebasUnder the radar Small and very mighty
-
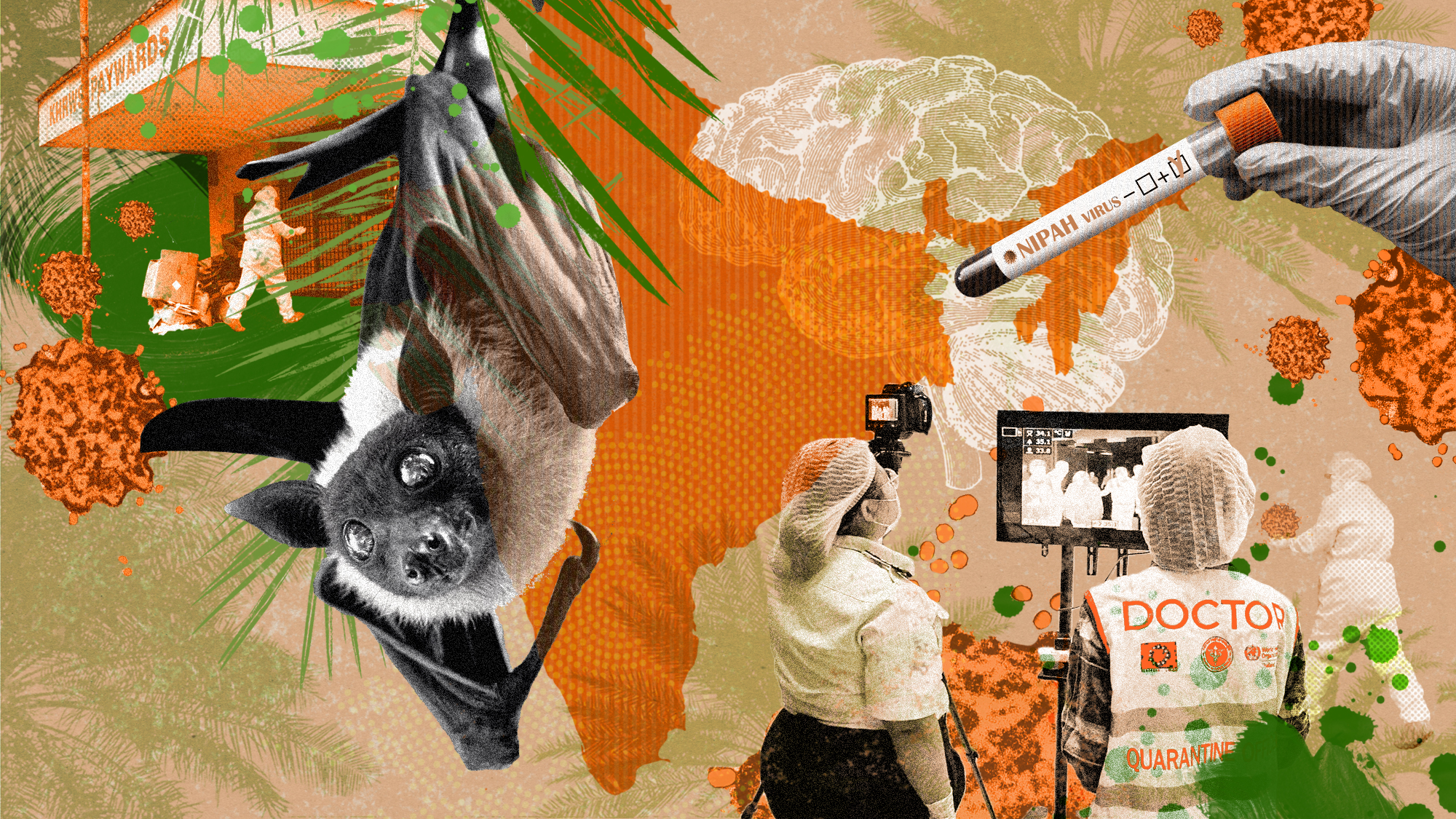 A Nipah virus outbreak in India has brought back Covid-era surveillance
A Nipah virus outbreak in India has brought back Covid-era surveillanceUnder the radar The disease can spread through animals and humans
-
 Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinations
Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinationsSpeed Read In a widely condemned move, the CDC will now recommend that children get vaccinated against 11 communicable diseases, not 17
-
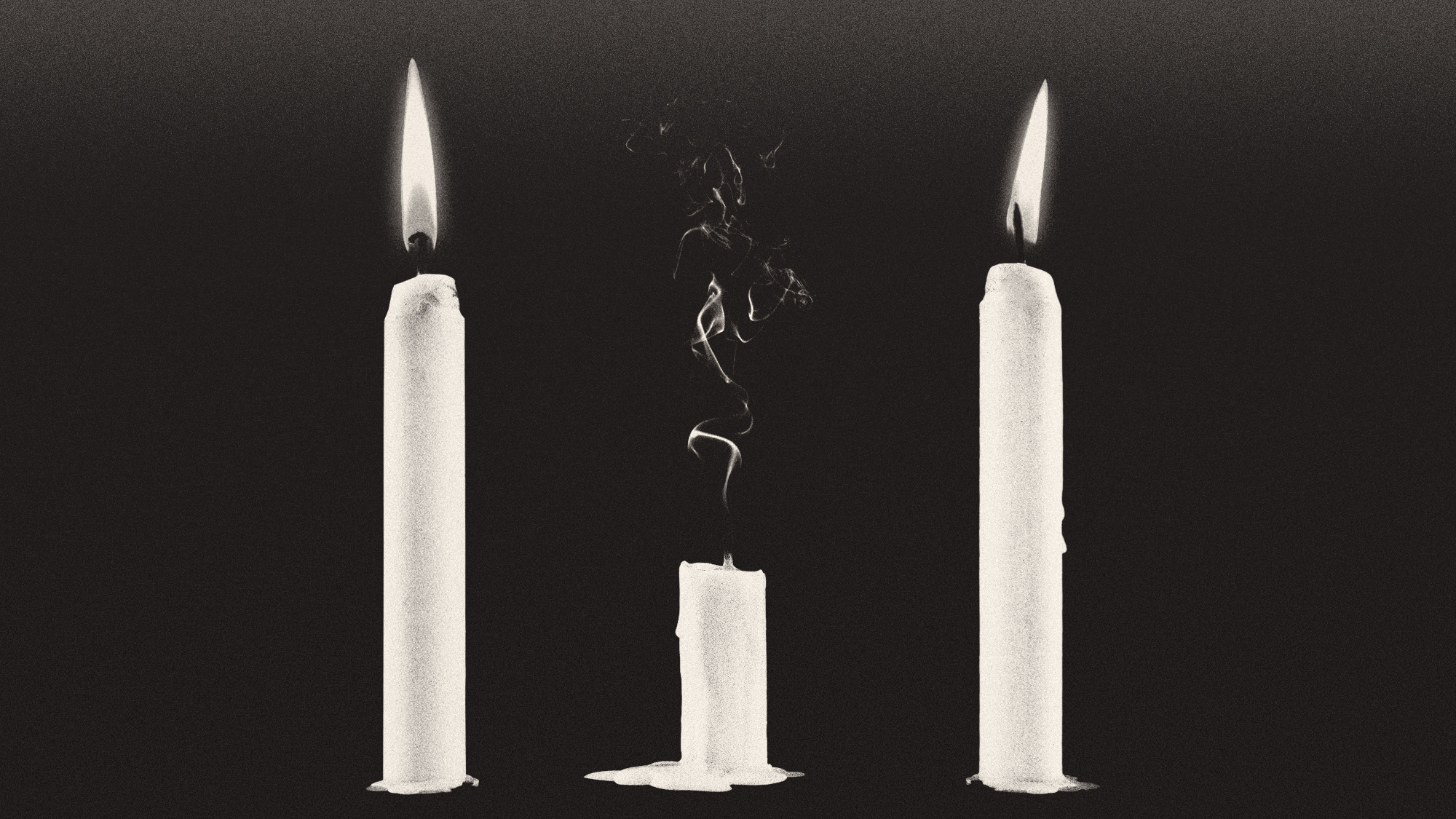 Deaths of children under 5 have gone up for the first time this century
