20 years after the Rwanda genocide, 'forgiveness is possible'
Chip Somodevilla/Getty Images


In the ultimate act of forgiveness, many survivors of the genocide in Rwanda are now working — and even forming friendships — with the same people who tried to kill them 20 years ago.
Beginning on April 7, 1994, ethnic Hutus killed more than one million Tutsis and moderate Hutus during a heinous, 100-day wave of ethnic violence. Since then, the government has pushed to create a single Rwandan identity, and organizations have been created to bring survivors and perpetrators together. "Forgiveness is possible. It's common here," Josephine Munyeli, a genocide survivor and director of peace and reconciliation programs for World Vision, tells The Asssociated Press. "Guilt is heavy. When one realizes how heavy it is the first thing they do to recuperate themselves is apologize."
Emmanuel Ndayisaba killed, by his own account, at least 18 people during the genocide. It was at one of these reconciliation groups that he saw Alice Mukarurinda, a Tutsi woman whose hand he chopped off after killing her baby and a niece so many years ago. He begged for her forgiveness, and after thinking it over and talking with her husband, Mukarurinda granted it. "We had attended workshops and trainings and our hearts were kind of free, and I found it easy to forgive," she told the AP. "The Bible says you should forgive and you will also be forgiven." Now, they work side by side for a program that builds houses for genocide survivors; she is the treasurer, and he is the vice president.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Catherine Garcia has worked as a senior writer at The Week since 2014. Her writing