NASA's plan to clean up space junk: Lasers
Forget giant orbital space nets. A laser mounted on the north pole can solve all our space garbage problems, says NASA
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
The earth is surrounded by an ever-growing cloud of broken satellites, missile parts, and shuttle debris, and no one knows quite how to deal with it. A Japanese firm came up with the radical-sounding idea of using a vast fishing net for cleanup, but NASA researchers have a simpler idea: Lasers. Here, an instant guide to the latest solution to our space garbage problems:
How serious is this space junk dilemma?
Pretty serious. Around 370,000 pieces of defunct satellite parts, abandoned shuttle parts, and scraps of metal and paint are orbiting Earth. Experts warned as long ago as 1978 that too much space garbage could result in "Kessler syndrome" — the point where the junk is so ubiquitous that space becomes too dangerous to fly in.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Why are scraps of metal so dangerous?
They wouldn't be harmful down here on Earth. But in orbit, everything moves at an incredible speed. Even a tiny bolt travelling at 5 miles per second could take out an entire GPS satellite. A larger hulk of rocket debris could vaporize a passing space shuttle.
How could a laser help destroy the garbage?
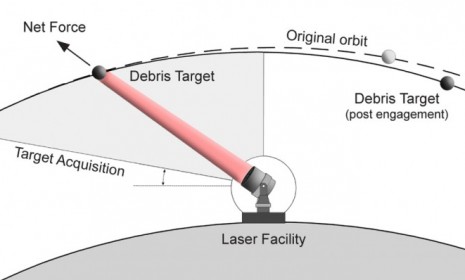
Actually, it wouldn't destroy it. Instead, NASA's plan is to move the garbage out of the path of satellites and spacecraft. The laser would ideally be mounted on one of the Earth's poles, where the atmosphere is thinner, and would send pulses of photon pressure to "nudge" objects out of the way.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Couldn't we just blast it out of the sky, though?
A weapons-grade laser might be able to do that — but building such a space weapon would undoubtedly raise the ire of China and Russia. And even if you did destroy large pieces of garbage, it would only break down into smaller pieces which have the potential to do at least as much damage.
Surely there are cheaper options?
Not likely. NASA says a laser would only cost about a million dollars. That's "absurdly cheap" when you compare it to the billions it costs to launch a satellite, says Evan Ackerman at DVICE. It could even "pay for itself" if it is used to adjust the orbit of existing satellites.
What are the odds of this happening?
It all depends on political will, says James Mason of the United Space Research Association, one of the NASA report's authors. Such a system would have to be built as an "international collaboration, because of the obvious security implications." If we can get China and India interested, a space laser could be a near-term possibility.
Sources: Technology Review, DVICE, Wired, PopSci
-
 The ‘ravenous’ demand for Cornish minerals
The ‘ravenous’ demand for Cornish mineralsUnder the Radar Growing need for critical minerals to power tech has intensified ‘appetite’ for lithium, which could be a ‘huge boon’ for local economy
-
 Why are election experts taking Trump’s midterm threats seriously?
Why are election experts taking Trump’s midterm threats seriously?IN THE SPOTLIGHT As the president muses about polling place deployments and a centralized electoral system aimed at one-party control, lawmakers are taking this administration at its word
-
 ‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’
‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day