Deaths of children under 5 have gone up for the first time this centuryUnder the radar Poor funding is the culprit
-
 A fentanyl vaccine may be on the horizon
A fentanyl vaccine may be on the horizonUnder the radar Taking a serious jab at the opioid epidemic
-
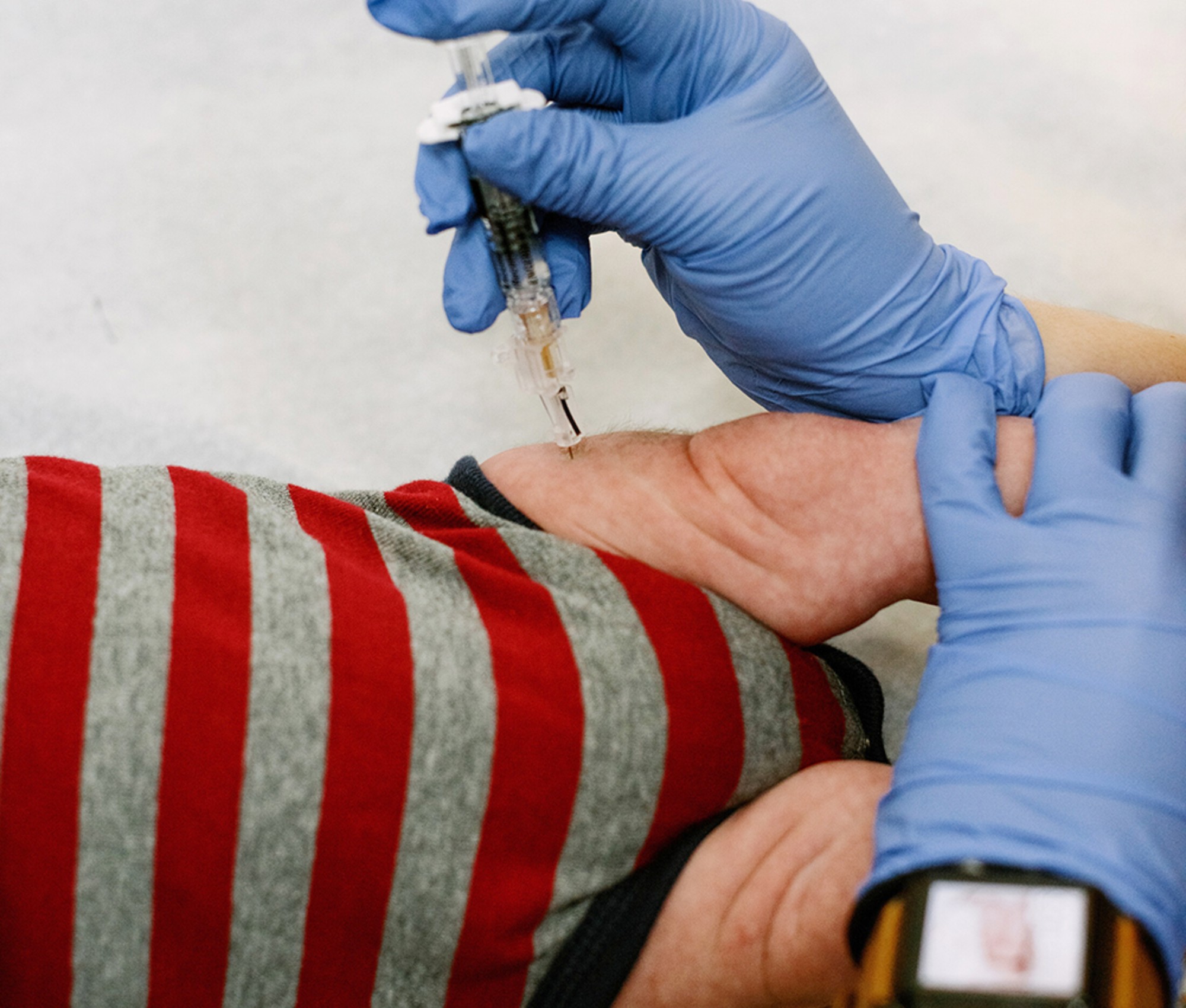 Health: Will Kennedy dismantle U.S. immunization policy?