and reporting have appeared in Entertainment Weekly, The New York Times, Wirecutter, NBC News and "The Book of Jezebel," among others. She's a graduate of the University of Redlands and the Columbia University Graduate School of Journalism.
-
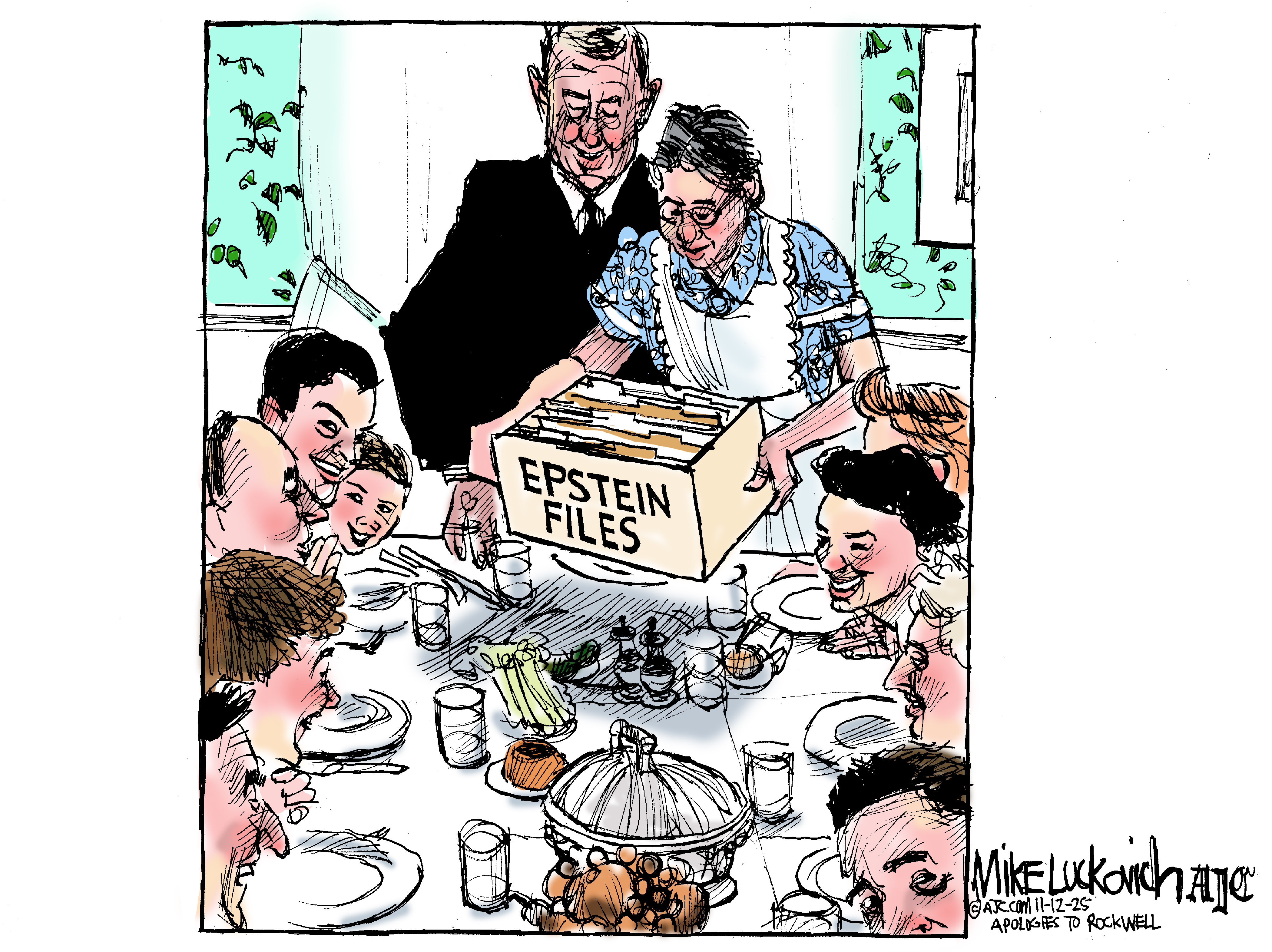 5 hilariously incriminating cartoons about the Epstein files
5 hilariously incriminating cartoons about the Epstein filesCartoons Artists take on an Epstein Thanksgiving, solving the puzzle, and more
-
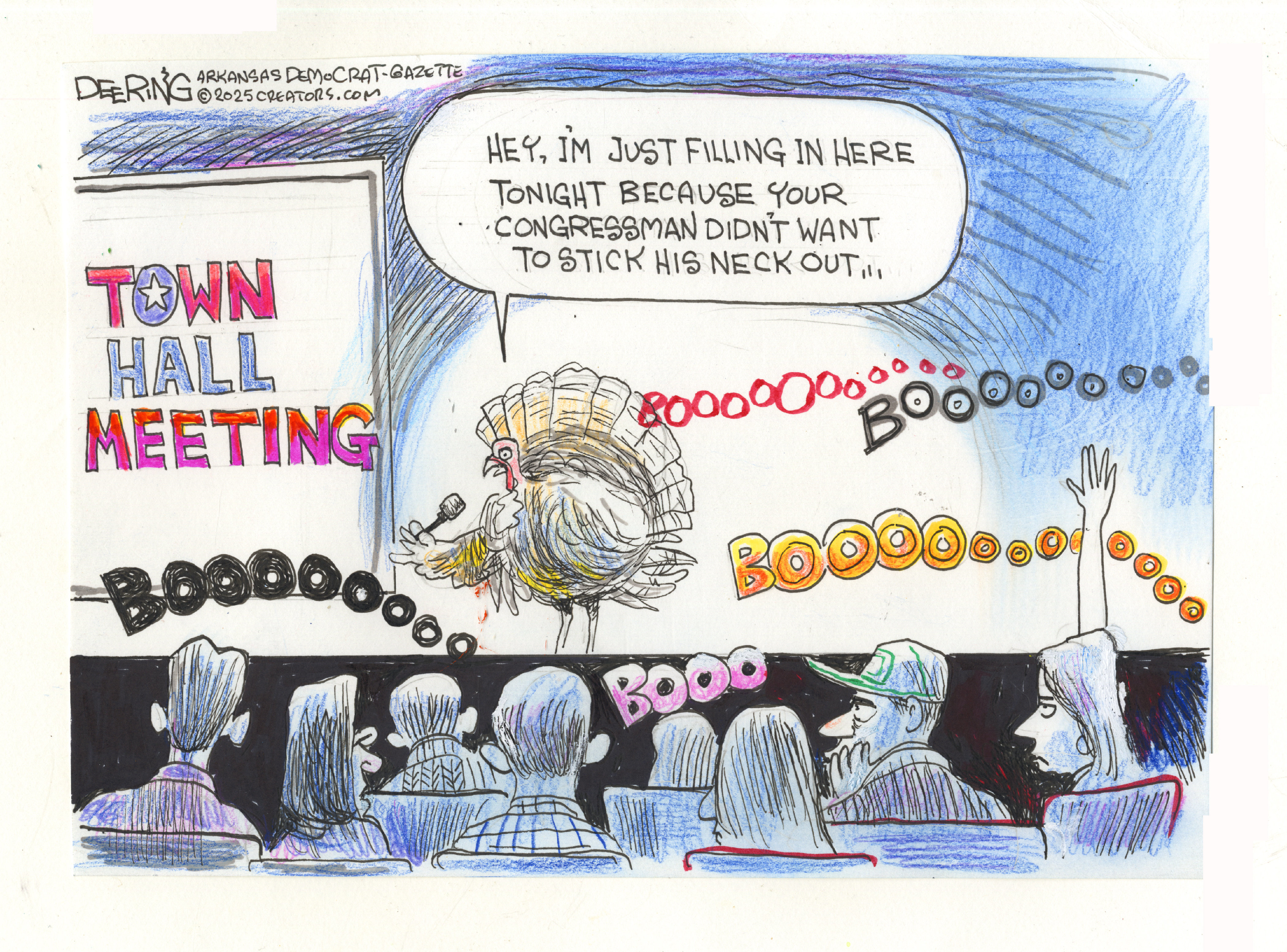 Political cartoons for November 15
