Why America is about to start freaking out about babies
The U.S. birthrate is headed down, down, down


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
The United States has long had an unexpectedly high fertility rate. We're quite a bit above some peer nations like Japan, Korea, or Germany, and fairly close to places like France and Sweden. That's remarkable because the U.S. spends virtually nothing on child benefits. France has made advising Korean and Japanese elites about how to boost their childbearing into something of a cottage industry, and the take home message is: Swamp parents with cash and benefits, regardless of marital status. But in the U.S., that doesn't seem to hold.
However that situation is something of a coincidence, and it's highly likely the U.S. birth rate is going to trend down as time passes. When it does, the stewards of serious bowtied policymaking in Washington, D.C. are going to start freaking out.
So why has the U.S. birth rate been so relatively high? In short, immigration and teen pregnancies. Many immigrants come from higher-birthrate countries like Mexico, and so tend to have more children on average. Meanwhile, the U.S. teen pregnancy rate has long been extremely high by industrialized standards — both helping to put the U.S. fertility rate at 2.12 children per woman (roughly replacement level) as of 2007.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
However, all those things are rapidly changing. The birth rate among U.S.-born women fell by 6 percent in the first years of the recession — but among immigrants it fell by 14 percent. What's more, birth rates in immigrants' origin countries, particularly Mexico, have also been falling for years. Teen pregnancies have also been trending sharply down for years; falling by roughly two-thirds among all racial groups since 1990.
Overall births have since bottomed out, but much of the increase was older women who had clearly been putting it off for economic reasons. Ultimately a secular decline in the U.S. birthrate seems extremely likely. Right now it's sitting at 1.87, and I'd bet that it will eventually land somewhere around Germany's 1.38 within a decade or two. The reason is that without paid leave and other benefits, having children is a terrific pain in the neck even for rich people.
You might be thinking: Well, that doesn't sound so bad. There are "too many people" in America anyway, and population growth is a serious strain on resources. That's true up to a point, but as I've argued before, when it comes to rich nations whose birthrate is already pretty low, the efficiency of a society matters much, much more than the absolute number of people. French carbon dioxide pollution per person is less than one-third that that of the U.S. — meaning that equaling their emissions would have a greater effect on climate change than cutting the population in half.
What's more, a sharp collapse in the birthrate of a society means enormous political strain. The retired, non-working share of the population will grow, and the share of workers supporting those retirees will shrink. In theory, so long as productivity growth is chugging along, it should be possible to thread that needle and give more to workers and retired people, but in practice it will mean more fighting between creditors and debtors, as can be seen in Japan. (It's also worth noting that U.S. productivity growth has been terrible of late.)
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
That doesn't mean we should aim for explosive birthrates, of course. Replacement level is a good goal, since it seems pretty hard to hit even for nations with very generous child benefits.
This is where the self-serious D.C. wonk brigades come in. According to standard economics, human beings are one of two major inputs to economic production (the other being capital) — so if the population starts plummeting, economic output is going to take a beating. And for the very serious thinkers at the Brookings Institute and elsewhere, that's the mortal sin to beat them all — so they'll soon be theorizing about what to do. (For example, Germany's need for future labor is a major reason behind their relatively generous response to the Syrian refugee crisis.)
The big question of the future will be whether the spreadsheet crowd can get clear of their traditional desire to enforce conservative social norms with family policy. These were the same people behind welfare reform, one major goal of which was to boost marriage rates (at which it failed utterly), so it's likely they'll be tempted to condition new family benefits on marriage, having a job, and so forth.
But the lesson of France and Sweden is that this will likely fail. Generous family benefits that pay out regardless of family status — like a universal child allowance, for example — seem to work much better than more conservative policy in Germany. There are a lot of social factors behind why people get married and have children, and benefit conditionality simply doesn't have much purchase on them. But what we can do is make sure that any child born in this country has a decent standard of living.
Ryan Cooper is a national correspondent at TheWeek.com. His work has appeared in the Washington Monthly, The New Republic, and the Washington Post.
-
 Film reviews: ‘Send Help’ and ‘Private Life’
Film reviews: ‘Send Help’ and ‘Private Life’Feature An office doormat is stranded alone with her awful boss and a frazzled therapist turns amateur murder investigator
-
 Movies to watch in February
Movies to watch in Februarythe week recommends Time travelers, multiverse hoppers and an Iraqi parable highlight this month’s offerings during the deep of winter
-
 ICE’s facial scanning is the tip of the surveillance iceberg
ICE’s facial scanning is the tip of the surveillance icebergIN THE SPOTLIGHT Federal troops are increasingly turning to high-tech tracking tools that push the boundaries of personal privacy
-
 The billionaires’ wealth tax: a catastrophe for California?
