Remdesivir: US buys world stock of key coronavirus drug
Trump administration goes on shopping spree leaving ‘nothing for Europe’
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
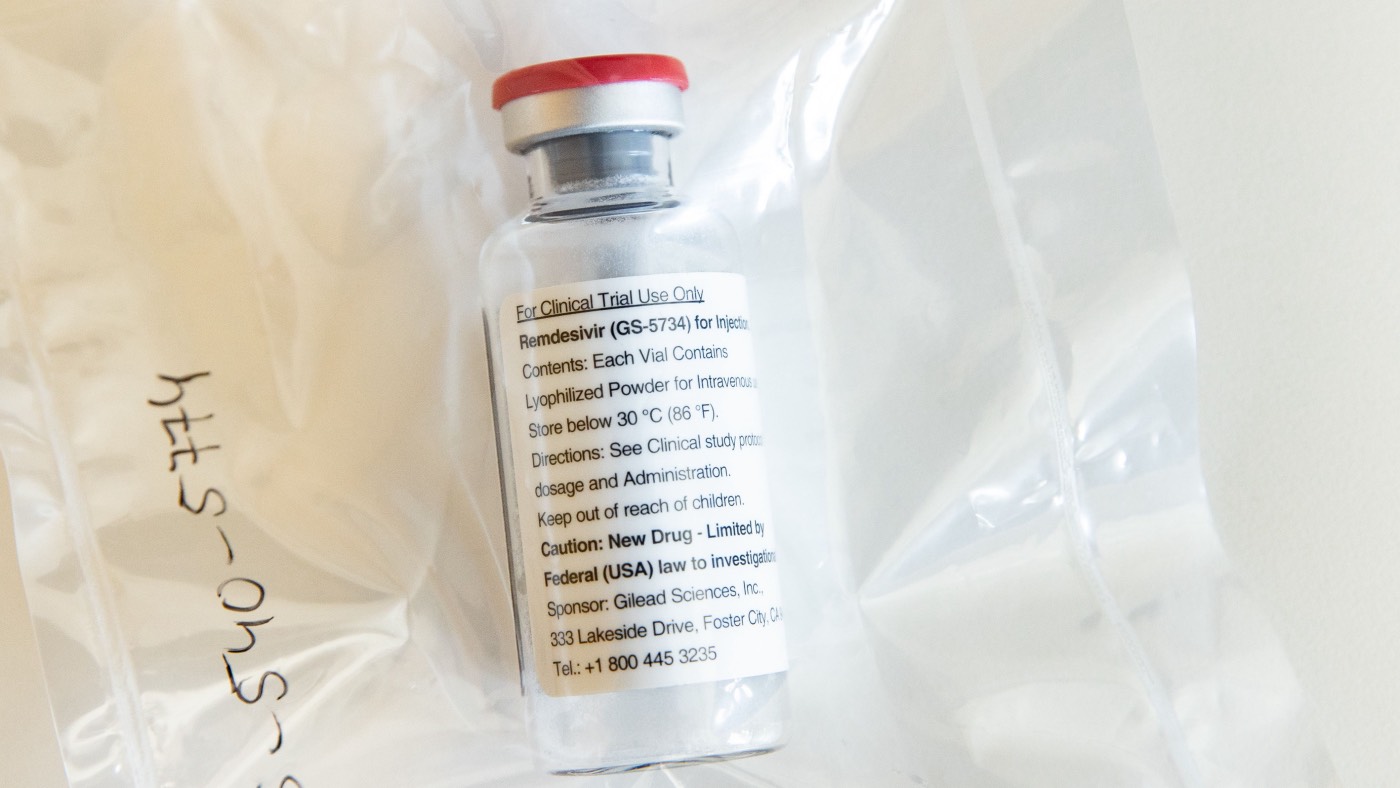
The US has bought the global stock of the key coronavirus drug remdesivir, leaving none for the UK, Europe or most of the rest of the world.
Remdesivir is the first drug approved by licensing authorities in the US to treat Covid-19, and one of just two drugs worldwide proven to combat the virus.
The Trump administration has bought more than 500,000 doses, which is all of the production of remdesivir for July and 90% of August and September, reports The Guardian.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
“President Trump has struck an amazing deal to ensure Americans have access to the first authorised therapeutic for Covid-19,” said the US health and human services secretary, Alex Azar.