Political cartoons for November 15Cartoons Saturday's political cartoons include cowardly congressmen, a Macy's parade monster, and more
-
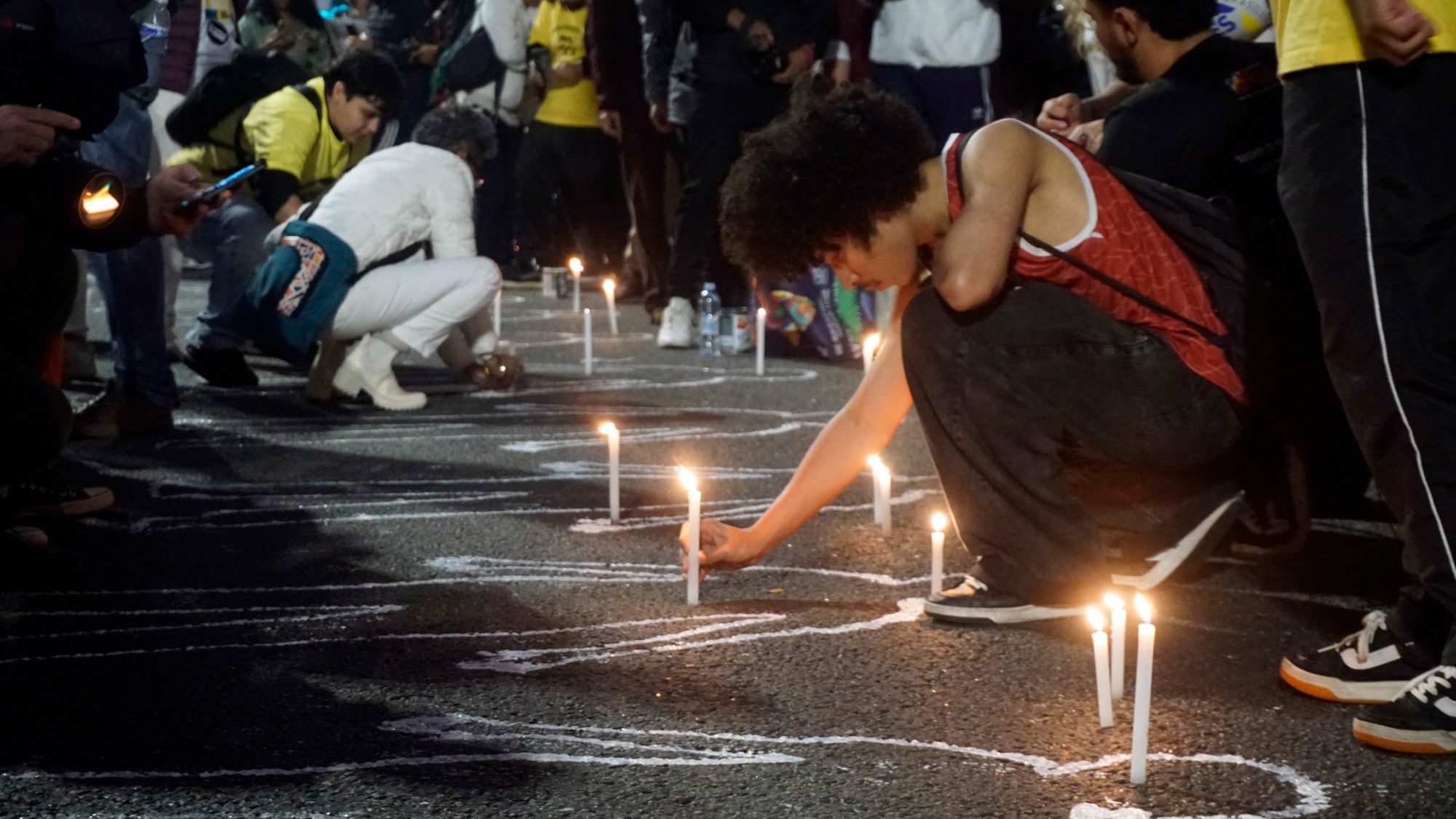 Massacre in the favela: Rio’s police take on the gangs
Massacre in the favela: Rio’s police take on the gangsIn the Spotlight The ‘defence operation’ killed 132 suspected gang members, but could spark ‘more hatred and revenge’
-
 Trump DOJ sues to block California redistricting
Trump DOJ sues to block California redistrictingSpeed Read California’s new congressional map was drawn by Democrats to flip Republican-held House seats
