Scientists discover a new way of diagnosing breast cancer — using artificial intelligence

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Scientists at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology are fighting to make breast cancer diagnosis more efficient — and they've turned to artificial intelligence to do so.
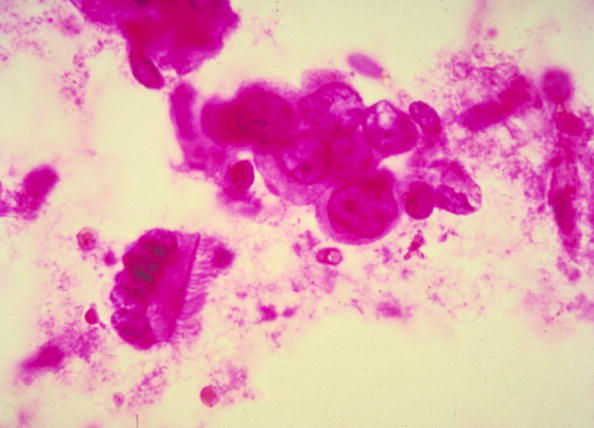
Traditionally, women undergo regular mammograms, which provide images of the breasts that doctors use to identify any lesions. But while mammograms can categorize lesions as "high risk," they cannot do so with foolproof accuracy, and a needle biopsy must be performed to determine whether the tissue is in fact cancerous. Ninety percent of these lesions are determined to be non-cancerous, MIT notes, but only after the invasive procedure has been performed.
That's where the AI comes in. Researchers at MIT's Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL), together with Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, developed a groundbreaking new model that uses machine learning to evaluate high-risk lesions before surgery. The model, known as a "random-forest classifier," is armed with information about more than 600 existing cases, and it uses that information to identify patterns across different data points, including demographics and medical history, to more accurately predict whether lesions will become cancerous without performing the biopsy.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Additionally, some doctors perform surgery in all cases of high-risk lesions, while others look only for specific types of lesions that are known to have a higher chance of becoming cancerous before operating. The team's model yielded more accurate diagnoses despite screening for more cancers, correctly diagnosing 97 percent of cancers, MIT said, as opposed to just 79 percent via surgery on traditional high-risk lesions.
Because the traditional diagnostic tools, like mammograms, are "so inexact," doctors tend to over-screen for breast cancer, said MIT CSAIL professor Regina Barzilay, a lead author on the study and recent MacArthur "genius grant" winner. That leads to the unnecessary, expensive surgeries that find legions to be benign. "A model like this ... hopefully will enable us to start to go beyond a one-size-fits-all approach to medical diagnosis," Barzilay said.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Kimberly Alters is the news editor at TheWeek.com. She is a graduate of the Medill School of Journalism at Northwestern University.
-
 6 of the world’s most accessible destinations
6 of the world’s most accessible destinationsThe Week Recommends Experience all of Berlin, Singapore and Sydney
-
 How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule works
How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule worksIn the Spotlight The law is at the heart of the Colbert-CBS conflict
-
 What is the endgame in the DHS shutdown?
