The dark side of cities
Trump supporters aren't wrong to view cities as distant and alien metropolises that have benefited at rural America's expense
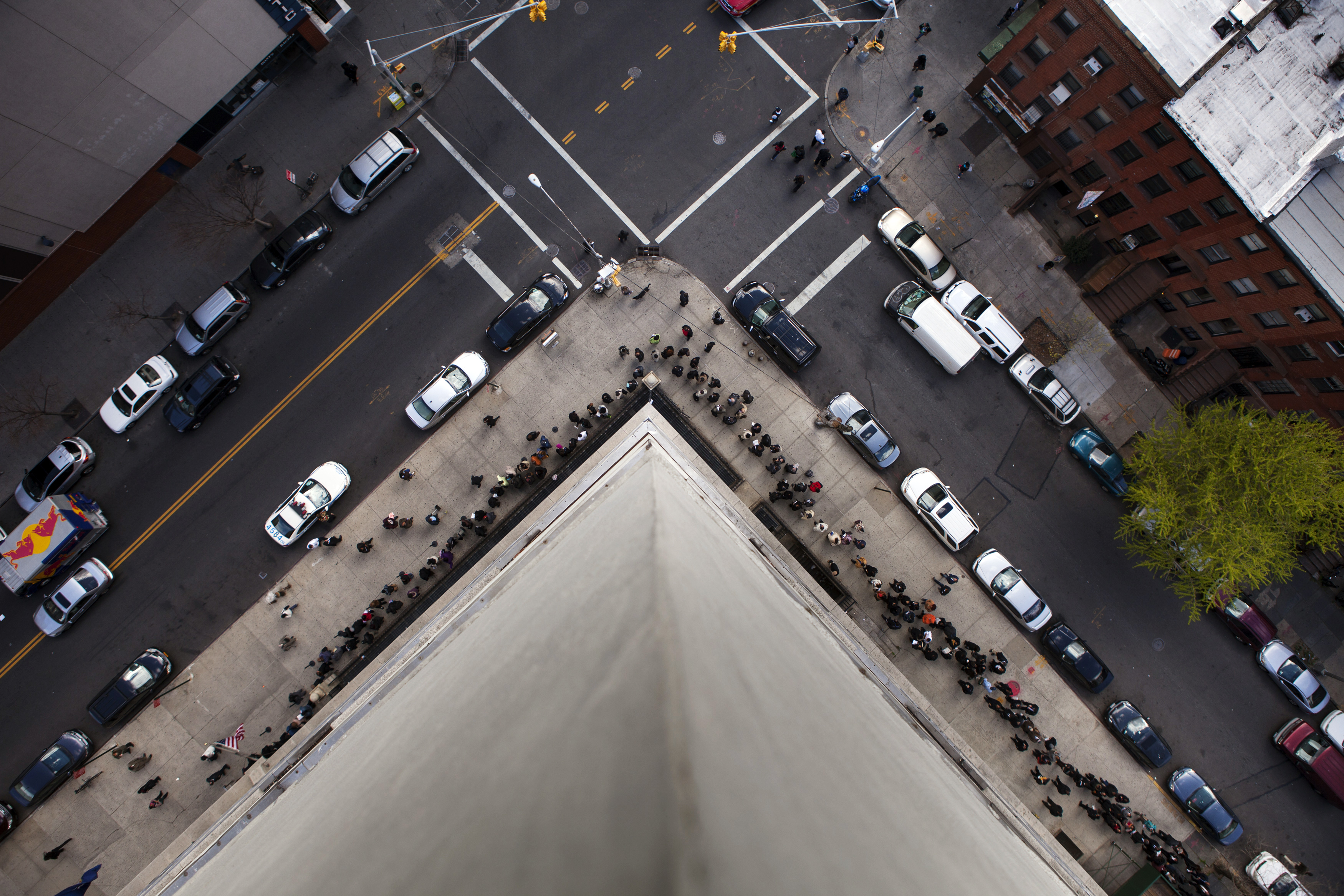


President Trump often paints Americans cities as either liberal elitist enclaves or crime-ridden hellholes. Meanwhile, cities' defenders praise their flourishing, dense, and diverse communities that thumb their nose at Trumpism.
But defenders of the city also go further: They argue that changing technology and the network effects of density all favor the creativity and innovation of diverse metropolises. In other words, cities are supposed to do better than other places, and everyone who doesn't live in one already should get moving. Cities dominate American society like never before because of what they did right, these promoters say.