-
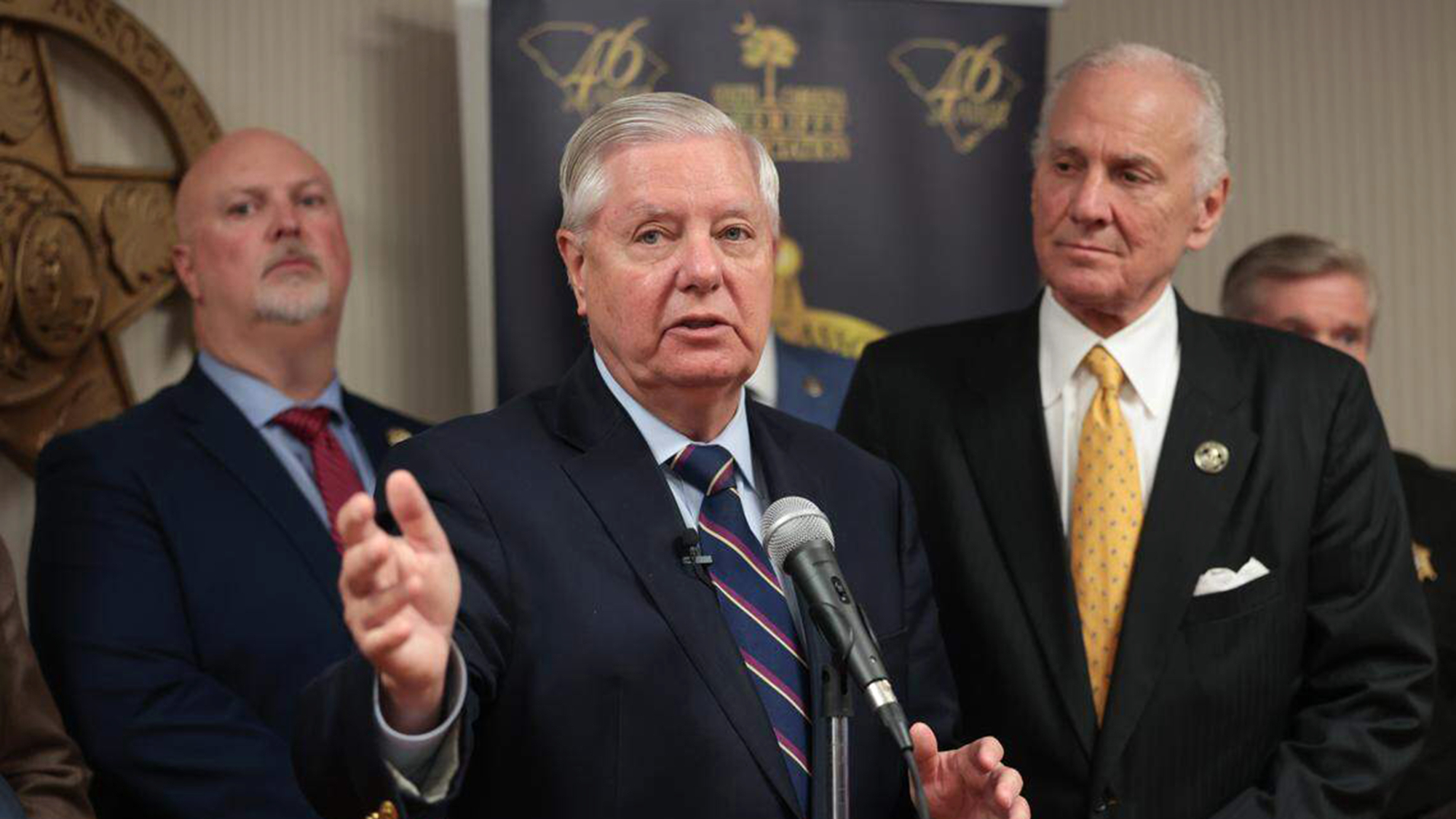 GOP retreats from shutdown deal payout provision
GOP retreats from shutdown deal payout provisionSpeed Read Senators are distancing themselves from a controversial provision in the new government funding package
-
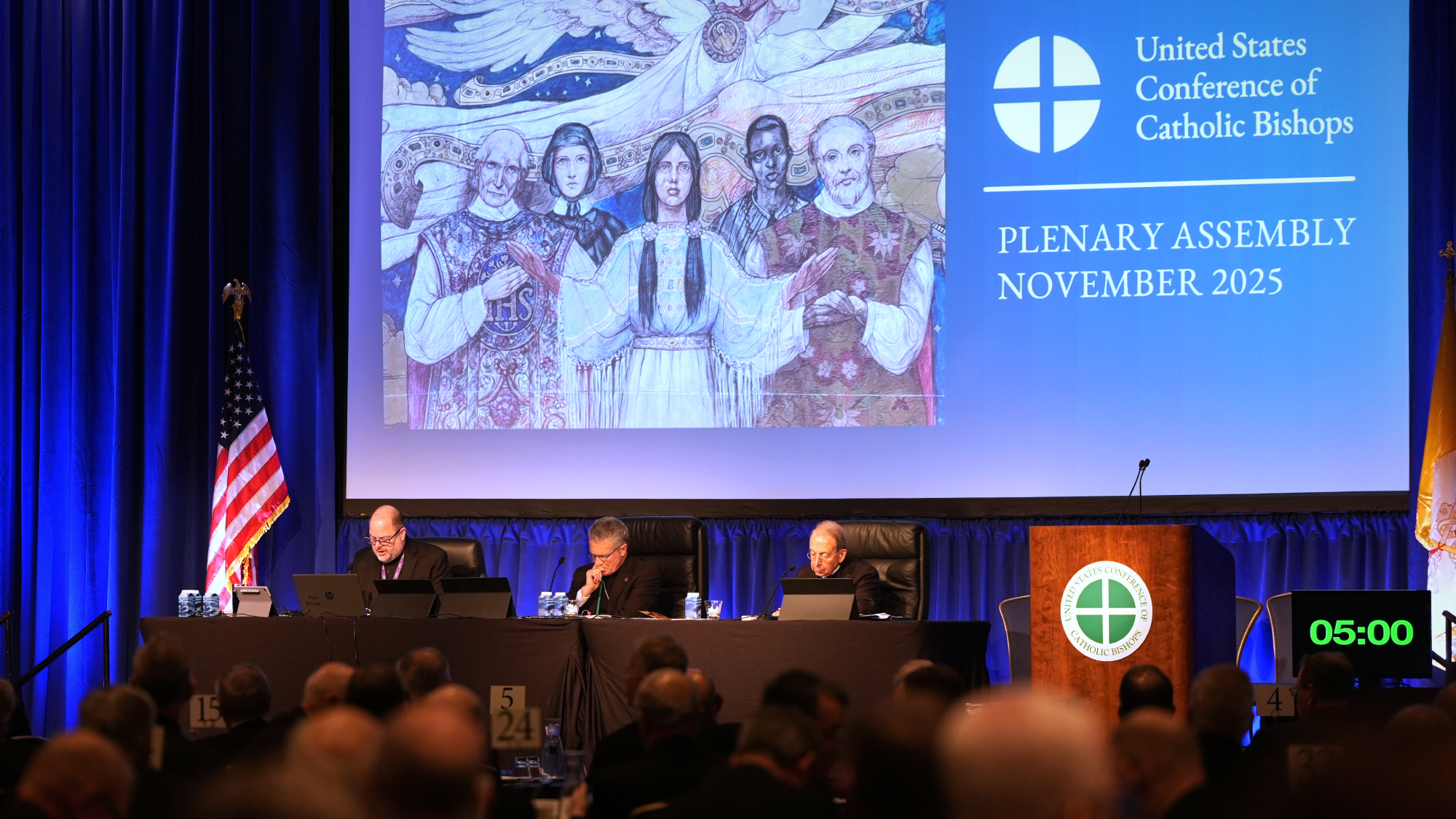 Catholic bishops rebuke Trump on immigration
Catholic bishops rebuke Trump on immigrationSpeed Read ‘We feel compelled’ to ‘raise our voices in defense of God-given human dignity,’ the bishops said
-
 House releases Epstein emails referencing Trump