What is the endgame in the DHS shutdown?Today’s Big Question Democrats want to rein in ICE’s immigration crackdown
-
 ‘One Battle After Another’ wins Critics Choice honors
‘One Battle After Another’ wins Critics Choice honorsSpeed Read Paul Thomas Anderson’s latest film, which stars Leonardo DiCaprio, won best picture at the 31st Critics Choice Awards
-
 Son arrested over killing of Rob and Michele Reiner
Son arrested over killing of Rob and Michele ReinerSpeed Read Nick, the 32-year-old son of Hollywood director Rob Reiner, has been booked for the murder of his parents
-
 Rob Reiner, wife dead in ‘apparent homicide’
Rob Reiner, wife dead in ‘apparent homicide’speed read The Reiners, found in their Los Angeles home, ‘had injuries consistent with being stabbed’
-
 Hungary’s Krasznahorkai wins Nobel for literature
Hungary’s Krasznahorkai wins Nobel for literatureSpeed Read László Krasznahorkai is the author of acclaimed novels like ‘The Melancholy of Resistance’ and ‘Satantango’
-
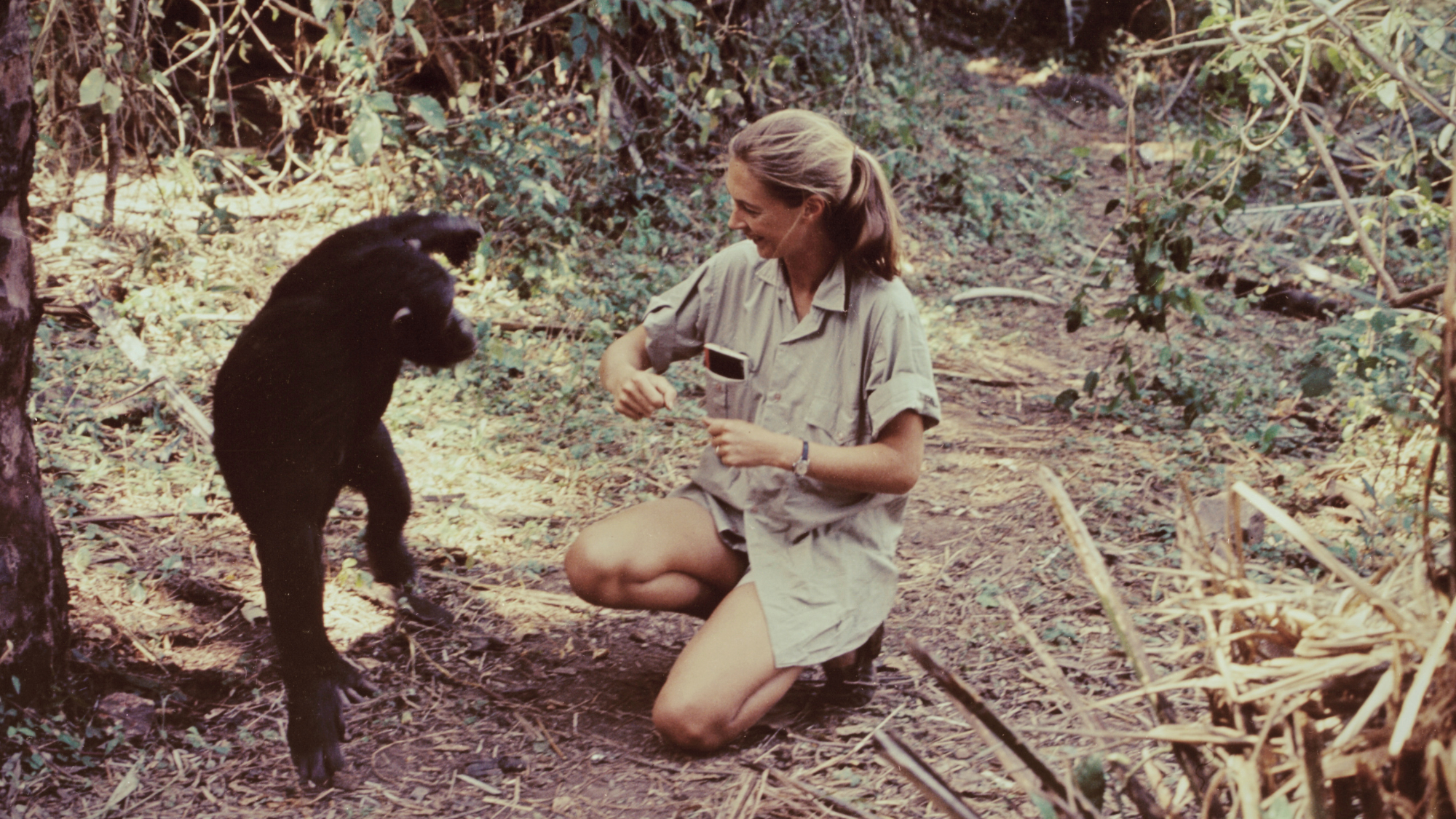 Primatologist Jane Goodall dies at 91
Primatologist Jane Goodall dies at 91Speed Read She rose to fame following her groundbreaking field research with chimpanzees
-
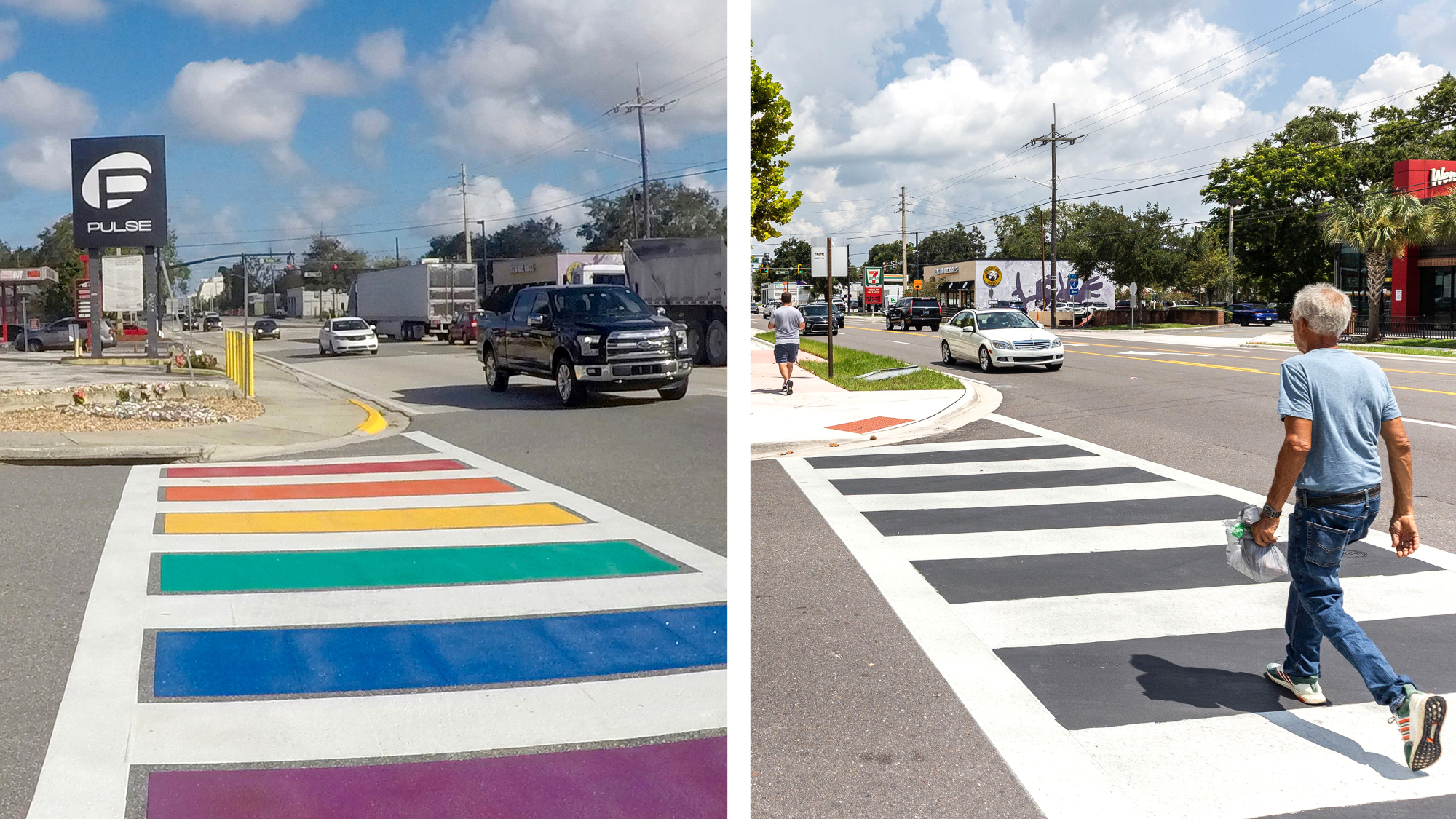 Florida erases rainbow crosswalk at Pulse nightclub
Florida erases rainbow crosswalk at Pulse nightclubSpeed Read The colorful crosswalk was outside the former LGBTQ nightclub where 49 people were killed in a 2016 shooting
-
