The long past and perilous future of gaming the Electoral College system
If Republicans had their way, Mitt Romney would have won a raft of electoral votes in swing states dominated by Obama

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Following another bitter presidential loss, Republicans in several states are pushing for rule changes that would boost their odds in future races — essentially, switching the Electoral College allocation method in Democratic-leaning swing states from the current winner-take-all system to one that would help Republicans capture at least some electoral votes in those battlegrounds.
In the short run, of course, such changes would probably help Republicans siphon off electoral votes in states like Virginia, Ohio, Michigan, and Pennsylvania. But these rule changes would also make a mockery of the concept of fair elections, and harm the twin Republican principles of conservativism and federalism.
Currently, all but two states award Electoral College votes using a winner-take-all system (called the Unit Rule). The Unit Rule is not mandatory. Other methods have been used in the past, including having the state legislature hand out the electoral votes however it sees fit. Another popular alternative method, one that is currently used by Maine and Nebraska, is giving one electoral vote to the winner of each congressional district.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
The Unit Rule is widely used today because of its political benefits. In the early days of the republic, it was not clear which system was best. Some politicians were strong proponents of the district-based system — including Thomas Jefferson. But this philosophical position quickly gave way to expediency. When Jefferson ran for president in 1800, his native Virginia transferred over to the Unit Rule to hand Jefferson the full allotment of his home state's votes.
In the ensuing elections, many states switched allocation methods. Eventually, the trend toward a more democratic system in the 1820s led to the phasing out of the state legislatures' allocating votes. At the same time, politicians realized that the district system diluted the impact of a state's vote, and prevented state lawmakers from delivering their entire electoral bounty to their preferred candidate. By 1836, all states except South Carolina used the winner-take-all method.
However, over the years, there have been occasional attempts to switch to a different plan to help various favored candidates. For instance, in 1892, Michigan switched to the district plan to help Grover Cleveland, and then switched back to the Unit Rule for the 1896 election.
Fast forward to the modern day. Since the super-tight 2000 election, there have been numerous attempts to switch the allocation methods of states. Republicans tried to loosen Democrats' stranglehold on deep-blue California by pushing for a district-based system, which would have been devastating to Democrats. Liberals have made similar noises about revising the laws of North Carolina and Colorado. None of these plans have come fruition.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Since Obama's landslide victory in November, all of the talk about changing the system — and there has been a lot of it — has been on the Republican side. Thanks to the GOP's big wins in the 2010 elections, Republicans control the legislatures and the governors' offices of a number of states that voted for Obama, including Michigan, Pennsylvania, Wisconsin, Ohio, and Virginia. These states are now targets for a switch to the district-based method.
This would clearly damage Democrats' short-term political prospects. For example, under the system proposed by Virginia, the state's electoral votes would have gone from 13 for Obama to 9-4 in favor of Mitt Romney — because he won a bunch of congressional districts despite decisively losing the state's popular vote.
Such rule changes would immediately nationalize state legislative elections. Thanks to their role in gerrymandering, state legislative elections are already receiving increased attention from national figures. If states started fussing with the rules of the Electoral College, this attention would skyrocket. Consider this: In the 2011 Wisconsin recalls of nine state senators, total campaign spending topped $44 million. Imagine how much would be spent if the presidency were thought to be on the line.
From the point of view of federalism, this would destroy the ideal of state governments as "laboratories of democracy." These state legislative races would no longer focus on local issues — instead, they would be decided by national topics that have nothing to do with an average legislator's job. We could also expect an increase in recall elections run to gain a majority in a closely divided legislature.
Gerrymandering, already a bipartisan blight on our political system, would only grow in importance. Mid-decade gerrymandering would become the norm. Essentially, every election would become an attempt to game the system.
We've actually seen this before. It goes on every four years, as states try to rejigger the rules, and especially the dates, of their presidential nominating contests. It is not pretty, and it is not a good way to run a system.
Another problem is with the conservative ideal of keeping the Electoral College intact. The Electoral College managed to survive the 2000 presidential debacle. Part of the reason was politics, and part of the reason was that there was a clear villain in the process, namely Florida's botched election system. But yet another part is that whatever the merits of the complaints against the Electoral College, it's a historic and relatively straightforward process — win a state, win its votes.
Of course, the current electoral allocation method skews attention to swing states, and ignores voters in any states that are solidly blue or red, including three of the four biggest states (California, New York, and Texas). Switching to the district-based system would result in more attention for these states' local issues. However, the district-based system may be more likely to misfire. It would have increased Bush's Electoral College totals in 2000, despite his losing the popular vote to Al Gore.