House releases Epstein emails referencing TrumpSpeed Read The emails suggest Trump knew more about Epstein’s sex trafficking of underage women than he has claimed
-
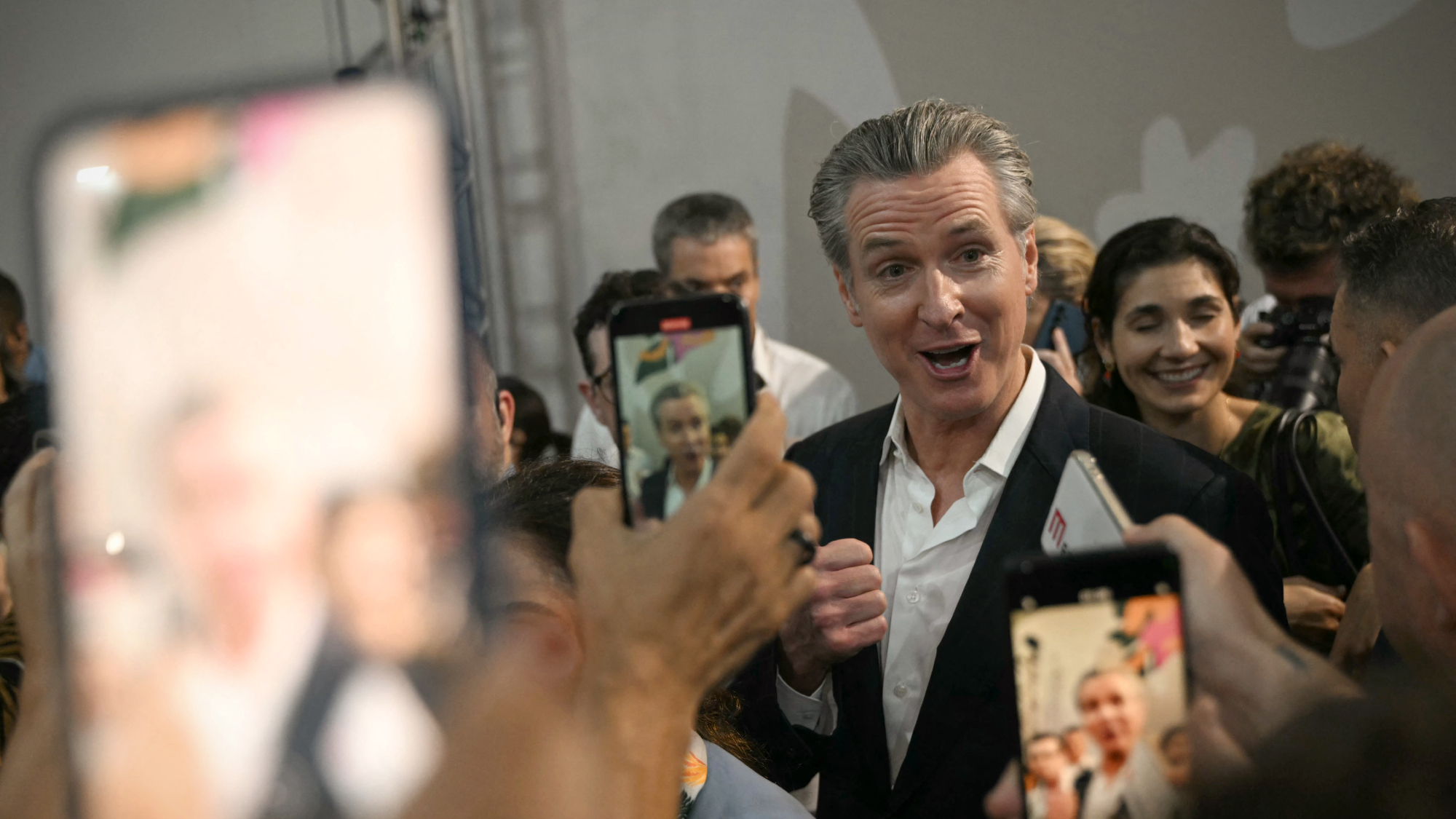 Newsom slams Trump’s climate denial at COP30
Newsom slams Trump’s climate denial at COP30speed read Trump, who has called climate change a ‘hoax,’ declined to send any officials to this week’s summit
-
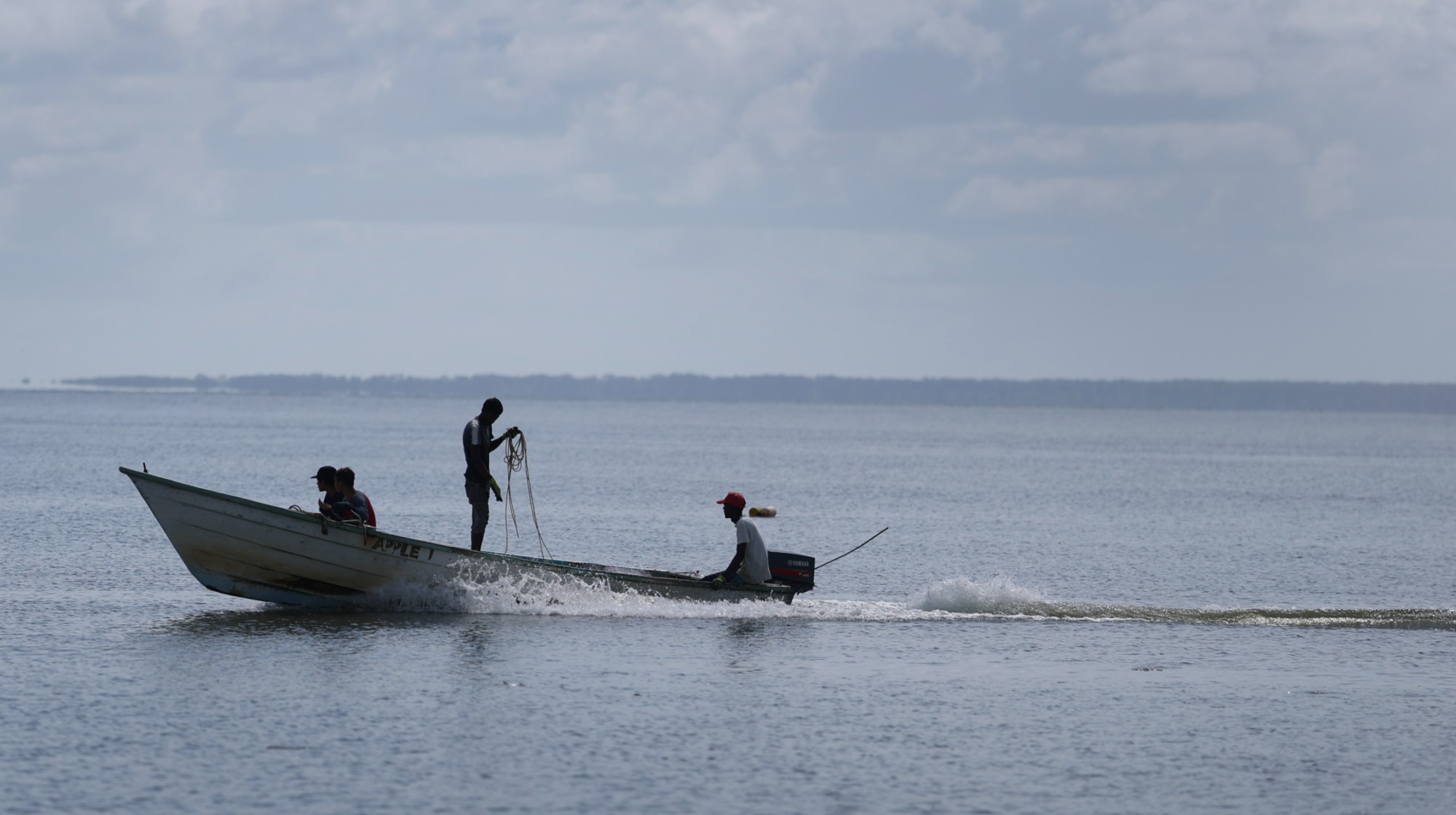 UK, Colombia halt intel to US over boat attacks
