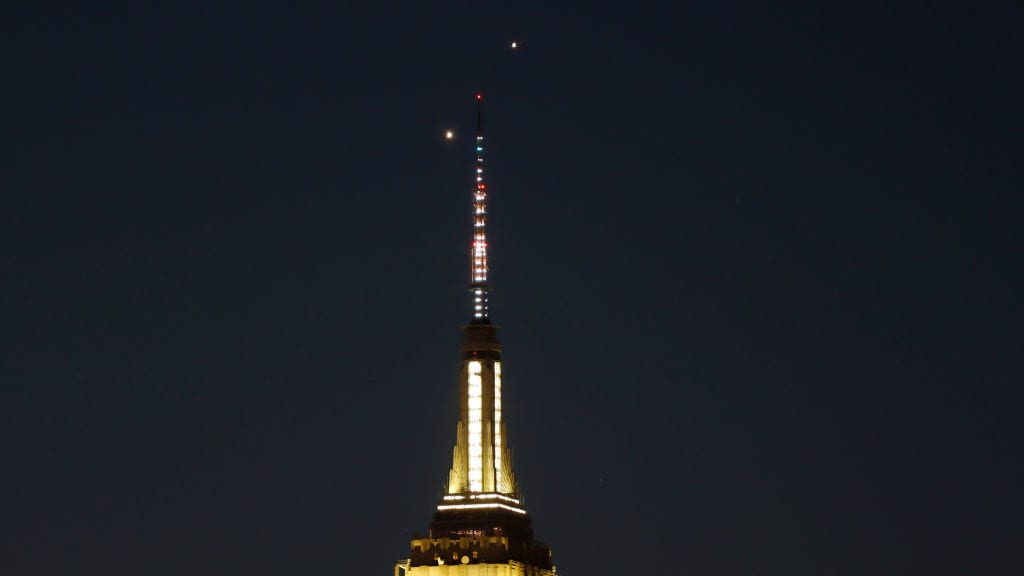
Jupiter and Venus to 'kiss' in the night sky Wednesday evening


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Jupiter and Venus have been getting closer to each other in the night sky and will meet on Wednesday evening before moving apart again. "It is an apparent close approach from our perspective, as the planets are in fact hundreds of millions of kilometers apart," said Paul Delaney, professor emeritus at the York University Department of Physics and Astronomy.
Venus, often called the "morning star" or "evening star" depending on its spot in the sky, is the brighter of the two planets. Jupiter, the solar system's largest planet, will be located slightly above it to the left. The planetary "kiss" occurs approximately once a year, according to CBC News.
"Venus and Jupiter are somewhat common conjunctions, occurring about once a year, but if you have clear skies it should still be a very fun object to view," remarked Elaina Hyde, director of York University's Allan I Carswell Observatory. "At magnitude –2.1 and –4, the planets Venus and Jupiter are two of our brightest objects to see in the night sky."
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
In addition to the planets crossing paths, some may also be able to see three of Jupiter's brightest moons: Io, Ganymede, and Callisto. Scientists recommend using binoculars to get the best view.
"Any time the brightest planets, as seen from Earth, 'get together,' it is worth the look," said Delaney. "I never tire of watching their dance with respect to the background stars."
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Devika Rao has worked as a staff writer at The Week since 2022, covering science, the environment, climate and business. She previously worked as a policy associate for a nonprofit organization advocating for environmental action from a business perspective.