The billionaires’ wealth tax: a catastrophe for California?Talking Point Peter Thiel and Larry Page preparing to change state residency
-
 Bari Weiss’ ‘60 Minutes’ scandal is about more than one report
Bari Weiss’ ‘60 Minutes’ scandal is about more than one reportIN THE SPOTLIGHT By blocking an approved segment on a controversial prison holding US deportees in El Salvador, the editor-in-chief of CBS News has become the main story
-
 Has Zohran Mamdani shown the Democrats how to win again?
Has Zohran Mamdani shown the Democrats how to win again?Today’s Big Question New York City mayoral election touted as victory for left-wing populists but moderate centrist wins elsewhere present more complex path for Democratic Party
-
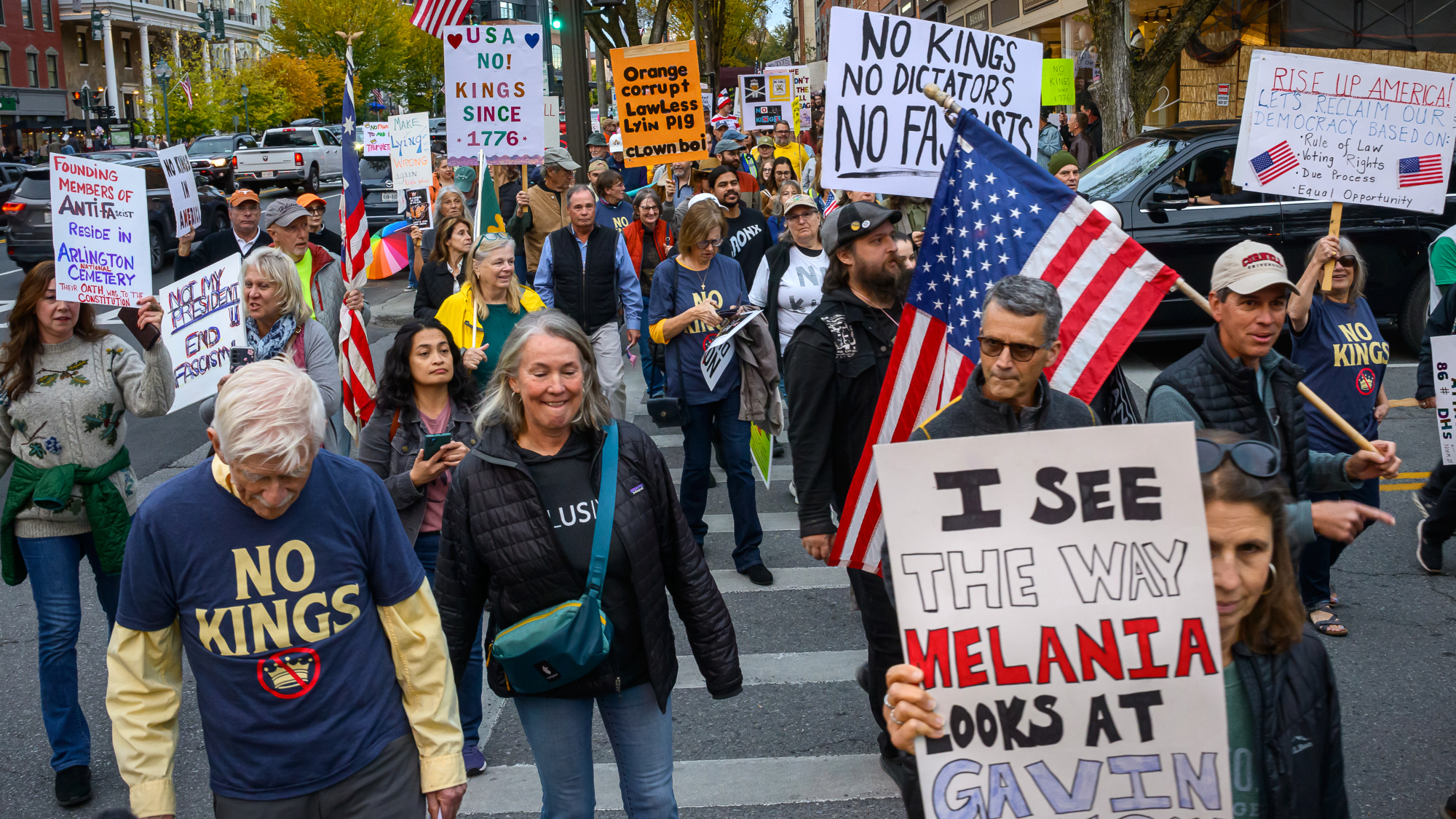 Millions turn out for anti-Trump ‘No Kings’ rallies
Millions turn out for anti-Trump ‘No Kings’ ralliesSpeed Read An estimated 7 million people participated, 2 million more than at the first ‘No Kings’ protest in June
