HIV home test kit: how does it work and is it reliable?
Self-testing kits hope to reduce the 'unacceptably high' number of people with undiagnosed HIV in the UK
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
The first legally-approved HIV self-testing kit has gone sale in the UK, in what manufactures are calling a significant step towards normalising HIV testing.
The test, developed by BioSure, is available online and delivers results in just 15 minutes. Charities are hopeful that the home tests will reduce the estimated 26,000 people who have undiagnosed HIV in the UK.
How do they work?
Article continues belowThe Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
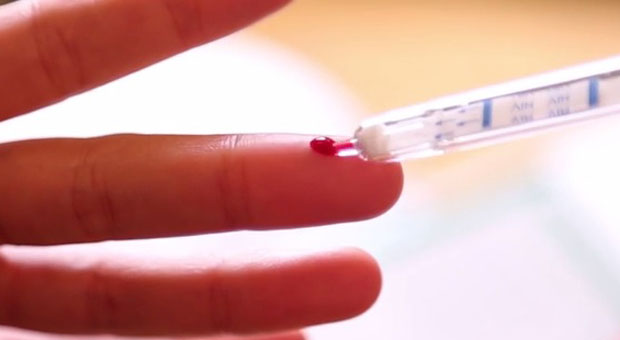
The test checks for antibodies for HIV, an immune response that occurs if a person is infected. The test requires a small drop of blood and delivers results in just 15 minutes. One line means the test is negative, two means that the test may be positive.
Are they reliable?
The tests claim to have a 99.7 per cent accuracy rate, higher than that of an average pregnancy test. However, they may not detect infections that have occurred within the last three months, so it is recommended that those at high-risk are tested every three months. All positive results will need to be confirmed by a health care professional.
Why has it taken so long for them to become available?
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Home testing kits for HIV have been available in the US for some time, but the law that outlawed them in the UK only changed last year. The Terrence Higgins Trust, the UK's leading HIV/Aids charity, campaigned for the change in legislation, arguing that early diagnosis would help people get treatment and prevent them from unwittingly passing on the disease to others.
What has the reaction been?
Doctors and charities have welcomed the home tests and say they will encourage more people to get checked for the virus, particularly those who are reluctant to see their doctor.
"There are a lot of people who are unaware of their HIV status who may be uncomfortable with accessing HIV testing in clinical settings or who don't know how to," Kat Smithson, of the National Aids Trust, told Sky News. "It also enables a lot of people who think they might be at increased risk of HIV to test more often."
Dr Michael Brady of Kings College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust described the kits as a "really exciting development" as rates of undiagnosed HIV remain "unacceptably high" in the UK and continue to contribute to unnecessary illness and onward transmission of the virus.
While the Terrence Higgins Trust welcomed the development, it also highlighted the need for further funding for NHS sexual health services. "It is important to make sure people can get quick access to support when they get their result," Dr Rosemary Gillespie, the charity's chief executive told the BBC.