“To the extent possible, we want to ensure that any American patient who needs remdesivir can get it. The Trump administration is doing everything in our power to learn more about life-saving therapeutics for Covid-19.”
The drug is under patent to Gilead, which means no other company countries can make it - and that means the US has a monopoly on the treatment.
“They’ve got access to most of the drug supply [of remdesivir], so there’s nothing for Europe,” said Dr Andrew Hill, senior visiting research fellow at Liverpool University.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
How does it work?
US officials say there is “clear-cut” evidence that remdesivir can cut the duration of symptoms, after clinical trials in hospitals around the world found it reduced it from 15 days down to 11.
Analysts say the drug could “have the potential to save lives, ease pressure on hospitals and allow parts of lockdown to be lifted” and the New York Times says US Food and Drug Administration already has plans to announce an emergency-use authorisation for remdesivir.
The drug is an antiviral and works by attacking an enzyme that a virus needs in order to replicate inside human cells. It was originally developed as a treatment for Ebola.
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––For a round-up of the most important stories from around the world - and a concise, refreshing and balanced take on the week’s news agenda - try The Week magazine. Start your trial subscription today –––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Dr Anthony Fauci who runs the NIAID said: “The data shows remdesivir has a clear-cut, significant, positive effect in diminishing the time to recovery.”
He claimed the results prove “a drug can block this virus” and were “opening the door to the fact that we now have the capability of treating” patients.
However, Professor Babak Javid, a consultant in infectious diseases at Cambridge University Hospitals, said remdesivir “is not a magic bullet”.
