Five planets line up in a row in rare cosmic event
The best way to see Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn as they all appear in the night sky
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
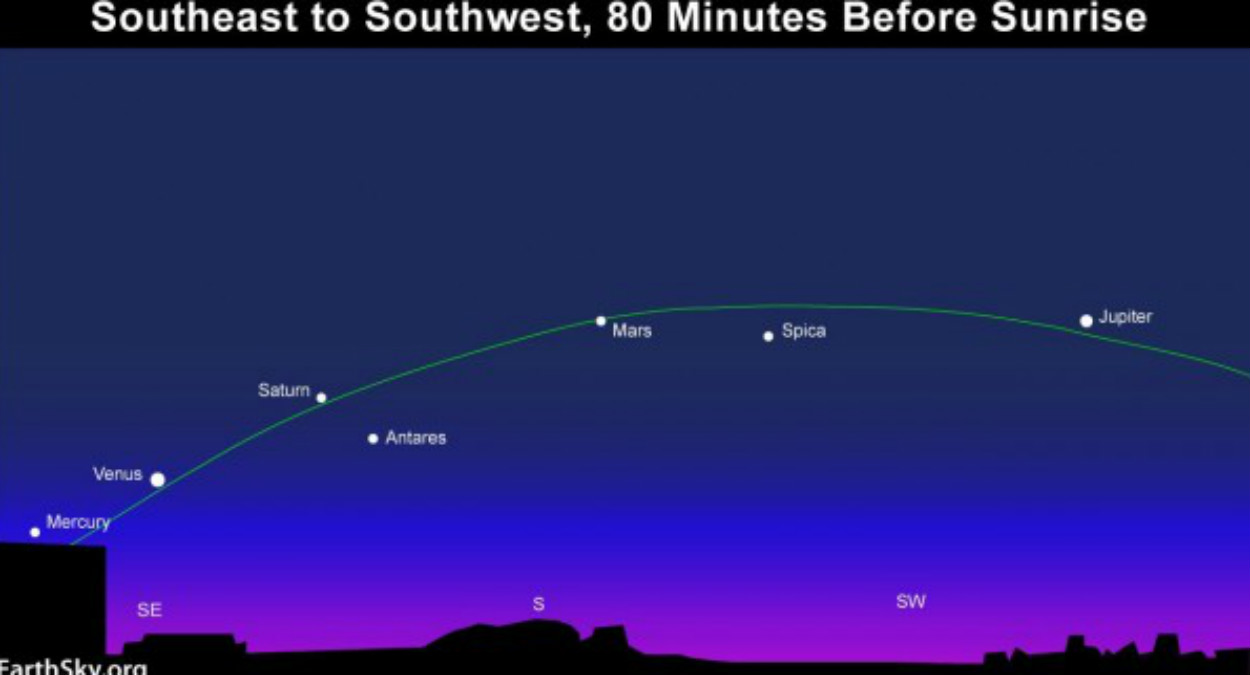
For the first time in ten years, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn will all be visible to the naked eye in the night sky. Space enthusiasts can observe the five planets without a telescope until 20 February. They each have different orbits, which makes moments of synchronisation such as this a rare event – and for keen amateur astronomers, one to look forward to.
When will the alignment happen?
If you're reading this in the UK, it's already happening. The alignment is visible over Britain from dawn on 20 January and is expected to remain so for the next month, with astronomers predicting 5 February to be the best day to enjoy the sight in its full glory.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
You'll need to be up before daybreak in order to get the clearest view, however, but while that may sound like a tall order on a frosty winter morning, Dr Robert Massey of the Royal Astronomical Society assures the Daily Telegraph the planetary display is "well worth getting up for".
What will the alignment look like?
The planets will appear as especially bright stars, scattered in a roughly diagonal line stretching away from the Moon towards the horizon. At first, there may only seem to be four, as Mercury lies just above the horizon and can be difficult to spot. Venus and Jupiter will be the brightest and thus the easiest to pick out.
For inexperienced stargazers wondering if they will be able to tell the planets from normal stars, Jason Kendall, of the Amateur Astronomers Association of New York, shares his top tip with the New York Times. "Close one eye, stretch out your arm and slowly pass your thumb over a bright dot in the sky," he says. "If the dot slowly dims out when your thumb passes over it, it’s a planet. If it quickly blinks out, it’s a distant star."
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Where is the best place to see it?
Visibility will be highly dependent on where you are located. Cloudy skies, fog or a high concentration of electric lights or tall buildings could all obscure the view. For the best chance of seeing the planets, enthusiasts should get out to the country - or the least built-up area possible - to minimise the effects of light pollution and crowded skylines.