Health: Will Kennedy dismantle U.S. immunization policy?Feature ‘America’s vaccine playbook is being rewritten by people who don’t believe in them’
-
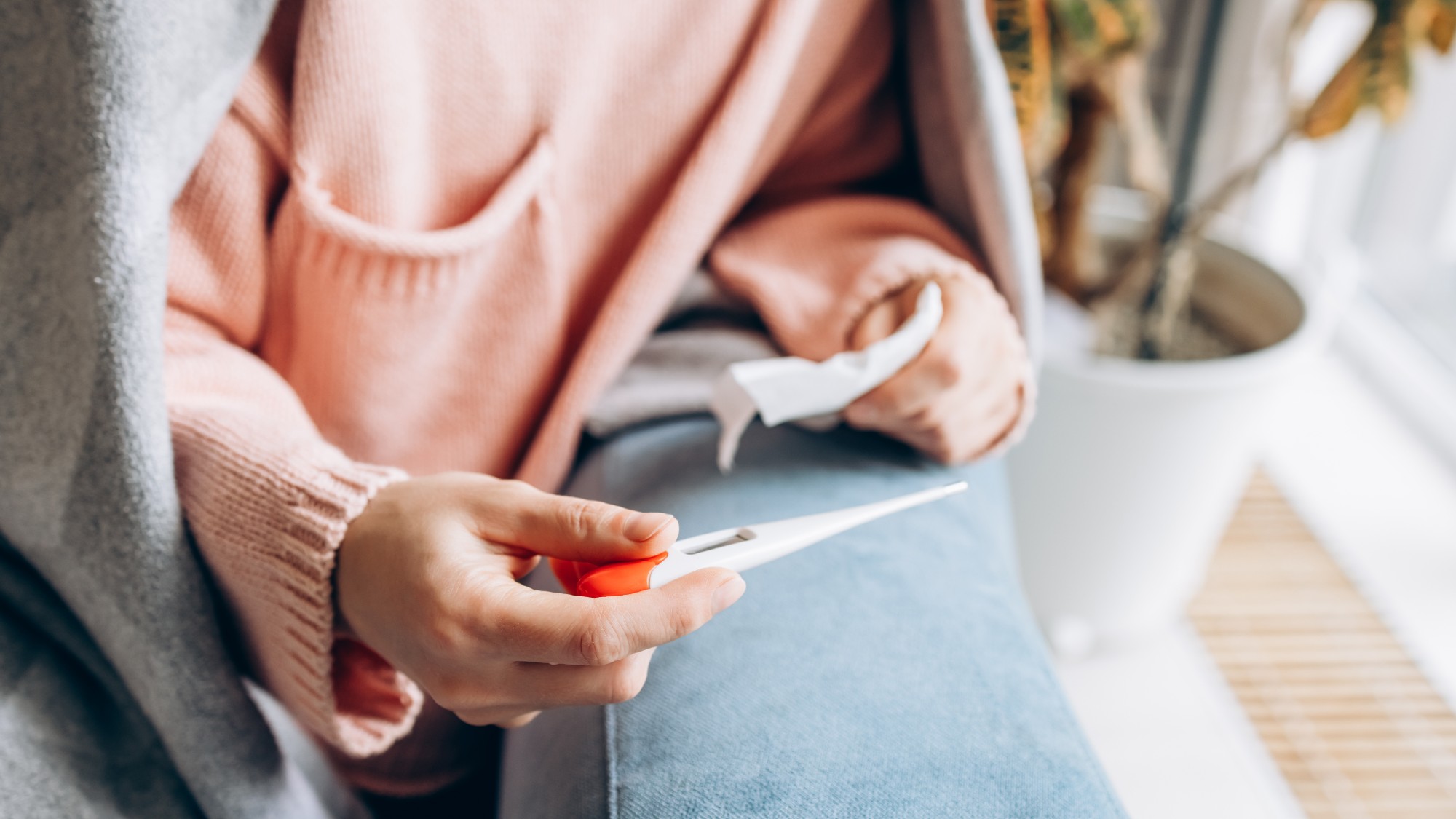 How dangerous is the ‘K’ strain super-flu?