Indeed, the district-based system proposed by Republicans (and occasionally, in the past, Democrats) would actually be designed to increase the likelihood of "wrong winners" — someone who loses the popular vote but wins the presidency.
Can the Electoral College handle being a continual contra-indicator of the national popular vote? It is likely that repeated misfires of the Electoral College would fatally undermine the system. Eventually, if one party is specifically disadvantaged, it would have to go all-in to replace the Electoral College with a national popular vote system. And at some point in the future, a party would accomplish that.
Attempts to game the Electoral College for short-term political gain may temporarily help Republican candidates. But in the long term, they would have a devastating impact on the concept of fair elections, and on the ideals of federalism and conservativism. Republicans would be well advised to consider whether the short-term pleasure is worth the long-term pain.
Joshua Spivak is a senior fellow at the Hugh L. Carey Institute for Government Reform at Wagner College. He writes the Recall Elections Blog.
Joshua Spivak is a senior fellow at the Hugh L. Carey Institute for Government Reform at Wagner College in New York, and writes The Recall Elections Blog.
-
 Political cartoons for February 21
Political cartoons for February 21Cartoons Saturday’s political cartoons include consequences, secrets, and more
-
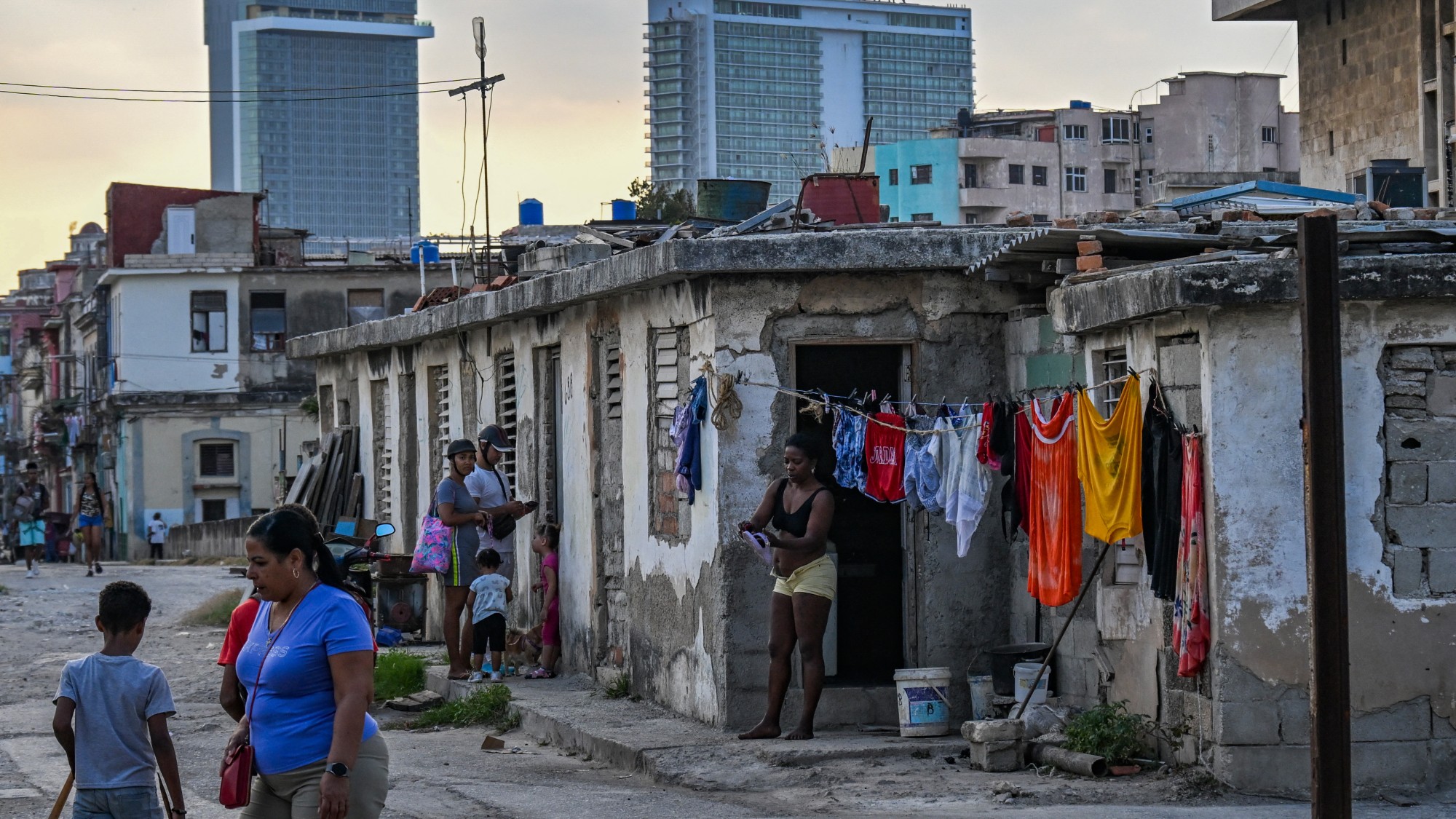 Crisis in Cuba: a ‘golden opportunity’ for Washington?
