The witchcraft myths haunting Africa's dementia patients
Lack of awareness of symptoms and shortage of specialists means sufferers are vulnerable to accusations and attacks
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
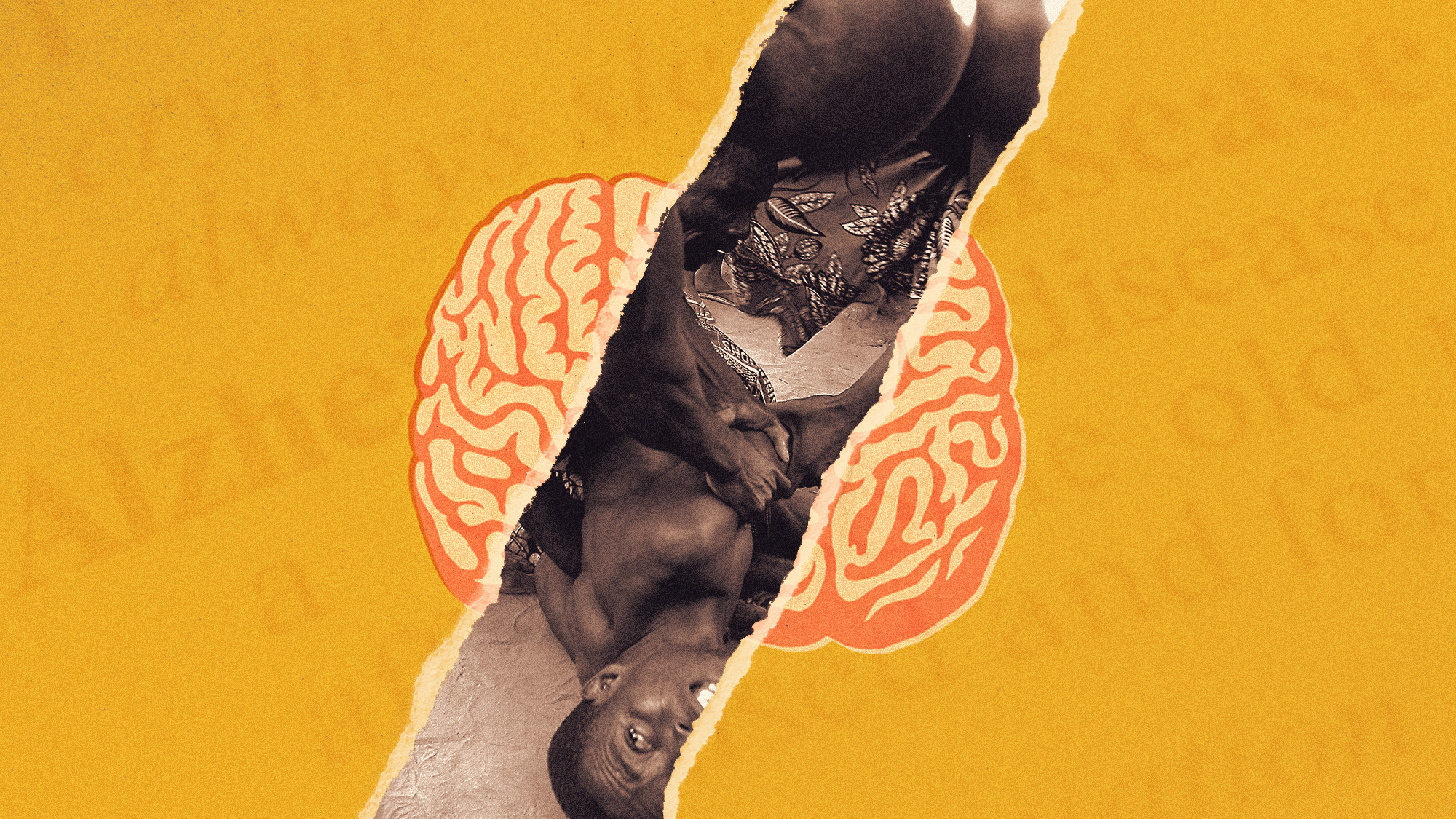
Africans living with dementia are often accused of witchcraft, with potentially devastating consequences.
Symptoms such as forgetfulness and changes in behaviour are "seen as evidence of evil", said The Guardian. People accused have been "set on fire, stoned, beaten to death and buried alive". It's often "disadvantaged and marginalised people" who are targeted – "and mostly women".
Although it is impossible to know how many such attacks occur, the UN estimated in 2020 that there were at least 20,000 victims of "harmful practices" across 60 countries between 2009 and 2019, including children. And the UN human rights commissioner "expects numbers to increase".
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
An 'escalating challenge'
Dementia is an "escalating challenge" in Africa, according to a study published in 2023, as the population both increases and ages.
The number of people living with dementia on the continent is hard to ascertain, as the disease often goes undiagnosed or misidentified as typical ageing. A 2017 report by Alzheimer's Disease International estimated that 2.13 million people were living with dementia in sub-Saharan Africa. Those numbers were projected to nearly double every 20 years, increasing to 3.48 million by 2030.
In 2022, The Lancet Public Health journal estimated that across southern Africa, nearly 300,000 people were living with the disease in 2019. That was projected to rise by 185% by 2050.
But the traditional system of caring for older people within families is "unravelling", said National Geographic, "even as people live longer" and the number suffering from degenerative brain diseases "swells".
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
"Modern life has eroded that [traditional care]," a social worker from South Africa-based organisation Dementia SA told the magazine. "With people getting more westernised, they think they're living for themselves and not for other people."
Meanwhile, many countries have a shortage of skilled medical specialists such as geriatricians, and expensive diagnostic brain scan technology is inaccessible to many. This slows down detection and prevents doctors from starting treatment early enough to make a difference.
'Signs of witchcraft'
Despite the growing prevalence of dementia, many in Nigeria have never heard of the disease. "There's a huge knowledge gap at community level about what dementia is," Dr Temitope Farombi, a consultant neurologist and founder of the Brain Health Initiative Nigeria, told The Guardian.
"Families are often embarrassed and lock their family members in, or out, or dump them in spiritual centres to pray for them, hoping evil spirits will be released."
Accusing someone of witchcraft is illegal in the country, punishable by up to two years in prison, but the law is "rarely enforced", according to Leo Igwe, the founder of Advocacy for Alleged Witches. "People believe the conception of a witch is seen as something that should not be accommodated or protected by the law," he told the paper.
Limited public health services and health education "increase the prevalence of accusations of witchcraft and ritual attacks", according to guidance by the African Union. Conditions such as autism, Down's syndrome, albinism and mental health issues like dementia are "routinely considered signs of witchcraft". Even some doctors reportedly believe it.
"If information and awareness about dementia is put out there," said Igwe, "it can help us drastically reduce, and end, the abuses."
Harriet Marsden is a senior staff writer and podcast panellist for The Week, covering world news and writing the weekly Global Digest newsletter. Before joining the site in 2023, she was a freelance journalist for seven years, working for The Guardian, The Times and The Independent among others, and regularly appearing on radio shows. In 2021, she was awarded the “journalist-at-large” fellowship by the Local Trust charity, and spent a year travelling independently to some of England’s most deprived areas to write about community activism. She has a master’s in international journalism from City University, and has also worked in Bolivia, Colombia and Spain.