How dangerous is the ‘K’ strain super-flu?The Explainer Surge in cases of new variant H3N2 flu in UK and around the world
-
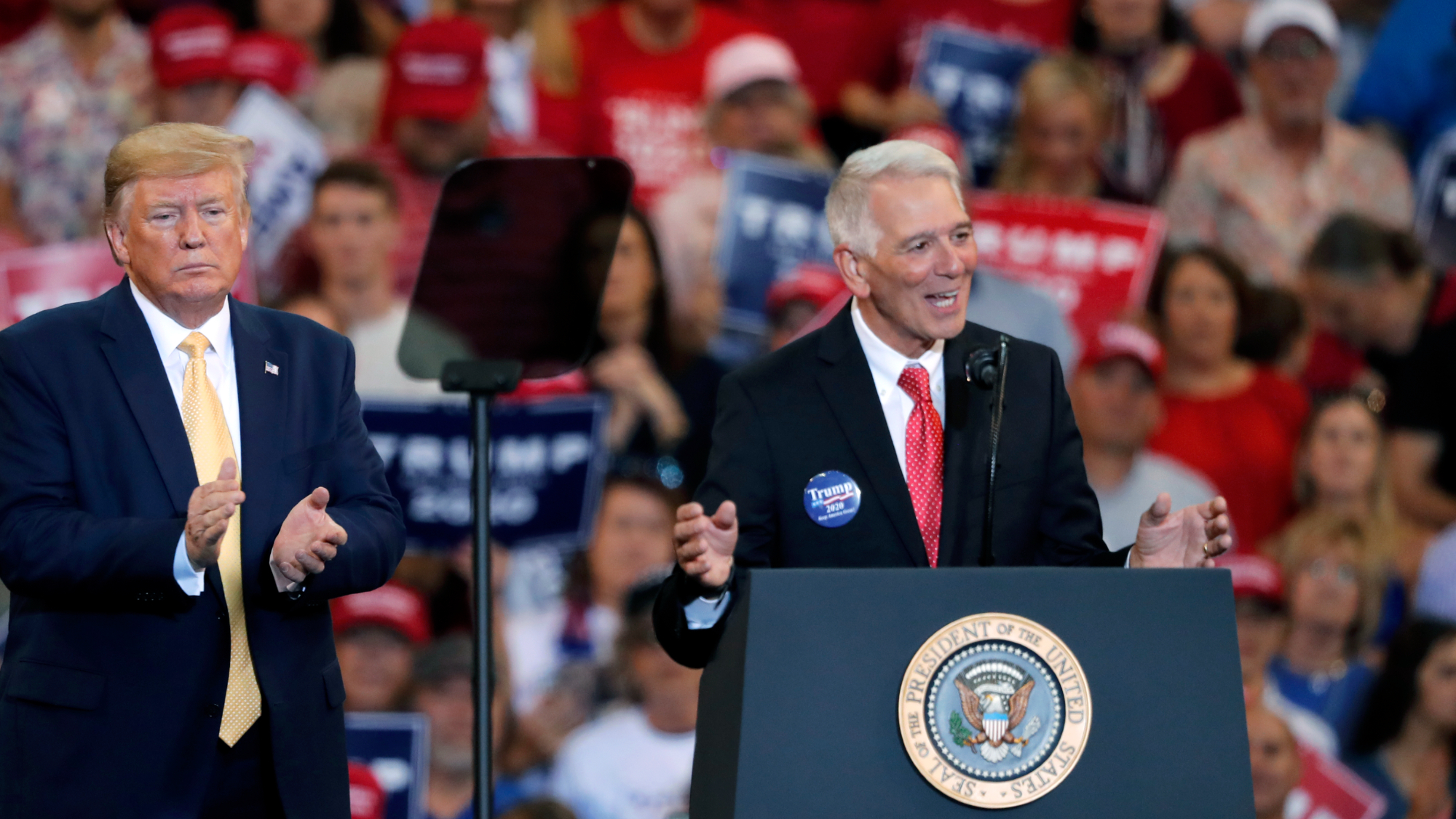 Vaccine critic quietly named CDC’s No. 2 official
Vaccine critic quietly named CDC’s No. 2 officialSpeed Read Dr. Ralph Abraham joins another prominent vaccine critic, HHS Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr.