Crisis in Cuba: a ‘golden opportunity’ for Washington?Talking Point The Trump administration is applying the pressure, and with Latin America swinging to the right, Havana is becoming more ‘politically isolated’
-
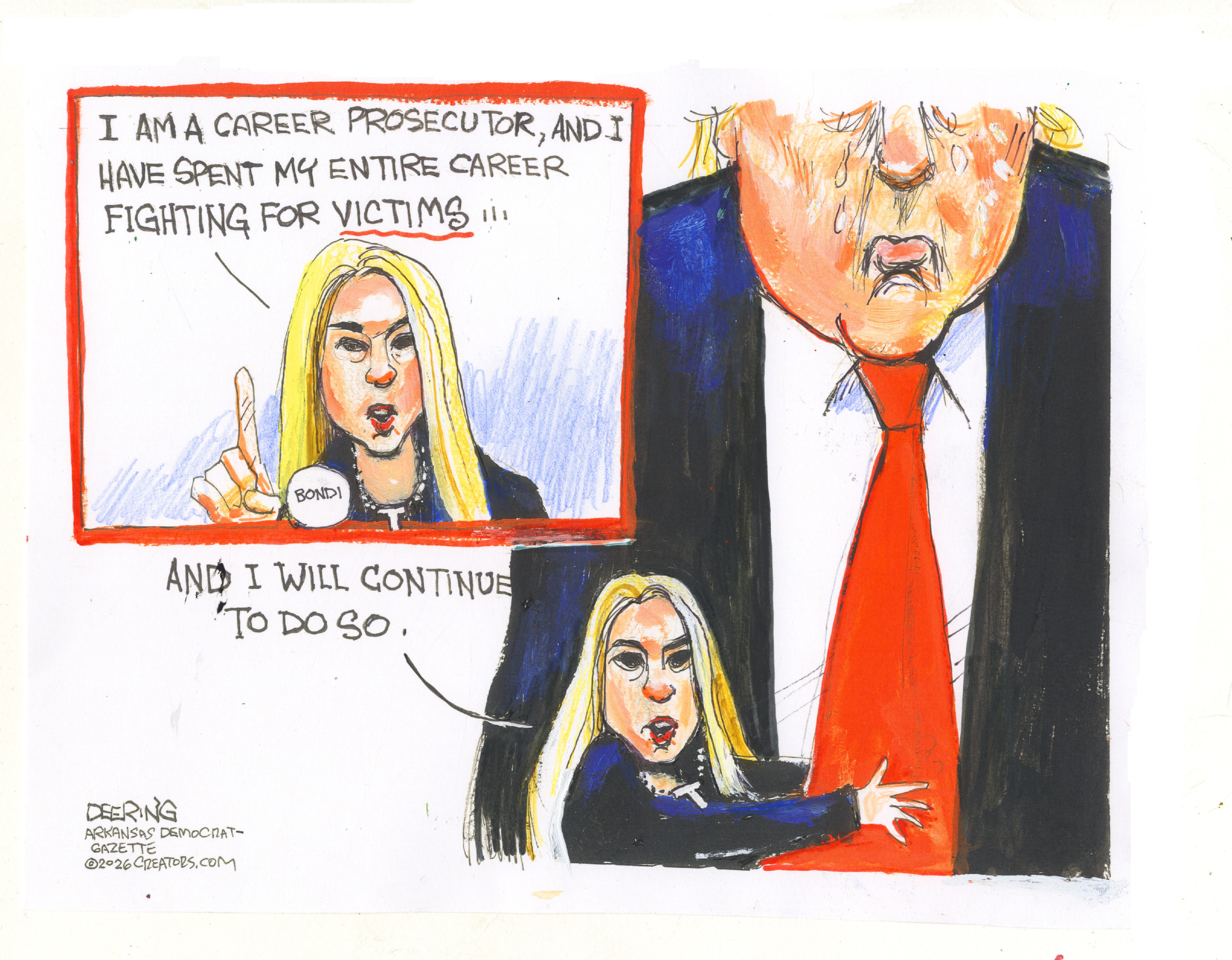 5 thoroughly redacted cartoons about Pam Bondi protecting predators
