NASA says its DART mission successfully changed asteroid's orbit

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
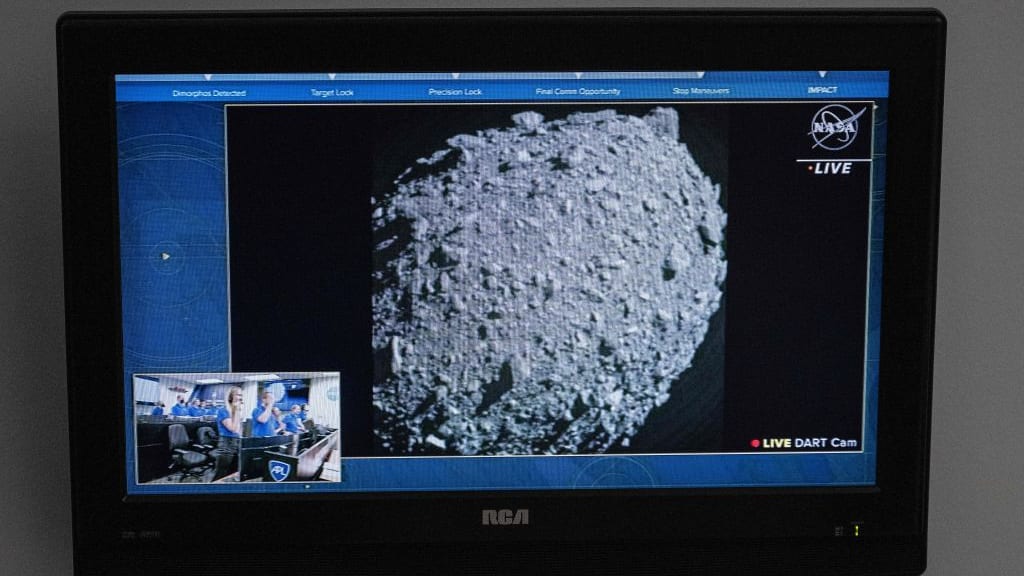
NASA's Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) spacecraft that crashed into a 560-foot-wide asteroid last month was able to change the space rock's orbit, the agency confirmed on Tuesday.
DART hit the asteroid, known as Dimorphos, at 14,000 miles per hour, and over the last several weeks, NASA officials have been looking at the data and images collected before, during, and after impact. This was the first real-life test of technology that could protect the Earth from asteroids with the potential of harming the planet; Dimorphos, which orbits a larger asteroid named Didymos, never posed a threat to the Earth.
Before DART hit Dimorphos, it took the asteroid 11 hours and 55 minutes to circle Didymos; NASA officials have used ground-based telescopes to determine the crash shortened Dimorphos' orbit by 32 minutes, to 11 hours and 23 minutes, NBC News reports. Now that the agency knows that "nudging" an asteroid can change its orbit, "NASA has proven we are serious as a defender of the planet," NASA Administrator Bill Nelson said in a statement, adding that the mission was "a watershed moment for planetary defense and all of humanity."
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Catherine Garcia has worked as a senior writer at The Week since 2014. Her writing and reporting have appeared in Entertainment Weekly, The New York Times, Wirecutter, NBC News and "The Book of Jezebel," among others. She's a graduate of the University of Redlands and the Columbia University Graduate School of Journalism.
-
 Local elections 2026: where are they and who is expected to win?
Local elections 2026: where are they and who is expected to win?The Explainer Labour is braced for heavy losses and U-turn on postponing some council elections hasn’t helped the party’s prospects
-
 6 of the world’s most accessible destinations
6 of the world’s most accessible destinationsThe Week Recommends Experience all of Berlin, Singapore and Sydney
-
 How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule works
How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule worksIn the Spotlight The law is at the heart of the Colbert-CBS conflict
-
 Nasa’s new dark matter map
Nasa’s new dark matter mapUnder the Radar High-resolution images may help scientists understand the ‘gravitational scaffolding into which everything else falls and is built into galaxies’
-
 Moon dust has earthly elements thanks to a magnetic bridge
Moon dust has earthly elements thanks to a magnetic bridgeUnder the radar The substances could help supply a lunar base
-
 How Mars influences Earth’s climate
How Mars influences Earth’s climateThe explainer A pull in the right direction
-
 The ‘eclipse of the century’ is coming in 2027
The ‘eclipse of the century’ is coming in 2027Under the radar It will last for over 6 minutes
-
 NASA discovered ‘resilient’ microbes in its cleanrooms
NASA discovered ‘resilient’ microbes in its cleanroomsUnder the radar The bacteria could contaminate space
-
 Artemis II: back to the Moon
Artemis II: back to the MoonThe Explainer Four astronauts will soon be blasting off into deep space – the first to do so in half a century
-
 The mysterious origin of a lemon-shaped exoplanet
The mysterious origin of a lemon-shaped exoplanetUnder the radar It may be made from a former star
-
 The 5 biggest astronomy stories of 2025
The 5 biggest astronomy stories of 2025In the spotlight From moons, to comets, to pop stars in orbit
