How the Supreme Court crippled direct democracy
The initiative process in dozens of states just got a whole lot weaker

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Gay marriage advocates won a big dual victory in two cases decided by the Supreme Court on Wednesday. But one of the two decisions, the ruling that effectively struck down California's Proposition 8, may have a very significant impact on governing that's separate from the gay-marriage issue.
The Prop 8 ruling may have dealt a body blow to the ideal of direct democracy.
California voters approved Prop 8 in 2008. A district court decision later overturned the Prop. 8 law, and California's elected officials refused to appeal. So the supporters of Proposition 8 sued instead. They won their case over whether they had the right to sue in the California Supreme Court. The U.S. Supreme Court saw things much differently. The Supreme Court, in a 5-4 decision, held that the plaintiffs lacked standing. The court ignored the underlying issue of gay marriage, and instead held that the anti-gay-marriage advocates couldn't show they were harmed by the state government's decision to ignore the initiative. The decision quotes an older Supreme Court ruling noting that the doctrine of standing "serves to prevent the judicial process from being used to usurp the powers of the political branches." But usurping the power of the political branches is exactly what the initiative is specifically designed to do.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
The entire reason for initiatives is to bypass the office-holders in government. Former California Gov. Hiram Johnson, who was responsible for the state's passage of the direct democracy provisions, said that the initiative would "give to the electorate the power of action when desired." Frequently, the laws passed by initiative are unpopular or politically unpalatable with elected officials. Consider, for instance, California's popularly approved initiative that stripped the power of redistricting from the state legislature.
The Supreme Court's decision may mean that initiatives are now at the mercy of elected officials. Imagine a popularly approved referendum that is challenged and struck down in court. The government can just elect not to appeal — and thanks to the Supreme Court, no private citizens can step in to fill this void.
The track record of elected officials acting against their perceived self-interest is not good. You don't just have to look at the sorry state of campaign finance laws, which frequently assist the incumbent, or in the use of redistricting to gerrymander impregnable districts. There's also the initiative's direct democracy cousin, the recall. In the past two years, we have seen numerous instances of elected officials across the country in local jurisdictions working to subvert the use of the recall against themselves or their colleagues. The officials may refuse to schedule a vote. In other cases, they sue under very questionable legal arguments to stop the recall from taking place. In one instance, a city council tried to kill the adoption of a recall law, only to be overturned by a charter commission and the voters.
Elected officials already have a great weapon. Supporters of recalls or initiatives have to pay legal fees out of their own pocket to force the elected officials to act. Elected officials usually have the luxury of defending the sometimes questionable decisions using government funds. But even that advantage pales in comparison to strength they've just been given by the Supreme Court.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Initiatives are frequently divisive and controversial, as Prop 8 shows. But the voters and officials of the 27 states with the initiative or popular referendum process in place are the ones who decided to grant people this power. They adopted these laws specifically to provide a way to bypass the governor and legislature and enact politically unpalatable laws. The Supreme Court may have just effectively shut that route down.
Joshua Spivak is a senior fellow at the Hugh L. Carey Institute for Government Reform at Wagner College in New York, and writes The Recall Elections Blog.
-
 The billionaires’ wealth tax: a catastrophe for California?
The billionaires’ wealth tax: a catastrophe for California?Talking Point Peter Thiel and Larry Page preparing to change state residency
-
 Bari Weiss’ ‘60 Minutes’ scandal is about more than one report
Bari Weiss’ ‘60 Minutes’ scandal is about more than one reportIN THE SPOTLIGHT By blocking an approved segment on a controversial prison holding US deportees in El Salvador, the editor-in-chief of CBS News has become the main story
-
 Has Zohran Mamdani shown the Democrats how to win again?