-
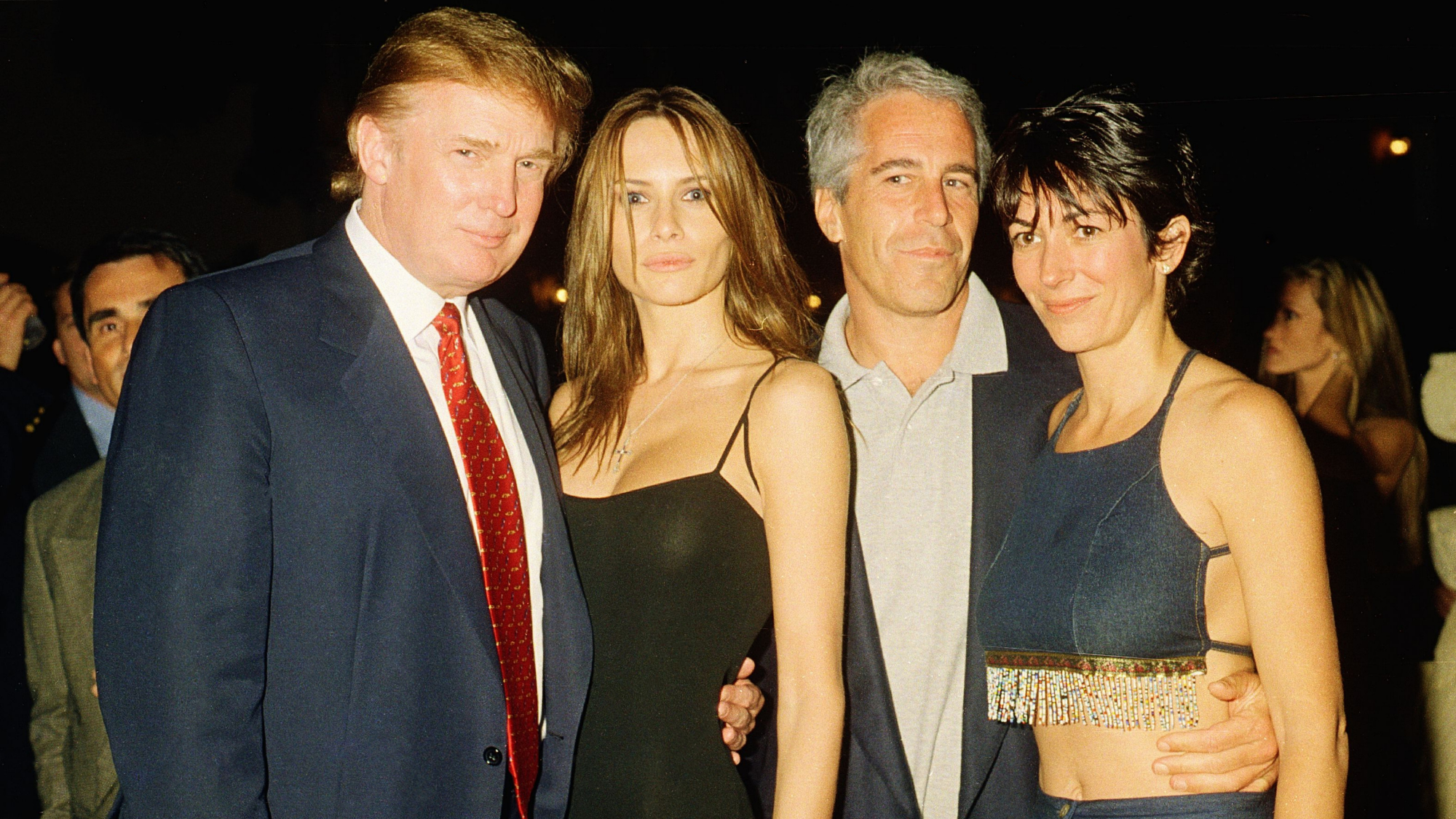 Ghislaine Maxwell: angling for a Trump pardon
Ghislaine Maxwell: angling for a Trump pardonTalking Point Convicted sex trafficker's testimony could shed new light on president's links to Jeffrey Epstein
-
 The last words and final moments of 40 presidents
The last words and final moments of 40 presidentsThe Explainer Some are eloquent quotes worthy of the holders of the highest office in the nation, and others... aren't
-
 The JFK files: the truth at last?
The JFK files: the truth at last?In The Spotlight More than 64,000 previously classified documents relating the 1963 assassination of John F. Kennedy have been released by the Trump administration
-
 'Seriously, not literally': how should the world take Donald Trump?
'Seriously, not literally': how should the world take Donald Trump?Today's big question White House rhetoric and reality look likely to become increasingly blurred