5 thoroughly redacted cartoons about Pam Bondi protecting predatorsCartoons Artists take on the real victim, types of protection, and more
-
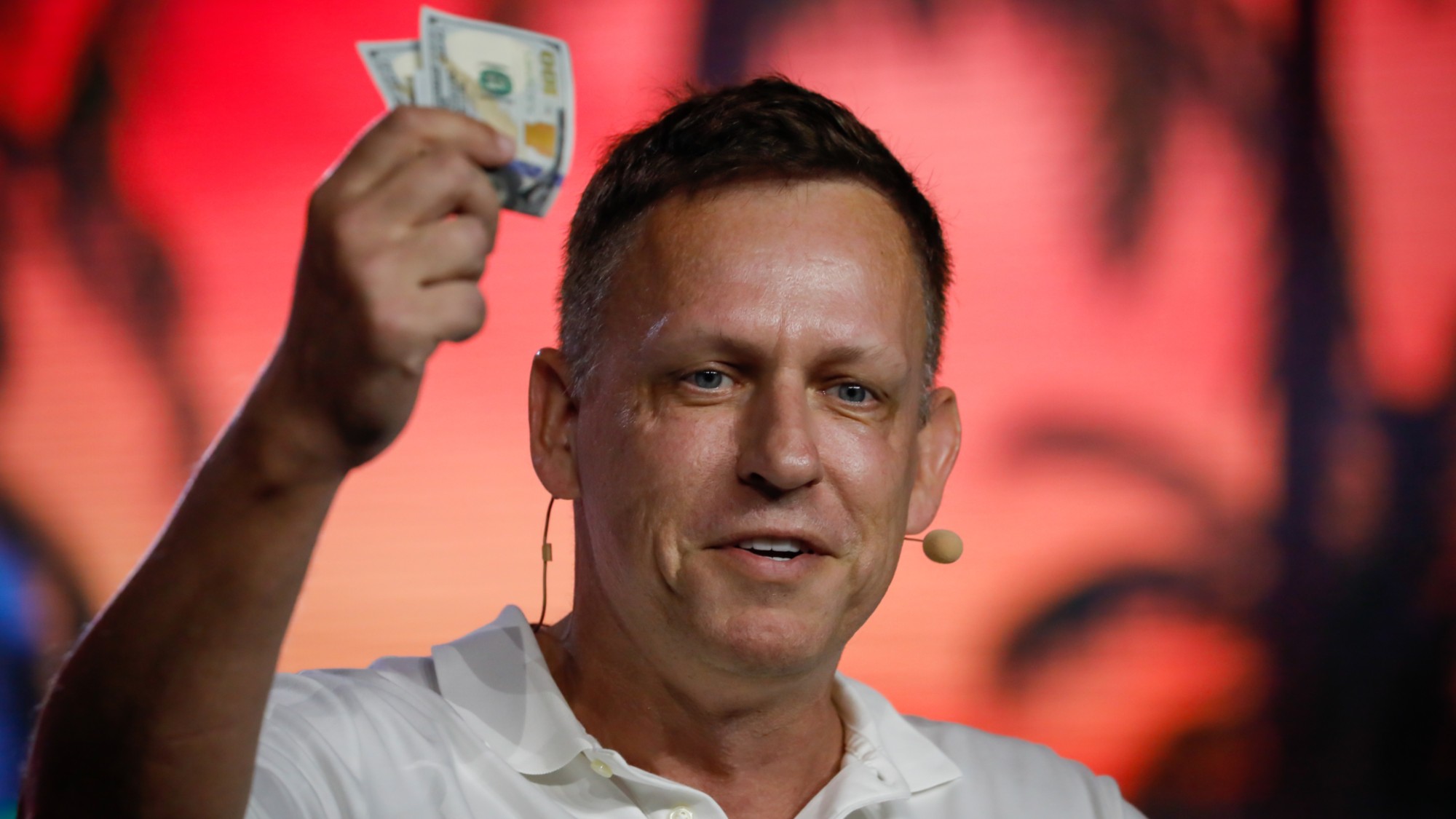 The billionaires’ wealth tax: a catastrophe for California?
