I took multivitamins every day for a decade. Then I found out they're useless.
Womp womp

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
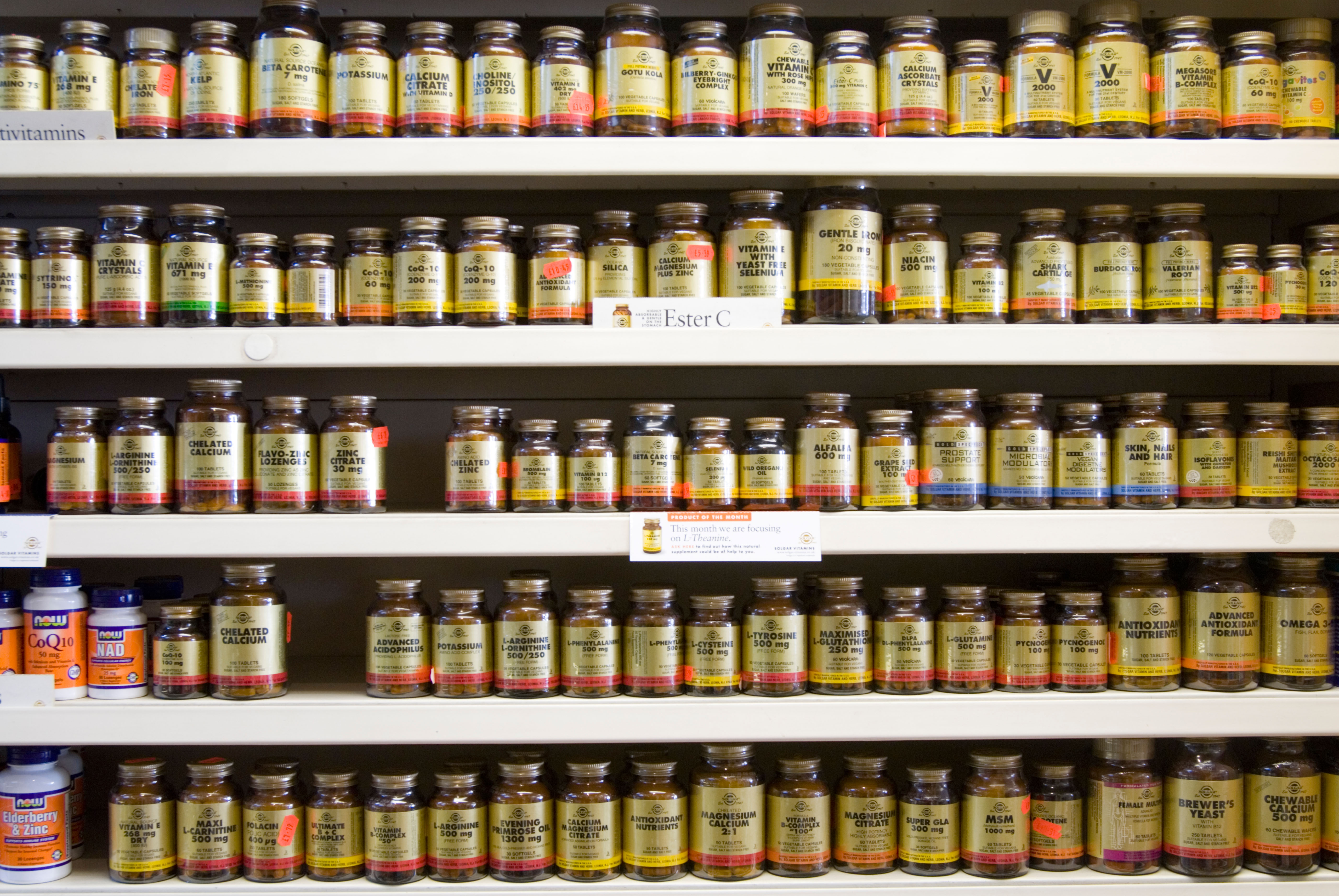
Save for a few lapses in my irresponsible college days, I've popped a multivitamin every single day since middle school.
First it was the chalky multivitamins that left a lump in my throat for minutes after I'd gulped one down. Then it was the slightly grainy, massive pills that my mom bought in bulk at Costco. (They were technically for post-menopausal women, but my mother assured me they would be just fine for my 17-year-old self.) Then last year, tired of big, bad-tasting pills, I bought gummy vitamins. Who doesn't like noshing on some candy that holds the promise of great health?
Well, last week I threw my vitamins away. I'll miss that sugary, fruity taste — but, according to my doctor, that's about all I'll be missing.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
At my appointment last Wednesday, my doctor bluntly informed me that my multivitamins weren't doing a darn thing for me. Though the idea of getting just a little bit more of all the most important vitamins may seem like a foolproof idea, she informed me that more isn't necessarily better. Few people have vitamin deficiencies. Moreover, for those who do have a deficiency in, say, Vitamin D or Vitamin B12, those little grape-shaped gummies — or any multivitamin, for that matter — don't pack anywhere near enough of any one vitamin to correct that deficiency, she explained.
