FDA approves cap that can reduce chemotherapy-induced hair loss

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
For some people, the thought of losing their hair is enough to keep them from starting chemotherapy, but a new treatment approved by the FDA has been shown to reduce the side effect.
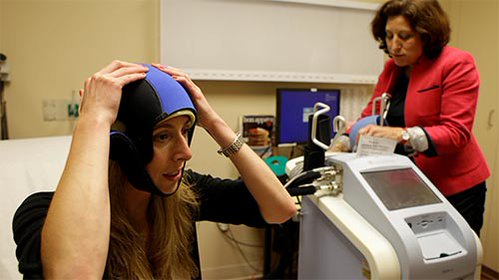
The Dignitana DigniCap Cooling System works like this: A patient puts on a cap, which is connected to a cooling machine. The cap chills the scalp, in turn constricting blood vessels so the chemotherapy cannot penetrate hair follicles. "Hair loss is probably the most dreaded of all the side effects of chemotherapy," Dr. Tessa Cigler, a medical oncologist at the Weill Cornell Breast Center, told ABC News. "There's women who refuse treatment because of hair loss. Being able to preserve one's hair during chemotherapy is very empowering."
The treatment originated in Sweden and is available in several European countries. During a clinical trial in the U.S., 7 out of 10 patients with early stage breast cancer receiving the treatment kept at least 50 percent of their hair, and no adverse side effects were reported. The DigniCap has only been cleared for use in women with breast cancer, as they were the participants in the clinical trial, and women with solid tumor cancers. After being diagnosed with breast cancer in January 2014, trial participant Donna Tookes had a mastectomy, and then started chemo. She went through 12 treatments wearing the DigniCap, and didn't lose any hair; she's now in remission. "At first it's like a brain freeze," she told ABC News, "but then after you get used to it really fast."
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Catherine Garcia has worked as a senior writer at The Week since 2014. Her writing and reporting have appeared in Entertainment Weekly, The New York Times, Wirecutter, NBC News and "The Book of Jezebel," among others. She's a graduate of the University of Redlands and the Columbia University Graduate School of Journalism.
