Milky Way’s neutron stars akin to a Ferrero Rocher praline
Experts make a mouth-watering breakthrough to explain structure of stars

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Scientists trying to understand the structure of neutron stars say they are akin to chocolate pralines.
Neutron stars, which were discovered 60 years ago, result from a supernova – the explosion that marks the collapse of a massive star. This, combined with gravitational collapse, compresses the star into an incredibly compact and dense form.
They have been compared to the mass of the Sun being compressed into a sphere the size of a large city but their structure has baffled experts for decades.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
A team at Goethe University in Frankfurt made their “tasty new point of reference” after using hundreds of thousands of equations, which aim to describe the stars’ properties, said Sky News. The news site added that the discovery means “the Milky Way is not the only cosmic entity with chocolatey connotations”.
Scientists used the “solar mass” measurement for their breakthrough. A solar mass means the mass of the Sun, which itself is estimated at 330,000 times the mass of the Earth. “Light” neutron stars have masses smaller than about 1.7 solar masses and “seem to have a soft mantle and a stiff core, whereas ‘heavy’ neutron stars (with masses larger than 1.7 solar masses) have a stiff mantle and a soft core”, said Sky News.
Professor Luciano Rezzolla, who led the team of scientists, said: “Neutron stars apparently behave a bit like chocolate pralines” because “light stars resemble those chocolates that have a hazelnut in their centre surrounded by soft chocolate, whereas heavy stars can be considered more like those chocolates where a hard layer contains a soft filling”.
However, despite these mouth-watering comparisons, you should not even think about approaching a neutron star. Their gravitational fields are “super intense”, said GizModo. “If a human observer went near one, they’d be torn apart at an atomic level.”
