The ‘wet bulb’ temperatures behind unprecedented heatwaves
Heat and humidity combine to create deadly conditions that will only get more common

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
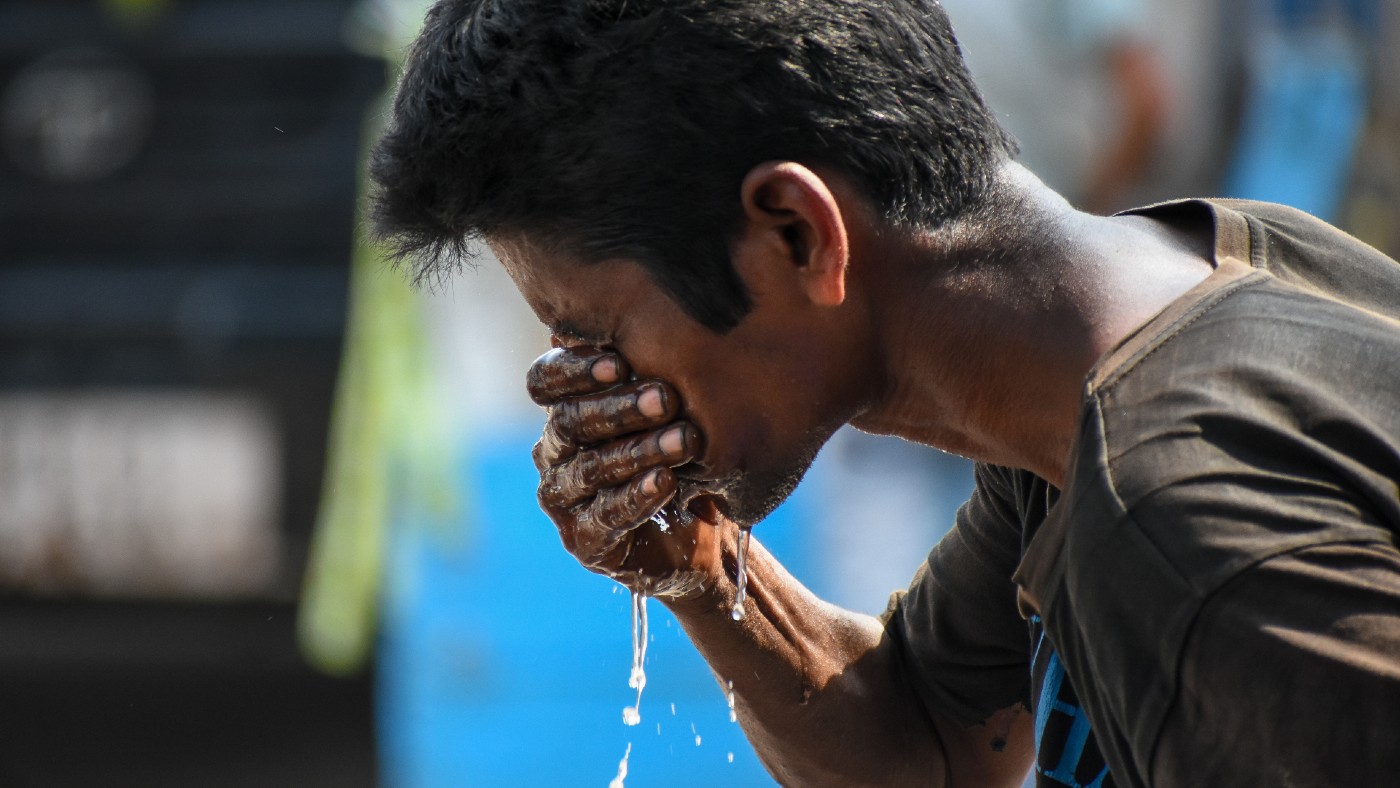
Scientists are warning that “wet-bulb” conditions could threaten the ability of humans to survive as extreme temperatures become more commonplace.
Across great swathes of the Indian subcontinent in April and May temperatures hit 45C, damaging harvests and leading to mass cases of heatstroke. It even caused the lights to flicker in some cities amid surging demand for air-conditioning, reported The New York Times.
What does wet-bulb temperature mean?