The billionaires’ wealth tax: a catastrophe for California?Talking Point Peter Thiel and Larry Page preparing to change state residency
-
 Bari Weiss’ ‘60 Minutes’ scandal is about more than one report
Bari Weiss’ ‘60 Minutes’ scandal is about more than one reportIN THE SPOTLIGHT By blocking an approved segment on a controversial prison holding US deportees in El Salvador, the editor-in-chief of CBS News has become the main story
-
 Has Zohran Mamdani shown the Democrats how to win again?
Has Zohran Mamdani shown the Democrats how to win again?Today’s Big Question New York City mayoral election touted as victory for left-wing populists but moderate centrist wins elsewhere present more complex path for Democratic Party
-
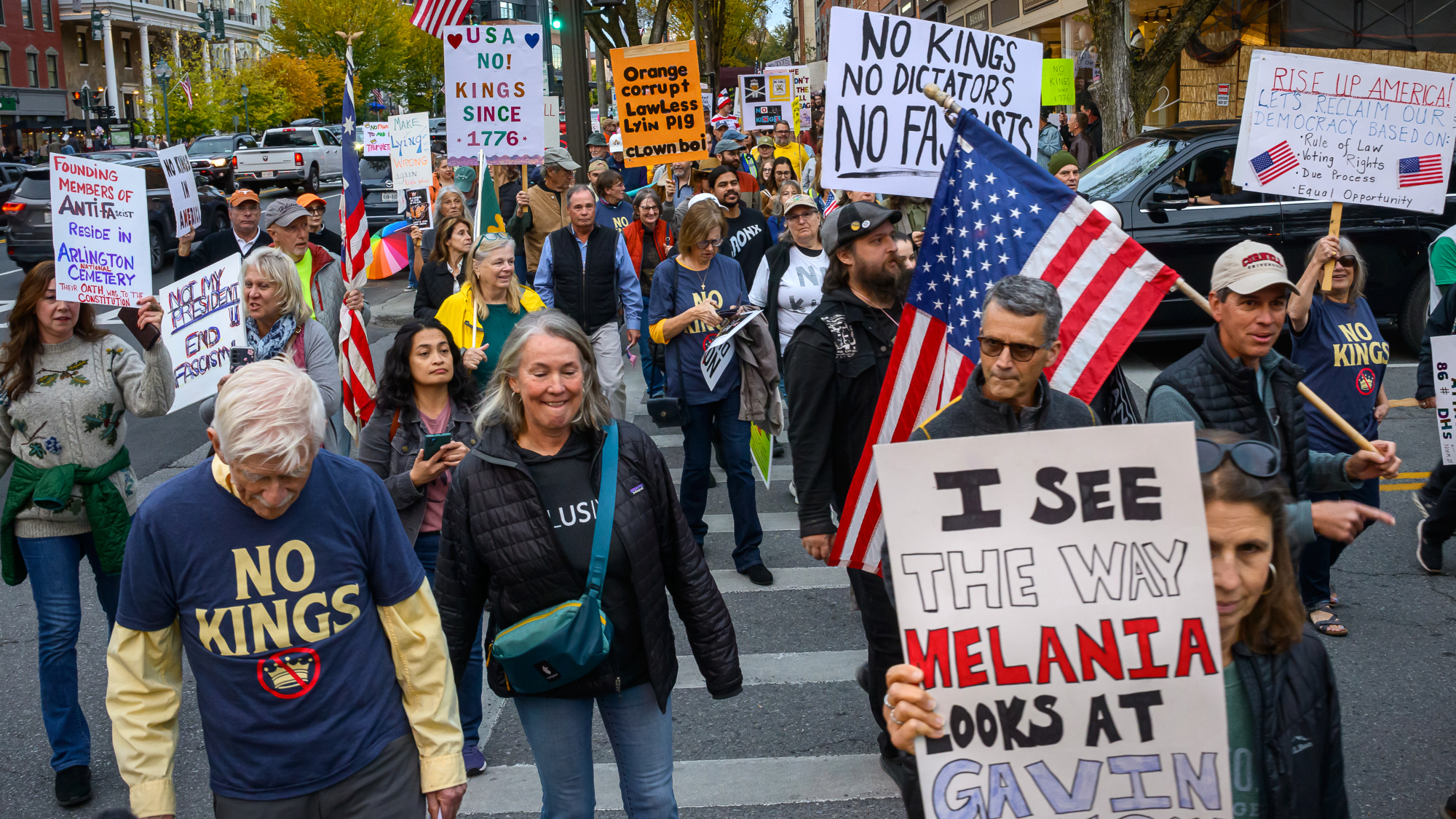 Millions turn out for anti-Trump ‘No Kings’ rallies
Millions turn out for anti-Trump ‘No Kings’ ralliesSpeed Read An estimated 7 million people participated, 2 million more than at the first ‘No Kings’ protest in June
-
