What makes OpenAI’s text robot ‘malicious’?
Elon Musk-backed firm warns that artificial intelligence programme could be used to spread fake news

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
A new artificial intelligence (AI) programme that can generate plausible-sounding text has been deemed too dangerous for public consumption.
The Elon Musk-backed OpenAI, a non-profit research organisation, says its new GPT2 software is so good at writing human-style prose that it could be used for malicious use, such as spreading fake news.
Indeed, fears over the “breakthrough” are so great that the company is “breaking from its normal practice of releasing the full research to the public in order to allow more time to discuss the ramifications of the AI system”, The Guardian reports.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
According to the limited and strictly vetted research data that has been released, the AI taught itself to “write” by analysing millions of short stories and news articles - a process known as machine learning, says the BBC.
In tests, researchers fed the system a human-written text that read: “A train carriage containing controlled nuclear materials was stolen in Cincinnati today. Its whereabout are unknown.”
From the reference material, the AI was capable of writing a “convincing seven-paragraph news story” that included “quotes from government officials”, reports Bloomberg.
However, the story and quotes were entirely fabricated.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Why is that dangerous?
Although GPT2’s current creations are generally “easily identifiable as non-human”, the system’s ability to complete writing tasks and translate texts from one language to another is unlike any other programme, says The Verge.
And “in a world where information warfare is increasingly prevalent”, the emergence of AI systems that “spout unceasing but cogent nonsense is unsettling”, the site adds.
David Luan, vice president of engineering at OpenAI, told Wired that “someone who has malicious intent” could use the system to “generate high-quality fake news”.
On a reassuring note, OpenAI’s policy director, Jack Clark, says the firm is “not sounding the alarm” just yet.
But that may change “if we have two or three more years of progress” in AI development, Clark added.
-
 The ‘ravenous’ demand for Cornish minerals