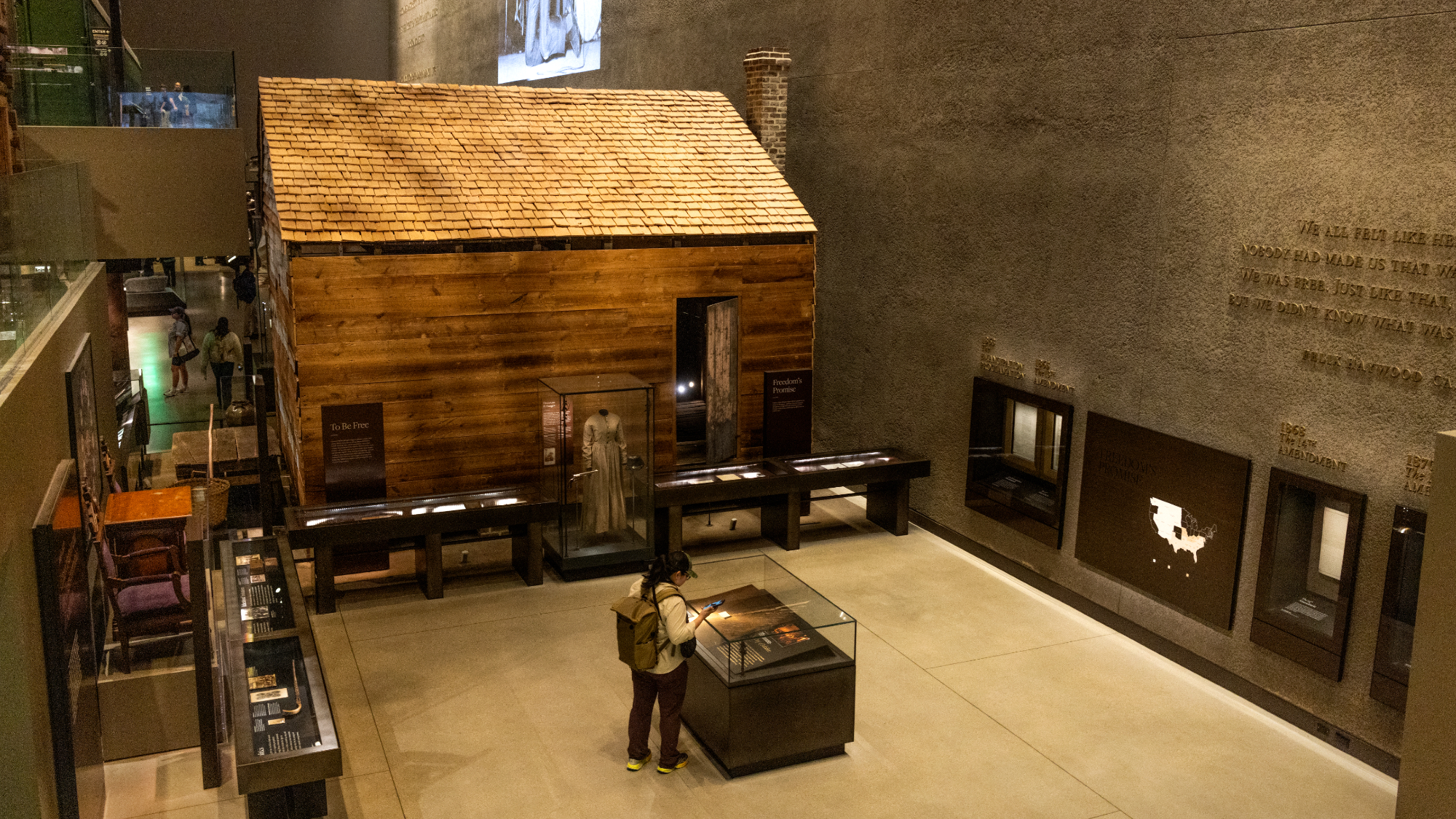 Trump says Smithsonian too focused on slavery's ills
Trump says Smithsonian too focused on slavery's illsSpeed Read The president would prefer the museum to highlight 'success,' 'brightness' and 'the future'
-
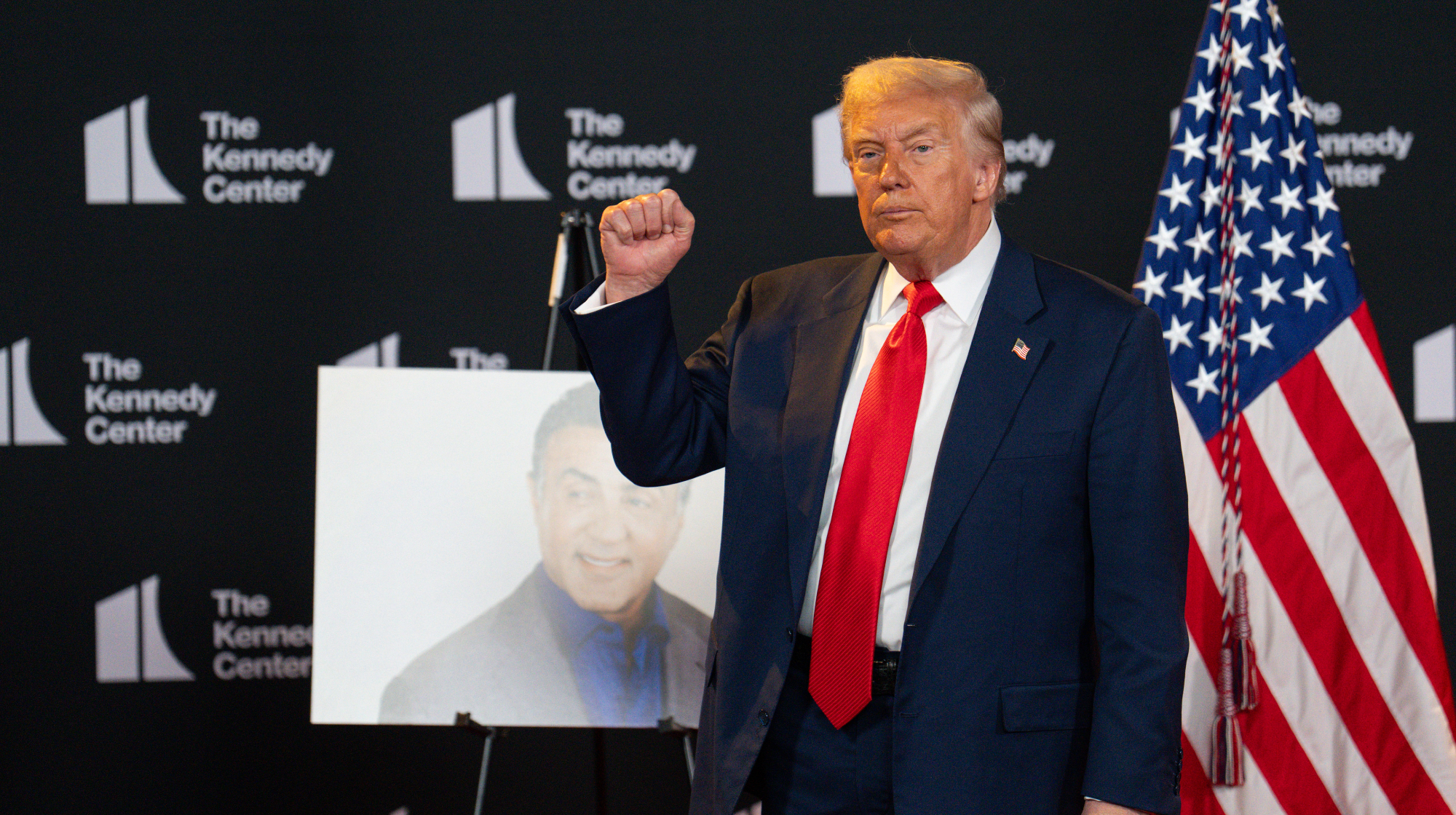 Trump to host Kennedy Honors for Kiss, Stallone
Trump to host Kennedy Honors for Kiss, StalloneSpeed Read Actor Sylvester Stallone and the glam-rock band Kiss were among those named as this year's inductees