Professor Mahesh Parmar, who has run the trial in Europe, also urged caution. He said: “Before this drug can be made more widely available, a number of things need to happen: the data and results need to be reviewed by the regulators to assess whether the drug can be licensed and then they need assessment by the relevant health authorities in various countries.
“While this is happening we will obtain more and longer term data from this trial, and other ones, on whether the drug also prevents deaths from Covid-19.”
Dr Maria Van Kerkhove, the World Health Organisation’s technical lead for the coronavirus response, told CNN: “Typically, you don't have one study that will come out that will be a game changer.”
A report in the Lancet says a trial of the same drug in China found it was ineffective. However, the China trial was incomplete because the success of lockdown in Wuhan meant doctors ran out of patients.
The BBC says there are several unanswered questions over the drug: “Is it allowing people who would have recovered anyway to do so more quickly? Or is it preventing people from needing treatment in intensive care?Did the drug work better in younger or older people? Or those with or without other diseases? Do patients have to be treated early when the virus is thought to peak in the body?”
-
 Why is the Trump administration talking about ‘Western civilization’?
Why is the Trump administration talking about ‘Western civilization’?Talking Points Rubio says Europe, US bonded by religion and ancestry
-
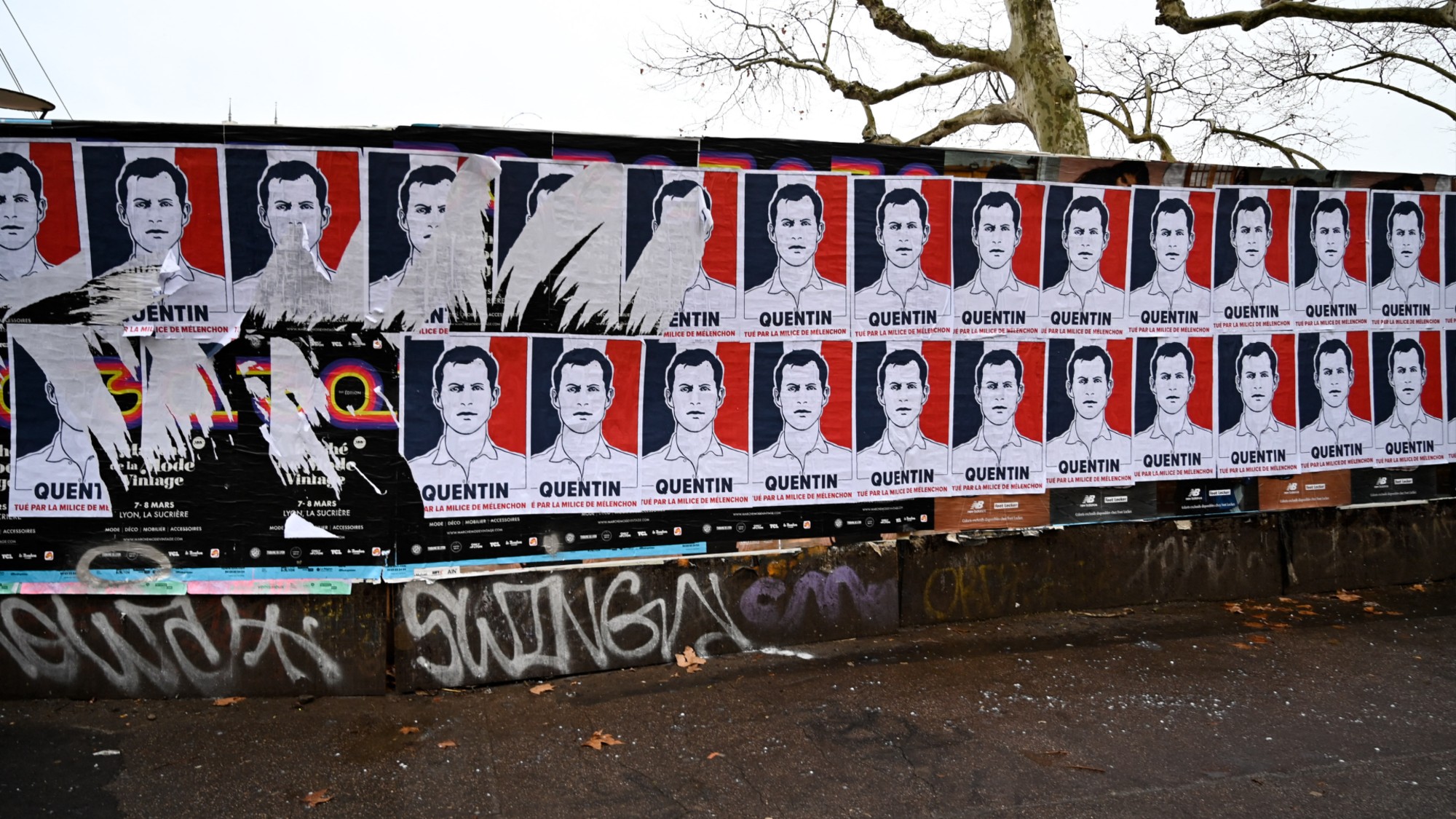 Quentin Deranque: a student’s death energizes the French far right
Quentin Deranque: a student’s death energizes the French far rightIN THE SPOTLIGHT Reactions to the violent killing of an ultra-conservative activist offer a glimpse at the culture wars roiling France ahead of next year’s elections.
-
 Secured vs. unsecured loans: how do they differ and which is better?