-
 Political cartoons for February 19
Political cartoons for February 19Cartoons Thursday’s political cartoons include a suspicious package, a piece of the cake, and more
-
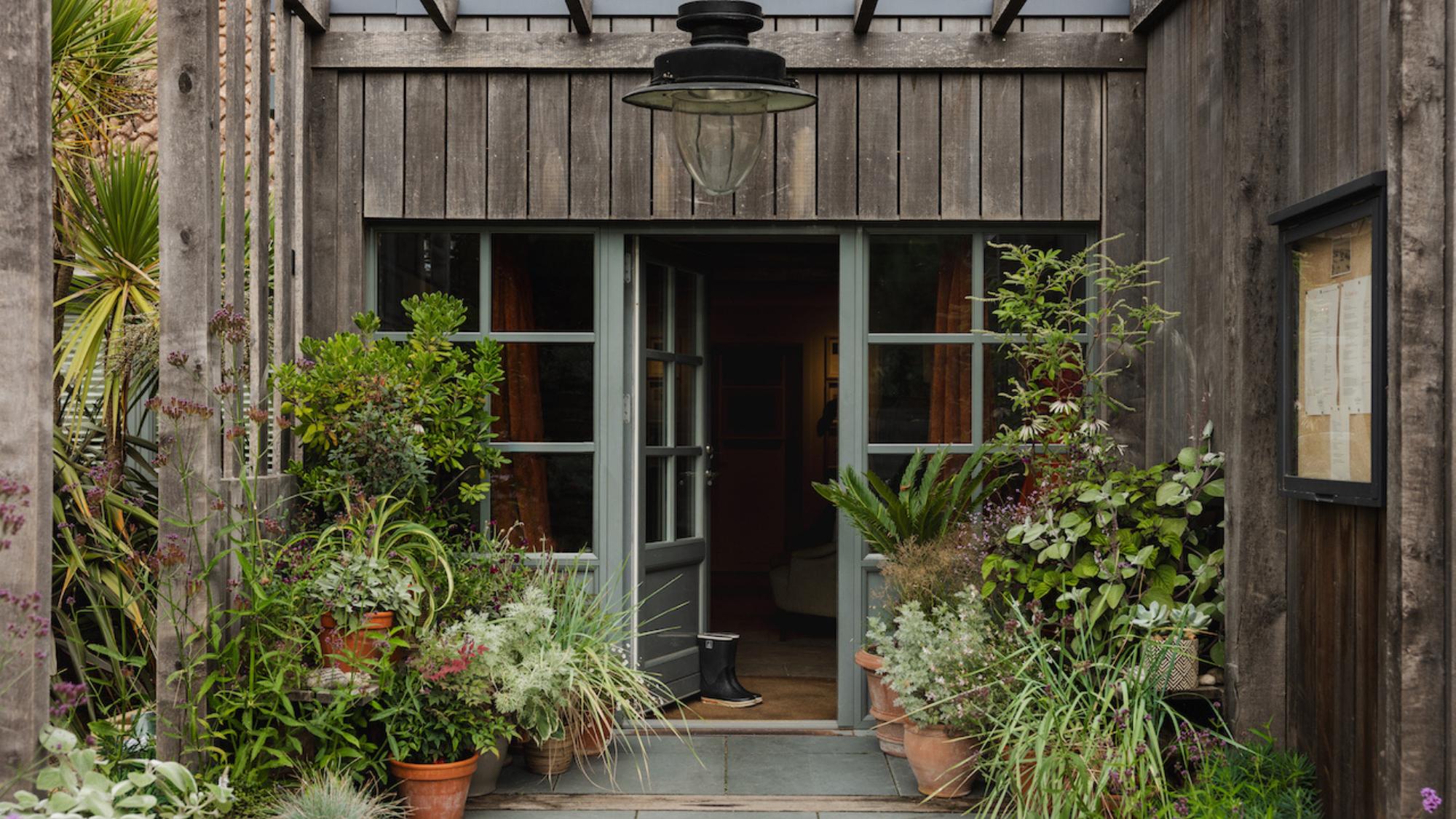 The Gallivant: style and charm steps from Camber Sands
The Gallivant: style and charm steps from Camber SandsThe Week Recommends Nestled behind the dunes, this luxury hotel is a great place to hunker down and get cosy
-
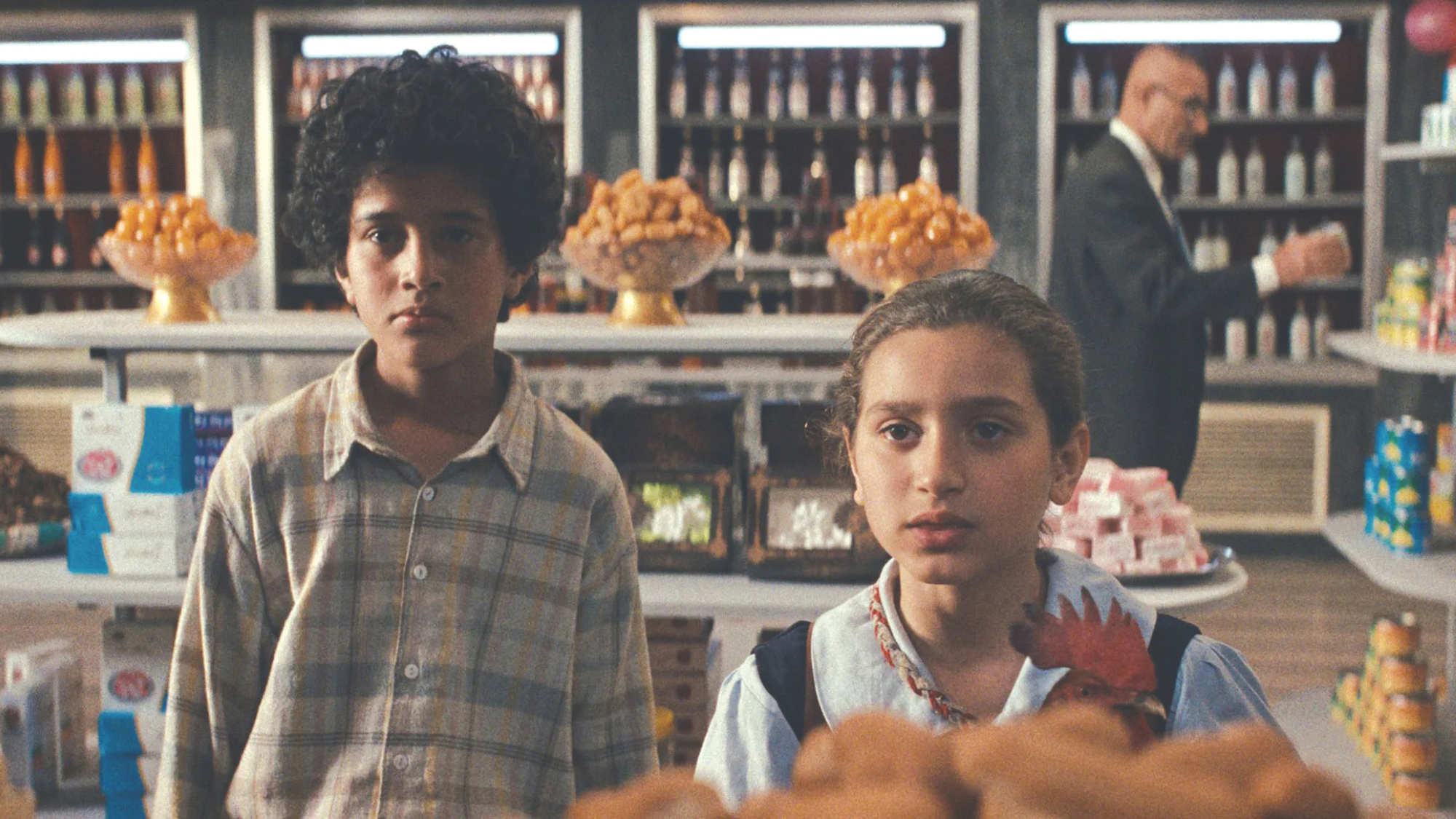 The President’s Cake: ‘sweet tragedy’ about a little girl on a baking mission in Iraq
The President’s Cake: ‘sweet tragedy’ about a little girl on a baking mission in IraqThe Week Recommends Charming debut from Hasan Hadi is filled with ‘vivid characters’
-
 NASA’s lunar rocket is surrounded by safety concerns
NASA’s lunar rocket is surrounded by safety concernsThe Explainer The agency hopes to launch a new mission to the moon in the coming months
-
 Nasa’s new dark matter map
Nasa’s new dark matter mapUnder the Radar High-resolution images may help scientists understand the ‘gravitational scaffolding into which everything else falls and is built into galaxies’
-
 Moon dust has earthly elements thanks to a magnetic bridge
Moon dust has earthly elements thanks to a magnetic bridgeUnder the radar The substances could help supply a lunar base
-
 How Mars influences Earth’s climate
How Mars influences Earth’s climateThe explainer A pull in the right direction
-
 The ‘eclipse of the century’ is coming in 2027
The ‘eclipse of the century’ is coming in 2027Under the radar It will last for over 6 minutes
-
 NASA discovered ‘resilient’ microbes in its cleanrooms
NASA discovered ‘resilient’ microbes in its cleanroomsUnder the radar The bacteria could contaminate space
-
 Artemis II: back to the Moon
Artemis II: back to the MoonThe Explainer Four astronauts will soon be blasting off into deep space – the first to do so in half a century
-
 The mysterious origin of a lemon-shaped exoplanet
The mysterious origin of a lemon-shaped exoplanetUnder the radar It may be made from a former star