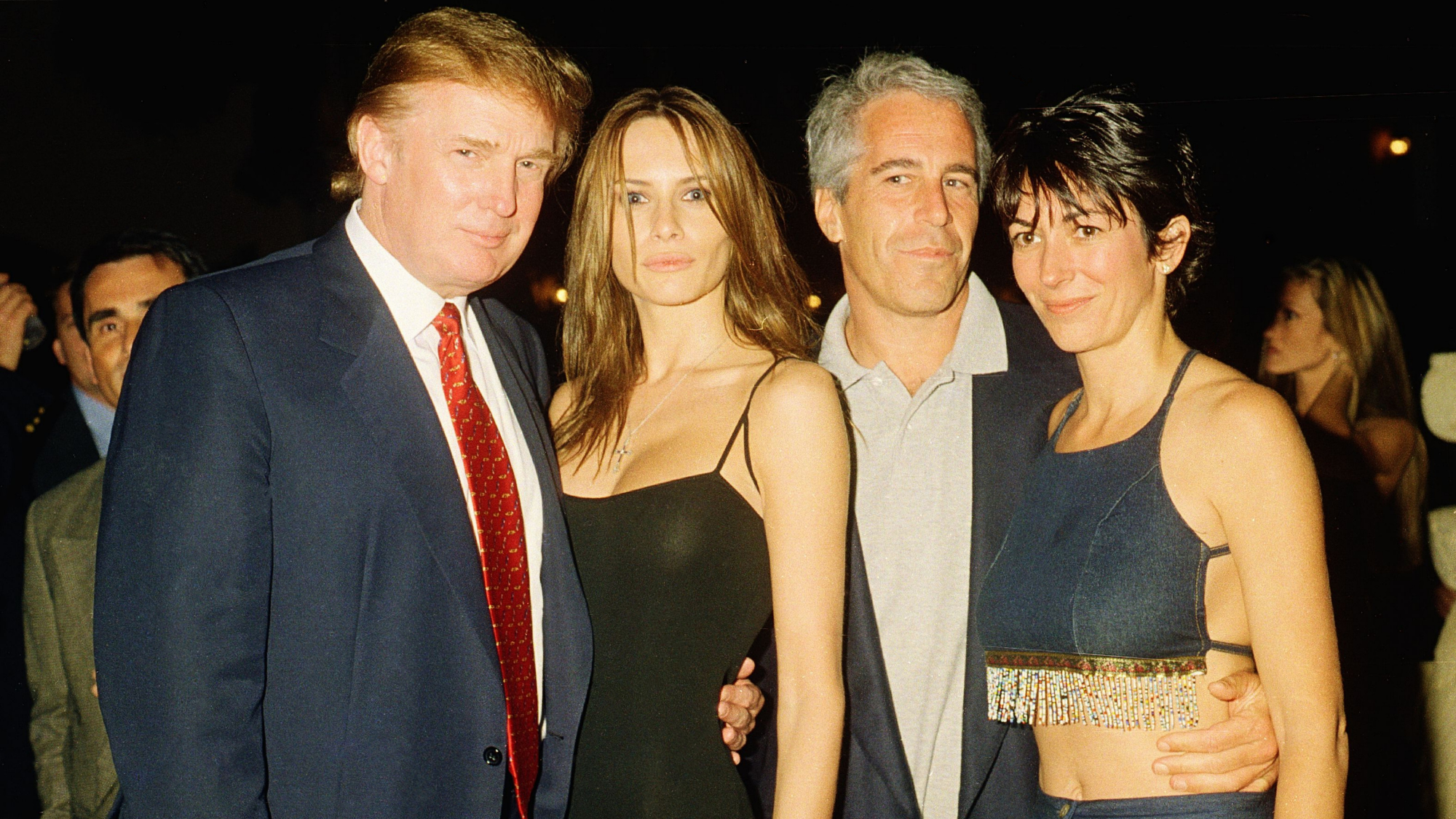 Ghislaine Maxwell: angling for a Trump pardon
Ghislaine Maxwell: angling for a Trump pardonTalking Point Convicted sex trafficker's testimony could shed new light on president's links to Jeffrey Epstein
-
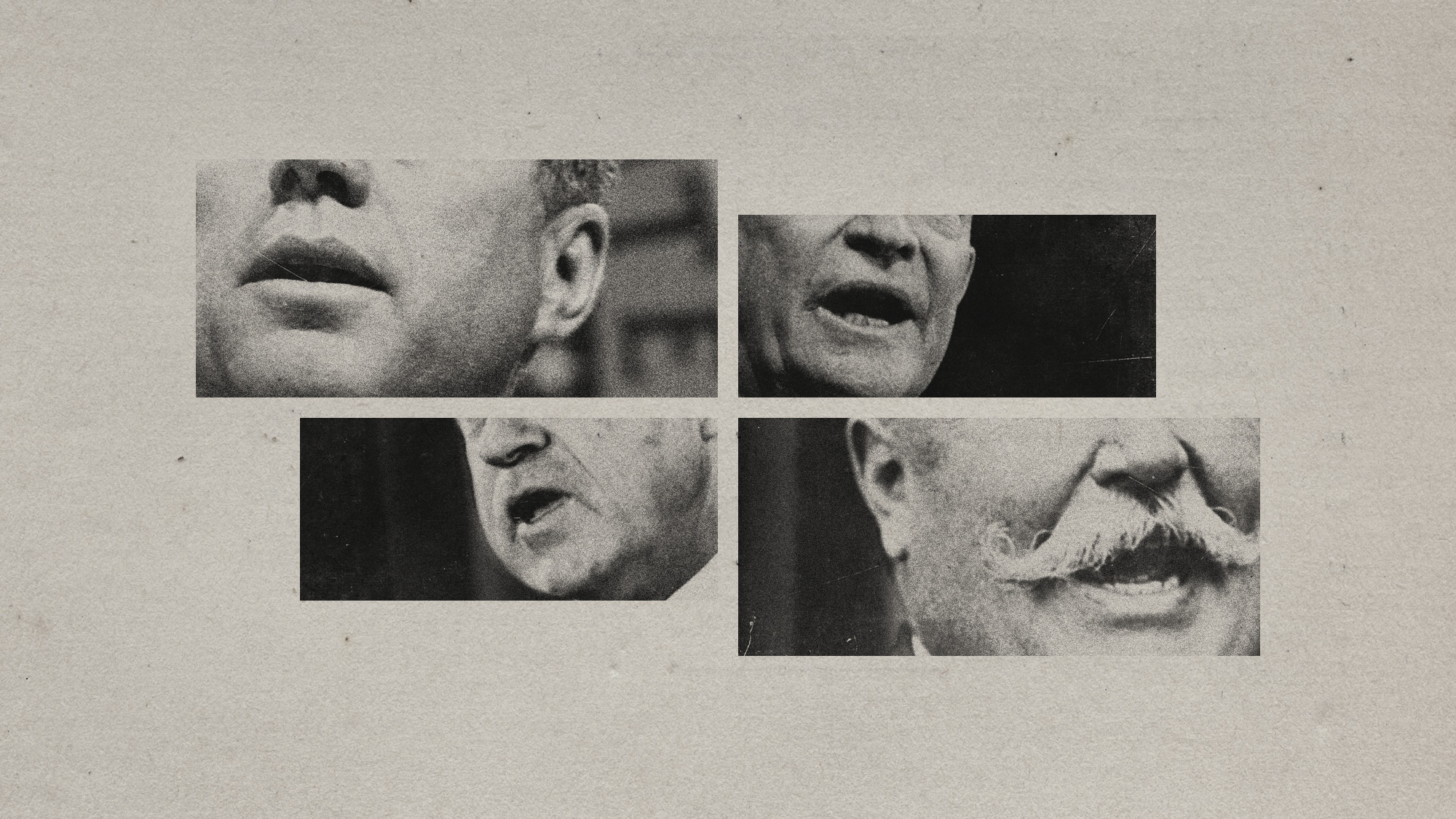 The last words and final moments of 40 presidents
The last words and final moments of 40 presidentsThe Explainer Some are eloquent quotes worthy of the holders of the highest office in the nation, and others... aren't
-