Secured vs. unsecured loans: how do they differ and which is better?the explainer They are distinguished by the level of risk and the inclusion of collateral
-
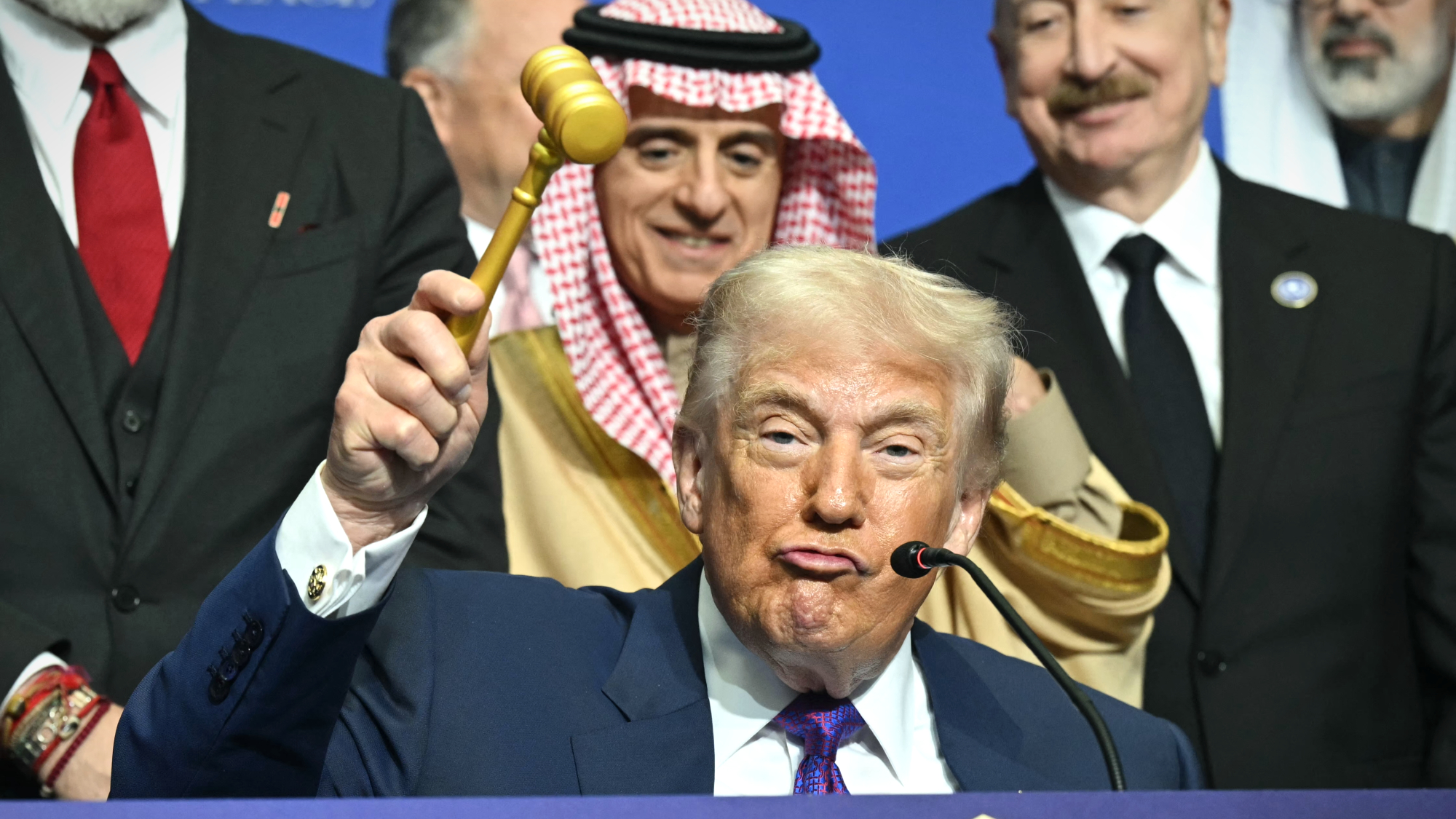 Trump touts pledges at 1st Board of Peace meeting
Trump touts pledges at 1st Board of Peace meetingSpeed Read At the inaugural meeting, the president announced nine countries have agreed to pledge a combined $7 billion for a Gaza relief package
-
 Why are election experts taking Trump’s midterm threats seriously?
Why are election experts taking Trump’s midterm threats seriously?IN THE SPOTLIGHT As the president muses about polling place deployments and a centralized electoral system aimed at one-party control, lawmakers are taking this administration at its word
-
 ‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’
‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
 Should the EU and UK join Trump’s board of peace?
Should the EU and UK join Trump’s board of peace?Today's Big Question After rushing to praise the initiative European leaders are now alarmed
-
 Witkoff and Kushner tackle Ukraine, Iran in Geneva
Witkoff and Kushner tackle Ukraine, Iran in GenevaSpeed Read Steve Witkoff and Jared Kushner held negotiations aimed at securing a nuclear deal with Iran and an end to Russia’s war in Ukraine
-
 Kurt Olsen: Trump’s ‘Stop the Steal’ lawyer playing a major White House role
Kurt Olsen: Trump’s ‘Stop the Steal’ lawyer playing a major White House roleIn the Spotlight Olsen reportedly has access to significant US intelligence
-
 Trump’s EPA kills legal basis for federal climate policy
Trump’s EPA kills legal basis for federal climate policySpeed Read The government’s authority to regulate several planet-warming pollutants has been repealed
-
 House votes to end Trump’s Canada tariffs
House votes to end Trump’s Canada tariffsSpeed Read Six Republicans joined with Democrats to repeal the president’s tariffs