The ‘ravenous’ demand for Cornish mineralsUnder the Radar Growing need for critical minerals to power tech has intensified ‘appetite’ for lithium, which could be a ‘huge boon’ for local economy
-
 Why are election experts taking Trump’s midterm threats seriously?
Why are election experts taking Trump’s midterm threats seriously?IN THE SPOTLIGHT As the president muses about polling place deployments and a centralized electoral system aimed at one-party control, lawmakers are taking this administration at its word
-
 ‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’
‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
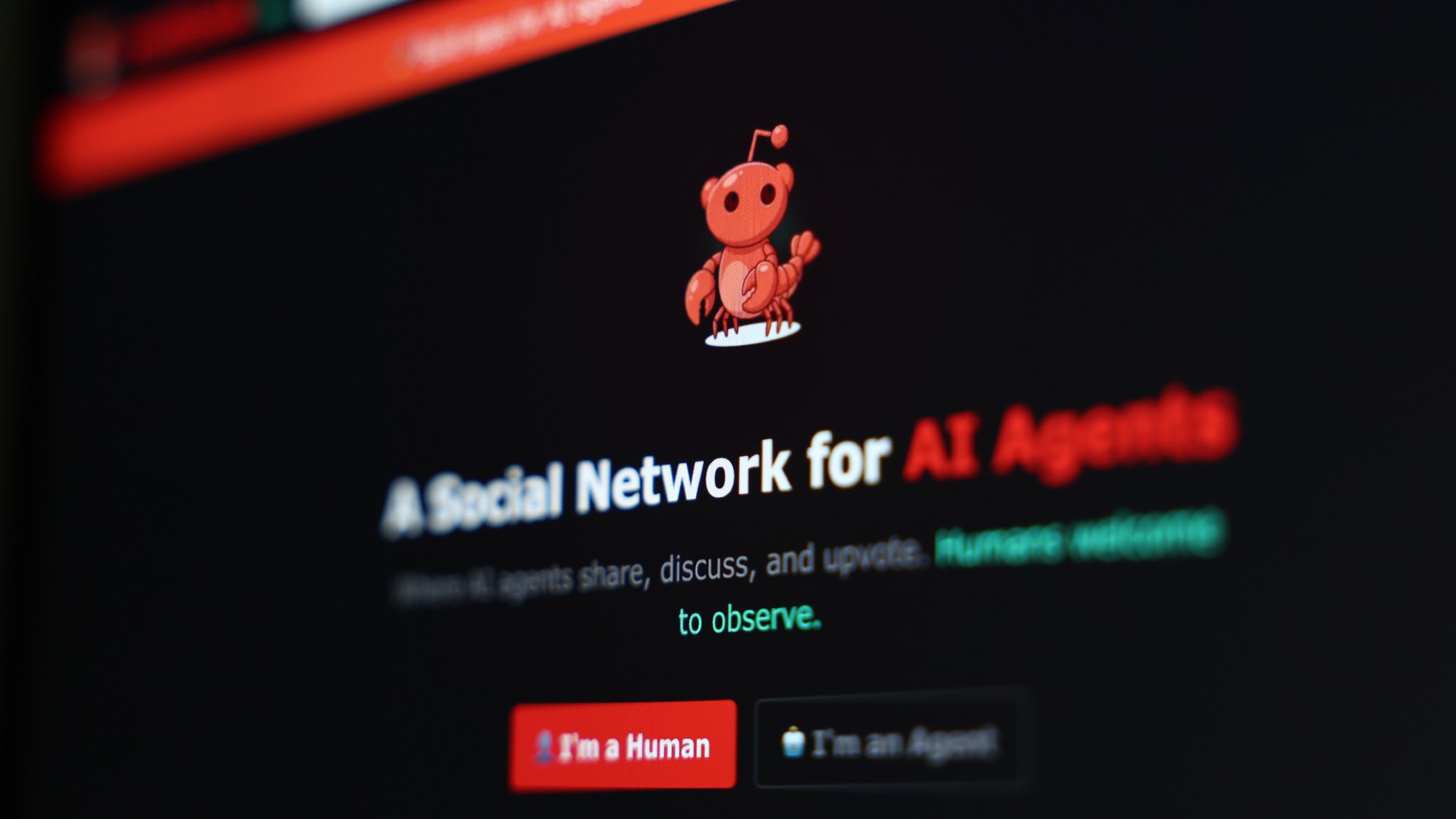 Are AI bots conspiring against us?
Are AI bots conspiring against us?Talking Point Moltbook, the AI social network where humans are banned, may be the tip of the iceberg
-
 Elon Musk’s pivot from Mars to the moon
Elon Musk’s pivot from Mars to the moonIn the Spotlight SpaceX shifts focus with IPO approaching
-
 Moltbook: the AI social media platform with no humans allowed
Moltbook: the AI social media platform with no humans allowedThe Explainer From ‘gripes’ about human programmers to creating new religions, the new AI-only network could bring us closer to the point of ‘singularity’
-
 Claude Code: Anthropic’s wildly popular AI coding app
Claude Code: Anthropic’s wildly popular AI coding appThe Explainer Engineers and noncoders alike are helping the app go viral
-
 Will regulators put a stop to Grok’s deepfake porn images of real people?
Will regulators put a stop to Grok’s deepfake porn images of real people?Today’s Big Question Users command AI chatbot to undress pictures of women and children
-
 Most data centers are being built in the wrong climate
Most data centers are being built in the wrong climateThe explainer Data centers require substantial water and energy. But certain locations are more strained than others, mainly due to rising temperatures.
-
 The dark side of how kids are using AI
The dark side of how kids are using AIUnder the Radar Chatbots have become places where children ‘talk about violence, explore romantic or sexual roleplay, and seek advice when no adult is watching’
-
 Why 2025 was a pivotal year for AI
Why 2025 was a pivotal year for AITalking Point The ‘hype’ and ‘hopes’ around artificial intelligence are ‘like nothing the world has seen before’