But actually, cities succeeded because of what the country did wrong.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
A small number of liberal urban clusters certainly do dominate America's economic output. Rates of productivity growth are higher in cities. And over the last few decades, rates of business and job creation during recoveries fell off a cliff in less-dense areas — but held stable in the most dense areas.
Yet the productivity growth rate and the GDP growth rate across the entire national economy slowed to near record lows as cities rose in prominence. Certainly, agglomeration effects and dense innovative cultural milieus have real economic value. But how much value compared to other forces is the question.
More to the point, rates of job and business creation in dense areas held stable as rural areas died. They didn't increase to compensate. Economic vibrancy and opportunity didn't move to the cities. They just drowned everywhere else, while cities became the economy's only remaining life rafts.
Defenders of the city respond that people haven't been able to flee to the life rafts in sufficient numbers. They call for reforming bad policies and local zoning regulations that hold back housing supply and drive up housing prices in major urban centers. Or they suggest new policies to get American workers to retrain for new jobs and relocate to new areas.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Those are all worthwhile goals on their own terms. But they also assume that the rise of cities and the death of rural America is some sort of act of God: All we can do is adapt to the new reality.
But that's not what happened. This new reality is the result of deliberate choices by the architects of America's national economic policy.
Decades ago, antitrust enforcement was ferocious, breaking up companies for reaching a mere 7 percent of market share. Tax rates were far higher on income, capital gains, and corporate profits. These practices prevented corporate behemoths from siphoning off the wealth created by their workers to a few far-flung locals. Instead, that wealth was plowed back into local communities in the form of investment and high wages for workers.
Government subsidies and regulations ensured that railroads, airlines, and shipping companies couldn't decline to service a more rural area just because it wasn't profitable. That kept less dense areas of the country plugged into the rest of the economy. Meanwhile, the New Deal and World War II shoved monetary and fiscal policy in a more Keynesian direction, promoting robust public investment by government. That kept the supply of jobs plentiful, wages high, unions strong, and labor markets tight.
All of that went away beginning in 1980, with the general rightward turn in U.S. policymaking. American society became far more unequal, centralized, and extractive. The national shortage of jobs became a chronic problem, pushing down workers' wages and sending the money off to circulate endlessly and uselessly in Wall Streets' financial markets.
Economists have long puzzled over what best promotes productivity growth. But perhaps the best explanation is the simplest: Productivity is high when there are perpetually more jobs than workers, forcing companies to do more with less. Without that constant pressure, businesses get fat and lazy.
The least privileged and most vulnerable Americans were of course the hardest hit by this shift. And plenty of them live in urban areas too: Lots of nonwhite Americans and working-class people struggle against racism, segregation, rising prices, and low wages. It's just that these days, those with privilege — the upper class and those with college degrees — are the only ones who still enjoy mid-century style wage growth, productivity growth, and job opportunities. They represent the last bulwarks of the old economy, who have not yet succumbed to the national economic rot. And they tend to cluster in cities.
So what's the fix? Well, first off, stop what we're doing wrong. Return to the old ways of robust public investment, antitrust enforcement, and tax and regulatory policy to force money back down the income ladder. Stop treating deficit reduction as a goal in itself; rather whatever deficit level maintains full employment is the right one. And yes, reform housing and land use regulations too.
More radical solutions could include a land value tax, to both encourage more construction within cities, while breaking up concentrations of capital and forcing them to disperse. Or a federal job guarantee, to secure well-paid employment for everyone who wants it, in the community where they already live.
Cities, of course, have always enjoyed outsized prominence in national economies, because density and agglomeration and general creative ferment do matter. But there are healthy degrees of prominence and unhealthy degrees, and America has shifted decisively toward the latter. Trump supporters' politics may be filtered through the perverse lenses of racial anxiety and cultural reaction. But they are not wrong to look upon cities as distant and alien metropolises that have benefited at rural America's expense.
Jeff Spross was the economics and business correspondent at TheWeek.com. He was previously a reporter at ThinkProgress.
