Experimental drug shown to 'significantly' slow progression of brain cancer

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
A new experimental drug was found to "significantly" reduce the progression of brain cancer, Reuters reported.
Vorasidenib, created by Servier Group, a private drug developer, was shown to slow the progression of brain tumors by an average of over 16 months, per Bloomberg. The results of the 331-patient study were published June 4 in The New England Journal of Medicine.
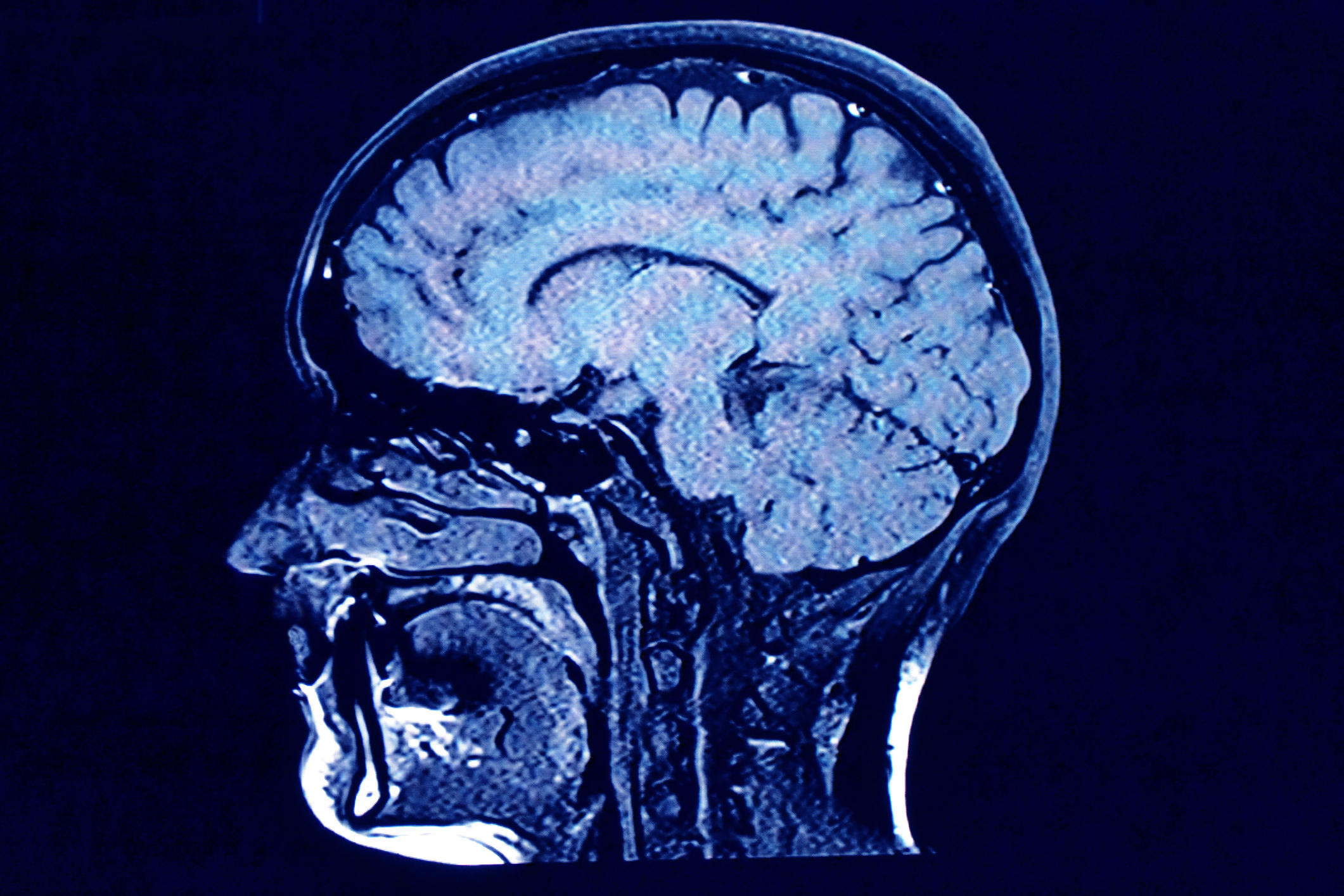
The study's lead author, Ingo Mellinghoff, described this as "a very big finding," adding that the drug "is the first molecularly targeted treatment for diffuse glioma." Vorasidenib specifically works on Grade 2 gliomas, which are "progressive, malignant brain tumors" that are "more common in adults but can also occur in children and teenagers," according to Reuters. The drug blocks a specific enzyme mutated in low-grade gliomas, keeping them from progressing and postponing the need for further treatment like chemotherapy.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
"What you just heard is a trial that was well done and well thought out: to use an oral, targeted, well-tolerated therapy to see if we could delay the use of our standard chemotherapy and radiation," Wake Forest Baptist Health's Dr. Glenn Lesser commented at an American Society of Clinical Oncology briefing. "The results are quite striking and they're statistically highly significant, and more importantly, they're clinically very, very significant."
Servier Group is working to get the drug approved by the Food & Drug Administration for use in the U.S.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Devika Rao has worked as a staff writer at The Week since 2022, covering science, the environment, climate and business. She previously worked as a policy associate for a nonprofit organization advocating for environmental action from a business perspective.