UK, Colombia halt intel to US over boat attacksSpeed Read Both countries have suspended intelligence sharing with the US over the bombing of civilian boats suspected of drug smuggling
-
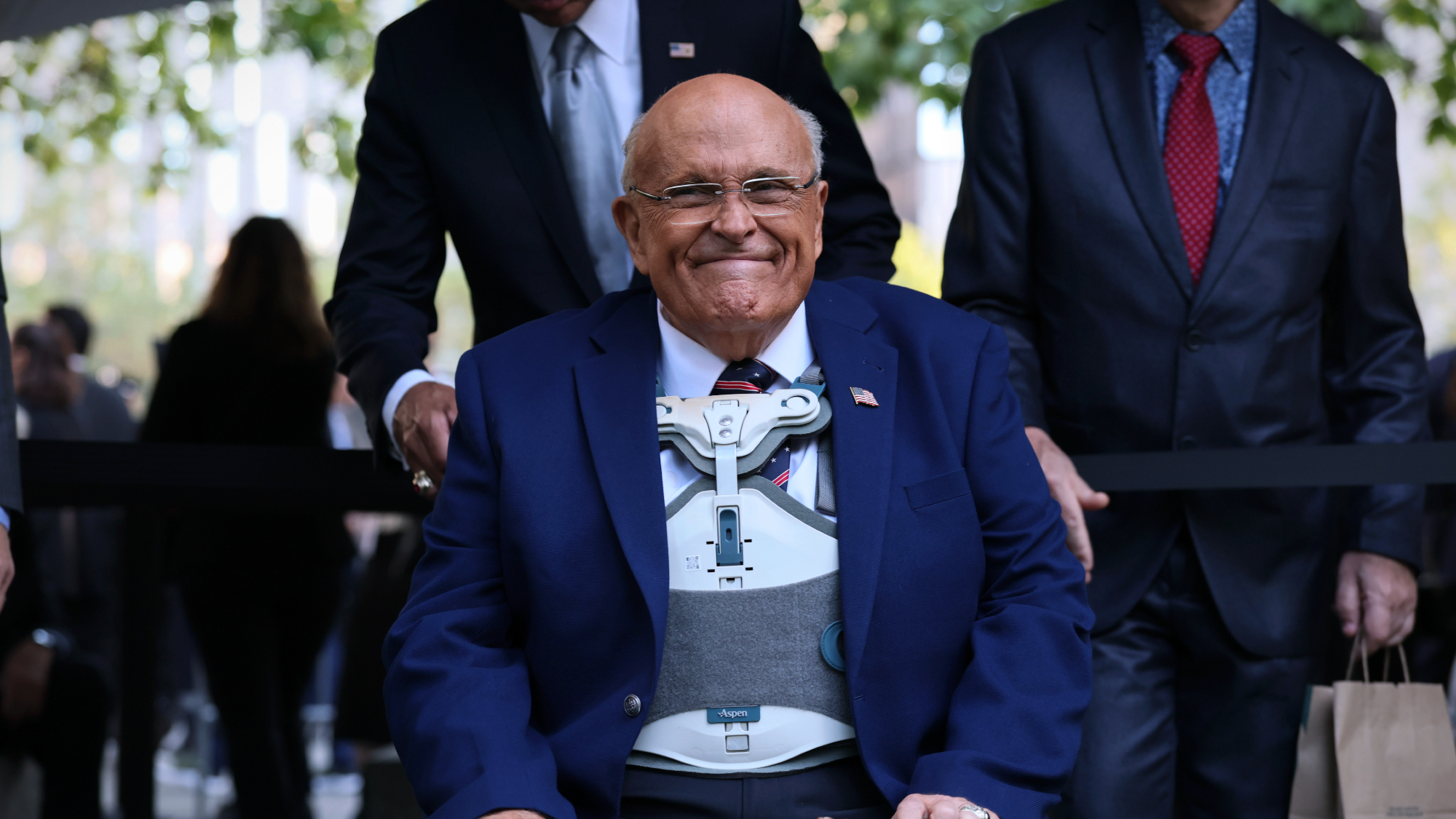 Trump pardons 2020 fake electors, other GOP allies
Trump pardons 2020 fake electors, other GOP alliesSpeed Read The president pardoned Rudy Giuliani and more who tried to overturn his 2020 election loss
-
 Supreme Court to decide on mail-in ballot limits
Supreme Court to decide on mail-in ballot limitsSpeed Read The court will determine whether states can count mail-in ballots received after Election Day