Has Zohran Mamdani shown the Democrats how to win again?Today’s Big Question New York City mayoral election touted as victory for left-wing populists but moderate centrist wins elsewhere present more complex path for Democratic Party
-
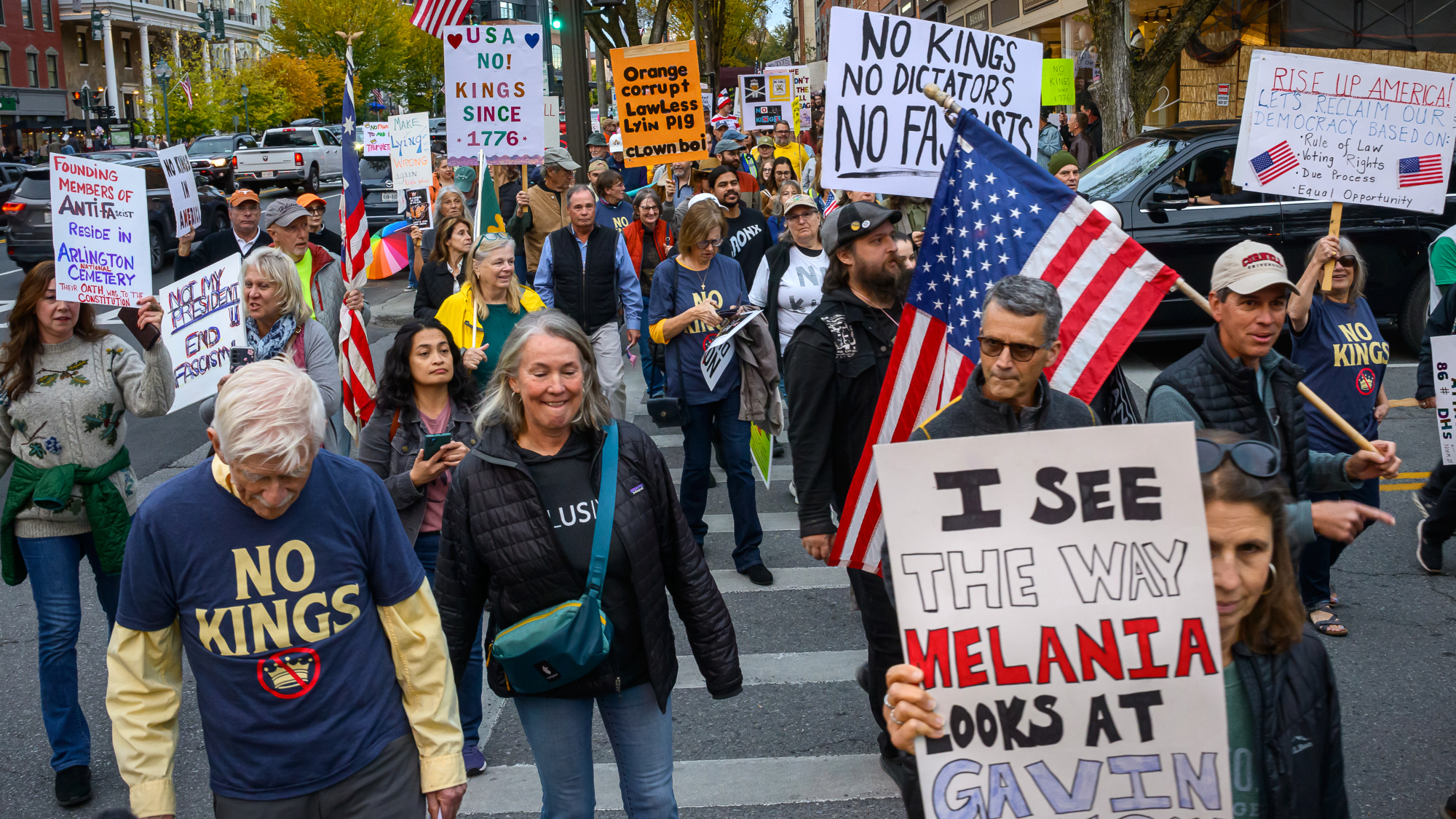 Millions turn out for anti-Trump ‘No Kings’ rallies
Millions turn out for anti-Trump ‘No Kings’ ralliesSpeed Read An estimated 7 million people participated, 2 million more than at the first ‘No Kings’ protest in June