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Meanwhile, physicists say there are still many mysteries to unravel when it comes to neutron stars.
-
 Health insurance: Premiums soar as ACA subsidies end
Health insurance: Premiums soar as ACA subsidies endFeature 1.4 million people have dropped coverage
-
 Anthropic: AI triggers the ‘SaaSpocalypse’
Anthropic: AI triggers the ‘SaaSpocalypse’Feature A grim reaper for software services?
-
 NIH director Bhattacharya tapped as acting CDC head
NIH director Bhattacharya tapped as acting CDC headSpeed Read Jay Bhattacharya, a critic of the CDC’s Covid-19 response, will now lead the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
-
 Epstein files topple law CEO, roil UK government
Epstein files topple law CEO, roil UK governmentSpeed Read Peter Mandelson, Britain’s former ambassador to the US, is caught up in the scandal
-
 Iran and US prepare to meet after skirmishes
Iran and US prepare to meet after skirmishesSpeed Read The incident comes amid heightened tensions in the Middle East
-
 Israel retrieves final hostage’s body from Gaza
Israel retrieves final hostage’s body from GazaSpeed Read The 24-year-old police officer was killed during the initial Hamas attack
-
 China’s Xi targets top general in growing purge
China’s Xi targets top general in growing purgeSpeed Read Zhang Youxia is being investigated over ‘grave violations’ of the law
-
 Panama and Canada are negotiating over a crucial copper mine
Panama and Canada are negotiating over a crucial copper mineIn the Spotlight Panama is set to make a final decision on the mine this summer
-
 Why Greenland’s natural resources are nearly impossible to mine
Why Greenland’s natural resources are nearly impossible to mineThe Explainer The country’s natural landscape makes the task extremely difficult
-
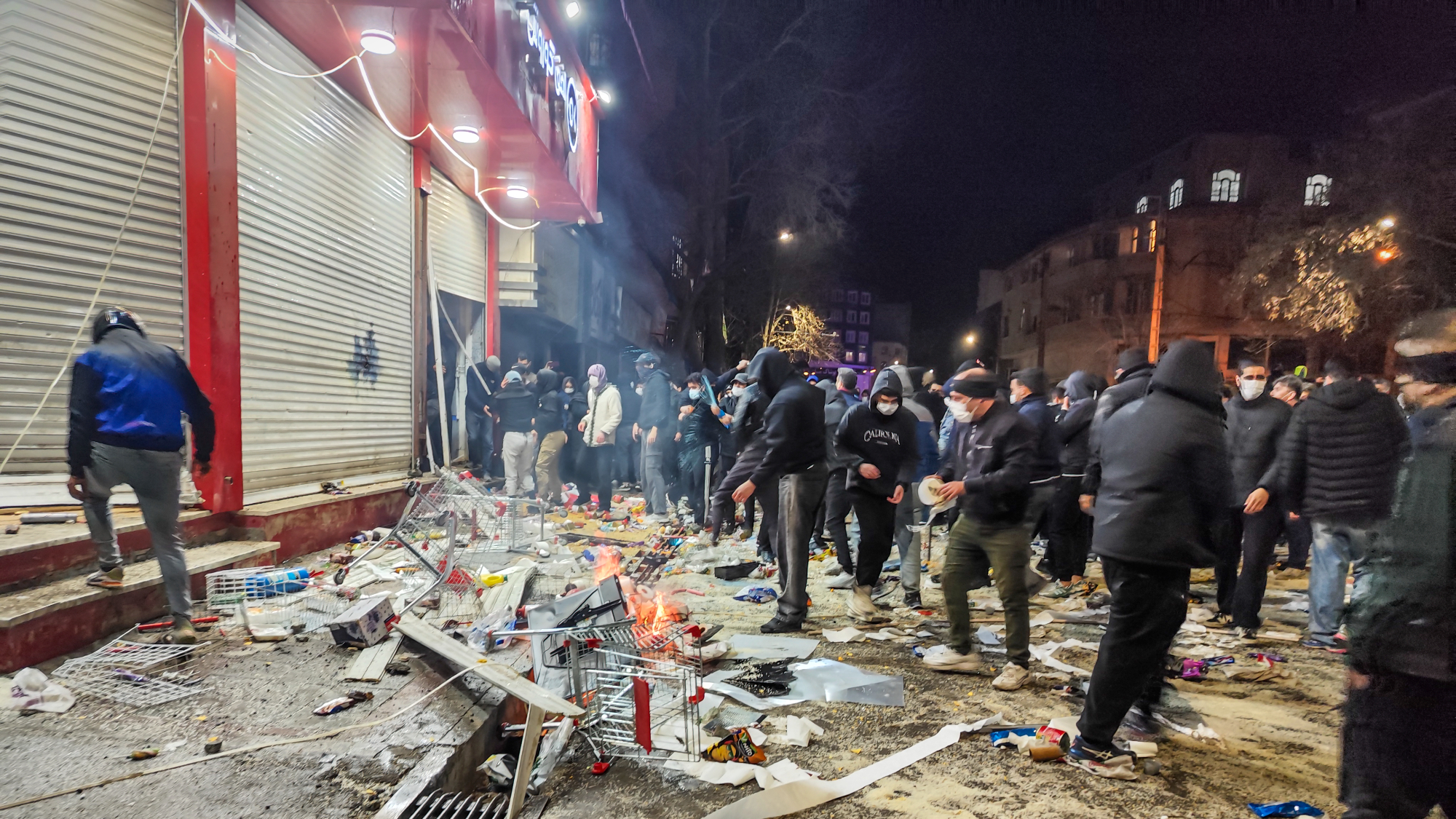 Iran cuts internet as protests escalate
Iran cuts internet as protests escalateSpeed Reada Government buildings across the country have been set on fire
-
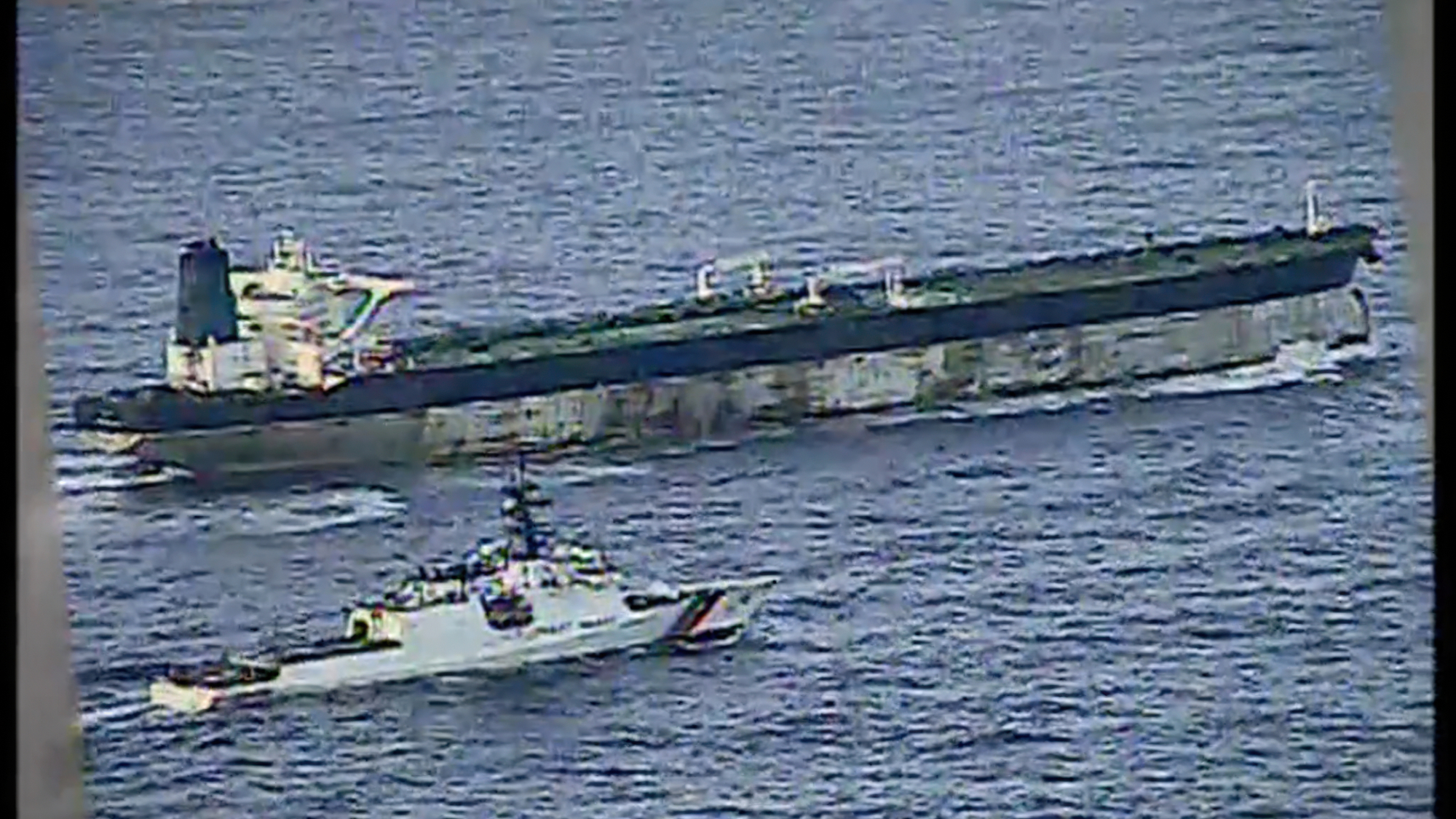 US nabs ‘shadow’ tanker claimed by Russia
US nabs ‘shadow’ tanker claimed by RussiaSpeed Read The ship was one of two vessels seized by the US military