-
 The best dark romance books to gingerly embrace right now
The best dark romance books to gingerly embrace right nowThe Week Recommends Steamy romances with a dark twist are gaining popularity with readers
-
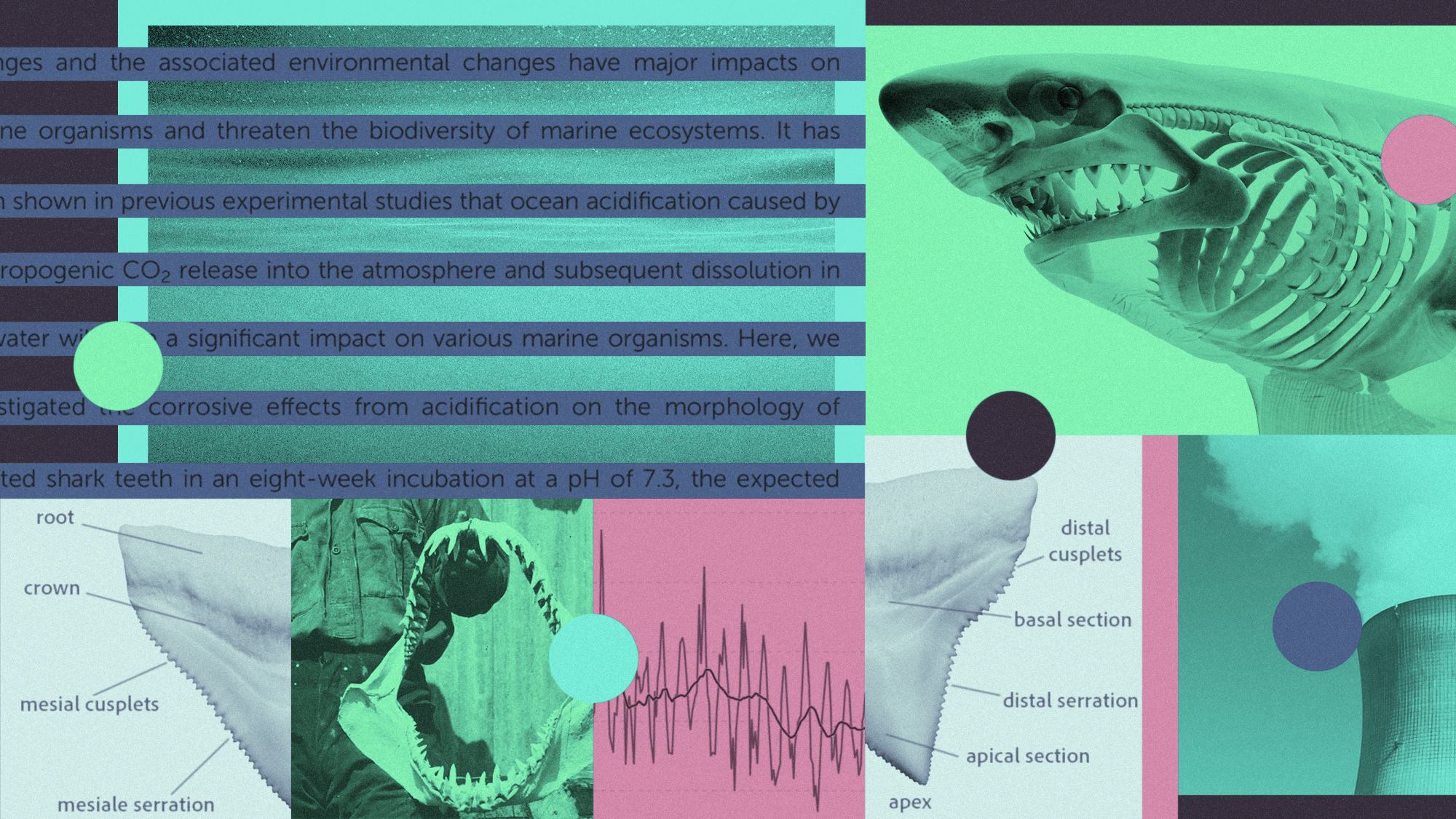 The ocean is getting more acidic — and harming sharks’ teeth
The ocean is getting more acidic — and harming sharks’ teethUnder the Radar ‘There is a corrosion effect on sharks’ teeth,’ a study’s author said
-
 6 exquisite homes for skiers
6 exquisite homes for skiersFeature Featuring a Scandinavian-style retreat in Southern California and a Utah abode with a designated ski room
-
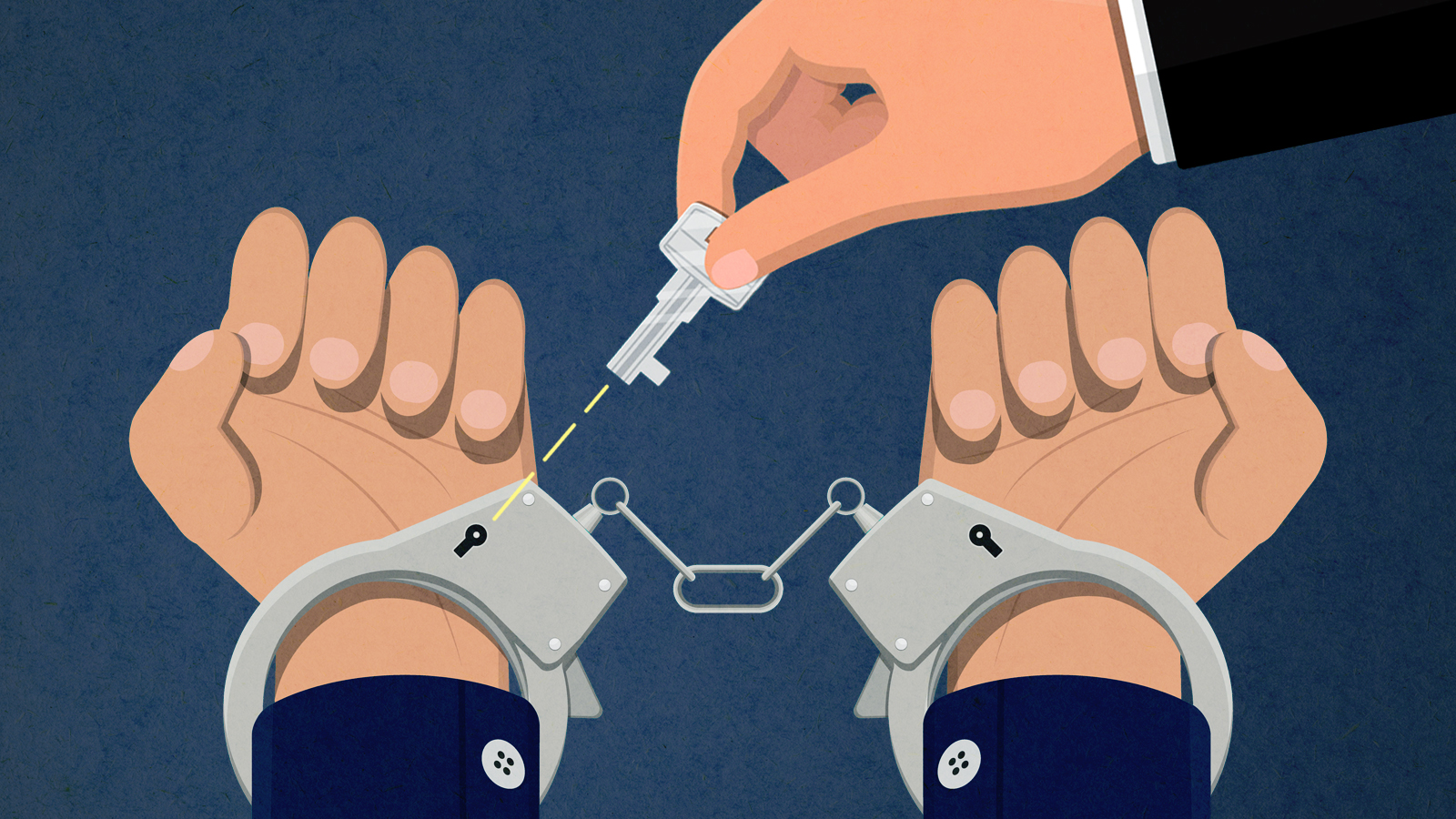 The pros and cons of noncompete agreements
The pros and cons of noncompete agreementsThe Explainer The FTC wants to ban companies from binding their employees with noncompete agreements. Who would this benefit, and who would it hurt?
-
 What experts are saying about the economy's surprise contraction
What experts are saying about the economy's surprise contractionThe Explainer The sharpest opinions on the debate from around the web
-
 The death of cities was greatly exaggerated
The death of cities was greatly exaggeratedThe Explainer Why the pandemic predictions about urban flight were wrong
-
 The housing crisis is here
The housing crisis is hereThe Explainer As the pandemic takes its toll, renters face eviction even as buyers are bidding higher
-
 How to be an ally to marginalized coworkers
How to be an ally to marginalized coworkersThe Explainer Show up for your colleagues by showing that you see them and their struggles
-
 What the stock market knows
What the stock market knowsThe Explainer Publicly traded companies are going to wallop small businesses
-
 Can the government save small businesses?
Can the government save small businesses?The Explainer Many are fighting for a fair share of the coronavirus rescue package
-
 How the oil crash could turn into a much bigger economic shock
How the oil crash could turn into a much bigger economic shockThe Explainer This could be a huge problem for the entire economy