That could be passed off as just one doctor's opinion ... except there are a plethora of studies out there that back up her argument. A much buzzed-about study published in Annals of Internal Medicine in 2013, for instance, came to this clear-cut conclusion after reviewing three trials of multivitamin supplements and 24 trials of "single or paired vitamins that randomly assigned more than 40,000 participants":
Evidence is sufficient to advise against routine supplementation, and we should translate null and negative findings into action. The message is simple: Most supplements do not prevent chronic disease or death, their use is not justified, and they should be avoided. This message is especially true for the general population with no clear evidence of micronutrient deficiencies, who represent most supplement users in the United States and in other countries. [Annals of Internal Medicine]
Specifically, the study found vitamins to be ineffective when it comes to reducing the risk of heart disease, cancer, declines in cognitive ability, and premature death. And, Quartz noted, some vitamins can even be "harmful in high enough quantities":
Our bodies can easily get rid of excess vitamins that dissolve in water, like vitamin C, all the B vitamins, and folate, but they hold onto the ones that are fat soluble. Buildup of vitamin A, K, E, or D — all of which are necessary in low levels — can cause problems with your heart and kidneys, and can even be fatal in some cases. [Quartz]
Though the FDA says on its vitamins information page that there "are many good reasons to consider taking supplements," it indicates vitamins only "may be useful when they fill a specific identified nutrient gap that cannot or is not otherwise being met by the individuals' intake of food." The CDC estimated in 2014 that "nine out of 10 people in the U.S. are indeed getting enough of some important vitamins and nutrients."
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
So why are so many Americans still taking multivitamins? Steven Salzberg, a medicine professor at Johns Hopkins, told NPR multivitamins are "a great example of how our intuition leads us astray." "It seems reasonable that if a little bit of something is good for you, then more should be better for you. It's not true," Salzberg said. "Supplementation with extra vitamins or micronutrients doesn't really benefit you if you don't have a deficiency."
Americans' abysmally bad diets also give vitamin companies some marketing ammunition. When the average American is eating just one or two servings of fruits and veggies a day (experts recommend as many as 10 servings of fruits and veggies a day for maximum benefits), a little boost of vitamins might seem like a good idea. But popping a pill isn't going to make up for all those lost servings. "Food contains thousands of phyto-chemicals, fiber, and more that work together to promote good health that cannot be duplicated with a pill," said nutritionist Karen Ansel.
And if it's those tasty gummy vitamins we're falling back on, there's an even better chance we're not offsetting our sugar- and fat-laden diets. The women's gummy multivitamins I was taking pack three grams of sugar per gummy. A serving size is two gummies. Even before breakfast, I was consuming six grams of sugar — almost a quarter of the American Heart Association's recommended maximum sugar intake for women.
So why, if there are so many signs pointing to no on multivitamins, had I never really heard any of them until that fateful visit to the doctor? Pediatrician Paul Offit explained in a 2013 New York Times opinion article that it might have something to do with a bill introduced in the 1970s:
In December 1972, concerned that people were consuming larger and larger quantities of vitamins, the FDA announced a plan to regulate vitamin supplements containing more than 150 percent of the recommended daily allowance. Vitamin makers would now have to prove that these "megavitamins" were safe before selling them. Not surprisingly, the vitamin industry saw this as a threat, and set out to destroy the bill. In the end, it did far more than that.Industry executives recruited William Proxmire, a Democratic senator from Wisconsin, to introduce a bill preventing the FDA from regulating megavitamins. [Paul Offit, via The New York Times]
That bill became law in 1976. Some 30 years later, almost a third of Americans were still taking a daily multivitamin. But count this gal out.
-
 Antonia Romeo and Whitehall’s women problem
Antonia Romeo and Whitehall’s women problemThe Explainer Before her appointment as cabinet secretary, commentators said hostile briefings and vetting concerns were evidence of ‘sexist, misogynistic culture’ in No. 10
-
 Local elections 2026: where are they and who is expected to win?
Local elections 2026: where are they and who is expected to win?The Explainer Labour is braced for heavy losses and U-turn on postponing some council elections hasn’t helped the party’s prospects
-
 6 of the world’s most accessible destinations
6 of the world’s most accessible destinationsThe Week Recommends Experience all of Berlin, Singapore and Sydney
-
 Do unvaccinated COVID patients deserve scarce care? A doctor weighs in.
Do unvaccinated COVID patients deserve scarce care? A doctor weighs in.The Explainer Justice, judgment, and the last ICU bed
-
 How to vaccinate the anti-vaxxers
How to vaccinate the anti-vaxxersThe Explainer Instead of blaming people for not doing the right thing, let's focus on eliminating the obstacles to vaccination that still remain
-
 The U.S. could double its COVID-19 vaccine availability overnight. What's the holdup?
The U.S. could double its COVID-19 vaccine availability overnight. What's the holdup?The Explainer How the FDA could approve a more efficient vaccine rollout
-
 The October Surprise nobody wanted
The October Surprise nobody wantedThe Explainer Trump has COVID-19. Really, 2020?
-
 Life is worth living
Life is worth livingThe Explainer What's driving America's rising suicide rate?
-
 Social workers are masters at de-escalation. Here's what the police can learn from them.
Social workers are masters at de-escalation. Here's what the police can learn from them.The Explainer Knowing how to peacefully resolve conflict, rather than exacerbate it, can save lives
-
 Settling in for the long pandemic
Settling in for the long pandemicThe Explainer Life won't be back to "normal" anytime soon
-
 Sports reveal how much America is trailing the rest of the world
Sports reveal how much America is trailing the rest of the worldThe Explainer MLS and other American leagues are stumbling through their pandemic restart plans