Wet-bulb temperatures account for both heat and humidity, unlike the more standard temperature measurement common in weather reports.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
It was originally measured by wrapping a wet cloth around the bulb of a thermometer and exposing it to air, but can perhaps most intuitively be thought of as a representation of “how effectively a person sheds heat by sweating”, reported Vice.
When there is too much moisture in the air and humidity is combined with high heat (31C or higher), the body cannot perform one of its primary cooling functions: sweating.
It is the reason that dry heat is commonly thought of as more comfortable than humid heat. “Such conditions can be fatal, and they’re happening earlier than anticipated,” said Insider.
Colin Raymond, of Nasa’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in southern California, who led a landmark 2020 study on extreme heat and humidity, said the highest wet-bulb temperature that humans can survive when exposed to the elements for at least six hours is about 35C.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Described by NBC News as “an esoteric measurement that was little known outside meteorology circles until now”, high wet-bulb temperatures could threaten the ability of humans to survive.
Which regions are most at risk?
Raymond’s study of wet-bulb temperatures published in Science Advances in 2020 found that some places on Earth have already experienced conditions too hot and humid for human survival.
Since 2005, wet-bulb temperature values above 35C have occurred for short periods of time on nine separate occasions in a few subtropical regions like Pakistan and the Persian Gulf.
It follows last June’s record heatwave that caused havoc across the Pacific Northwest. Southeastern states have also reported multiple incidences of wet-bulb temperatures at or above 31C in recent years, while parts of Arizona and California have reported wet-bulb temperatures as high as 35C.
Why is it likely to get worse?
As the globe warms and bodies of water evaporate at higher rates than before, raising humidity levels, “wet bulb temperatures will continue to rise”, said The Washington Post.
“Heat waves are the deadliest form of natural disaster,” said Vice, and like many other effects of global warming, “typically place socially vulnerable populations at disproportionate risk”.
A 2021 study published in Geophysical Research Letters said that in Bangladesh, India and Pakistan more than 3.3 billion people have experienced days where the wet-bulb temperature is above 35C – “and these rates are only going to compound under current warming goals”, said Vice.
According to Nasa, climate models predict that the areas most at risk of excessive wet-bulb temperatures in the next 30 to 50 years include South Asia, the Persian Gulf, and the Red Sea by around 2050; and Eastern China, parts of Southeast Asia, and Brazil by 2070.
-
 The ‘ravenous’ demand for Cornish minerals
The ‘ravenous’ demand for Cornish mineralsUnder the Radar Growing need for critical minerals to power tech has intensified ‘appetite’ for lithium, which could be a ‘huge boon’ for local economy
-
 Why are election experts taking Trump’s midterm threats seriously?
Why are election experts taking Trump’s midterm threats seriously?IN THE SPOTLIGHT As the president muses about polling place deployments and a centralized electoral system aimed at one-party control, lawmakers are taking this administration at its word
-
 ‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’
‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
 Earth is rapidly approaching a ‘hothouse’ trajectory of warming
Earth is rapidly approaching a ‘hothouse’ trajectory of warmingThe explainer It may become impossible to fix
-
 The plan to wall off the ‘Doomsday’ glacier
The plan to wall off the ‘Doomsday’ glacierUnder the Radar Massive barrier could ‘slow the rate of ice loss’ from Thwaites Glacier, whose total collapse would have devastating consequences
-
 Can the UK take any more rain?
Can the UK take any more rain?Today’s Big Question An Atlantic jet stream is ‘stuck’ over British skies, leading to ‘biblical’ downpours and more than 40 consecutive days of rain in some areas
-
 As temperatures rise, US incomes fall
As temperatures rise, US incomes fallUnder the radar Elevated temperatures are capable of affecting the entire economy
-
 The world is entering an ‘era of water bankruptcy’
The world is entering an ‘era of water bankruptcy’The explainer Water might soon be more valuable than gold
-
 Climate change could lead to a reptile ‘sexpocalypse’
Climate change could lead to a reptile ‘sexpocalypse’Under the radar The gender gap has hit the animal kingdom
-
 The former largest iceberg is turning blue. It’s a bad sign.
The former largest iceberg is turning blue. It’s a bad sign.Under the radar It is quickly melting away
-
 How drones detected a deadly threat to Arctic whales
How drones detected a deadly threat to Arctic whalesUnder the radar Monitoring the sea in the air