-
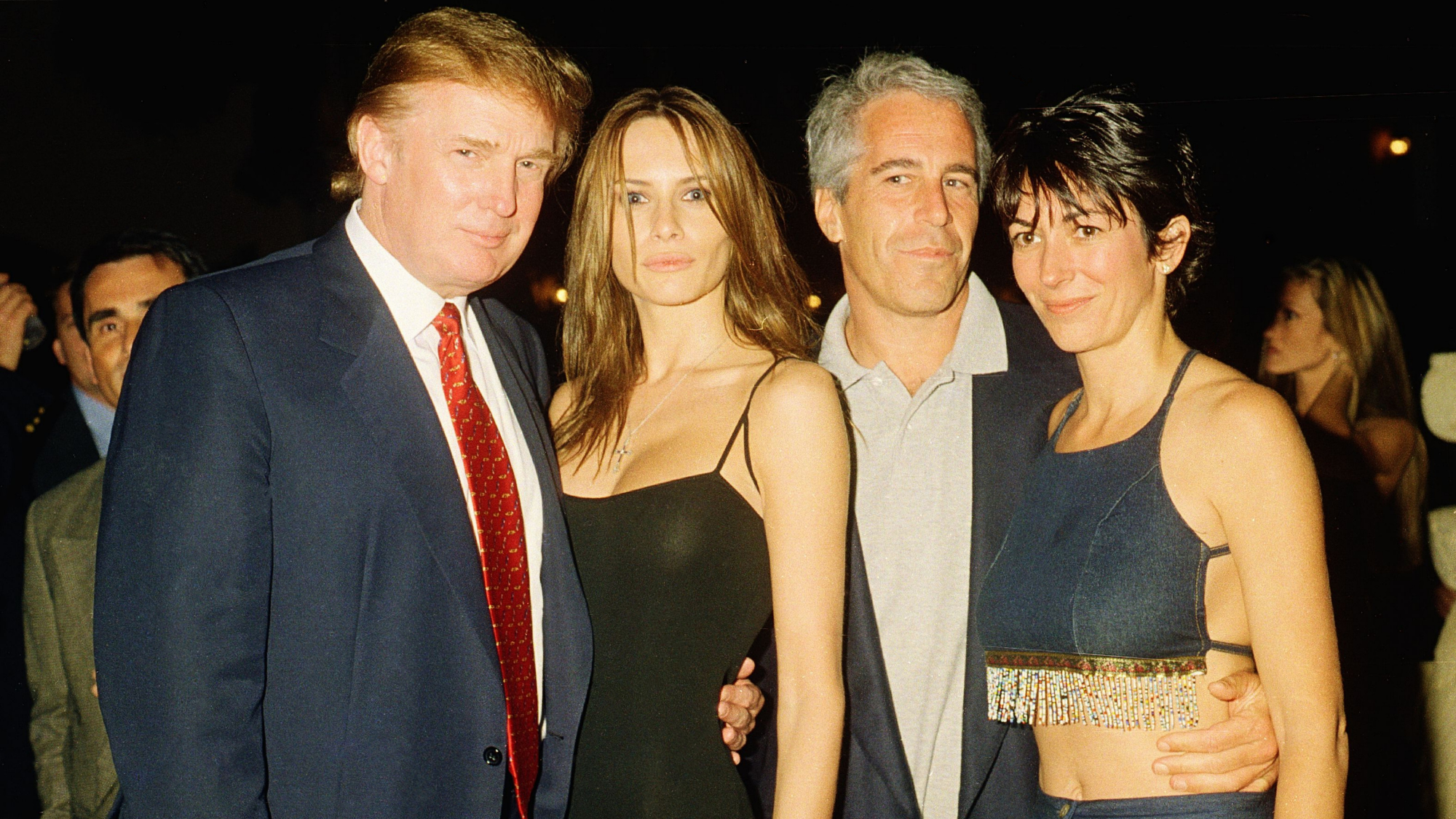 Ghislaine Maxwell: angling for a Trump pardon
Ghislaine Maxwell: angling for a Trump pardonTalking Point Convicted sex trafficker's testimony could shed new light on president's links to Jeffrey Epstein
-
 The last words and final moments of 40 presidents
The last words and final moments of 40 presidentsThe Explainer Some are eloquent quotes worthy of the holders of the highest office in the nation, and others... aren't
-