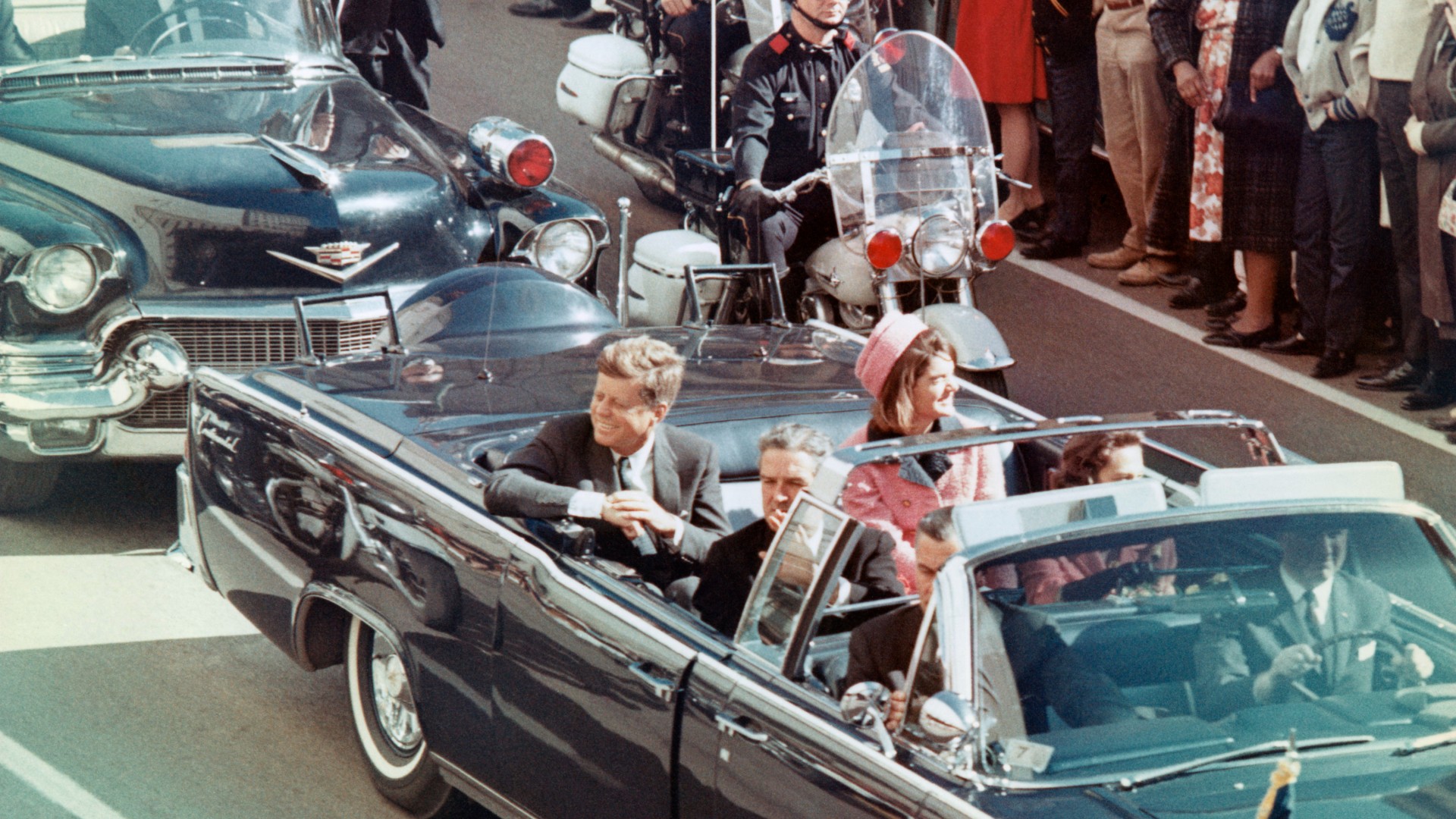 The JFK files: the truth at last?
The JFK files: the truth at last?In The Spotlight More than 64,000 previously classified documents relating the 1963 assassination of John F. Kennedy have been released by the Trump administration
-
 'Seriously, not literally': how should the world take Donald Trump?
'Seriously, not literally': how should the world take Donald Trump?Today's big question White House rhetoric and reality look likely to become increasingly blurred