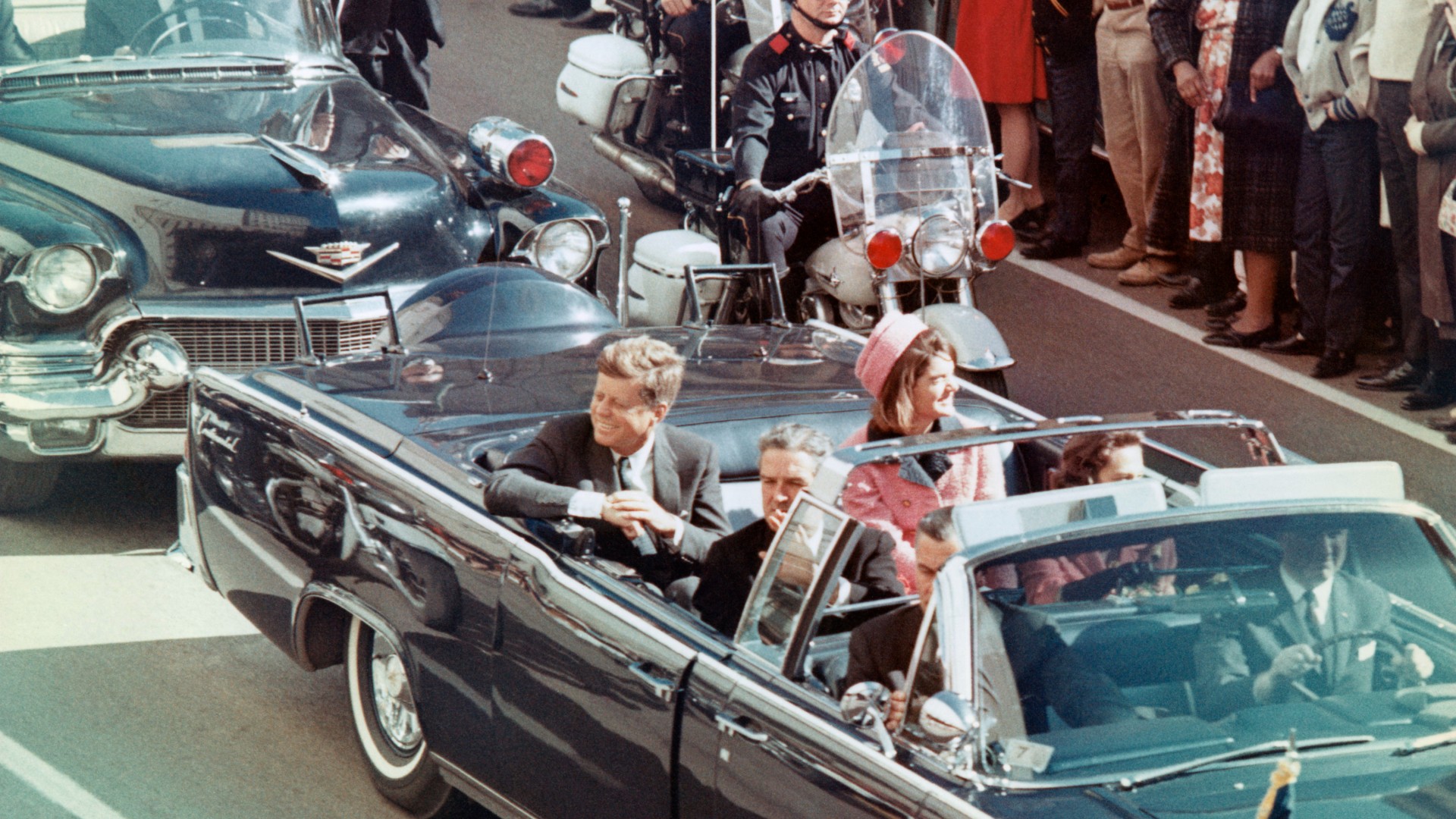 The JFK files: the truth at last?
The JFK files: the truth at last?In The Spotlight More than 64,000 previously classified documents relating the 1963 assassination of John F. Kennedy have been released by the Trump administration
-
 'Seriously, not literally': how should the world take Donald Trump?
'Seriously, not literally': how should the world take Donald Trump?Today's big question White House rhetoric and reality look likely to become increasingly blurred