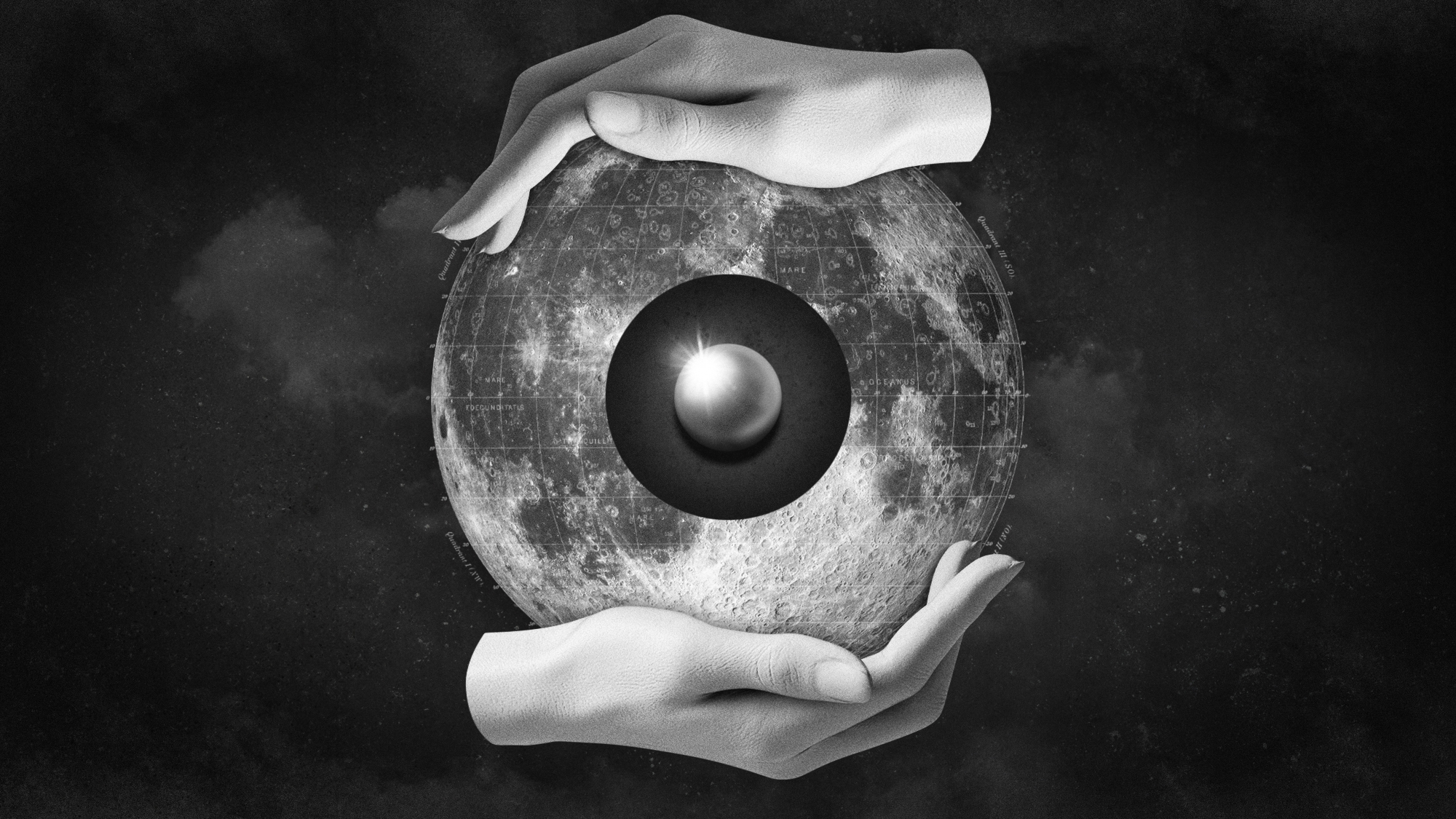
The treasure trove of platinum on the moon
This kind of bounty could lead to commercial exploitation


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
The moon is likely to become the next mining hot spot, as there may be extensive platinum and other metal deposits in its craters. Guidelines about resource mining on the moon are still not solidified, so this could lead to problems with more countries and private companies trying to stake their claim. But the potential for platinum could also entice private companies to invest more in space exploration.
Mine on the moon
There might be more than $1 trillion worth of platinum deposits on the moon, according to a paper published in the journal Planetary and Space Science. Of the 1.3 million craters on the moon with a diameter greater than one kilometer, "nearly 6,500 were made by asteroids containing commercial quantities of platinum," said New Scientist. This "highlights the potential viability and profitability of lunar mining endeavors compared to mining asteroids in orbit," said the paper.
Countries have already been involved in a modern space race to put humans back on the moon, and the profit potential could bring more interested parties. Nobody owns the moon because of the Outer Space Treaty of 1967. But as the potential for resources becomes imminent, the rules are likely to change.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
The treaty notably "leaves key questions unanswered," said Rebecca Connolly, an adjunct senior lecturer at the University of Sydney Law School, to New Scientist. This includes "clarity on the rules and governance for ownership of extracted resources, commercial licensing rights, equitable benefits sharing, environment protection standards to avoid harm, and regulations for long-term occupation and permanent infrastructure on the moon."
To address some of the unknowns, NASA and the U.S. spearheaded the Artemis Accords in 2020. These "provide a common set of principles to enhance the governance of the civil exploration and use of outer space," said NASA. Though the accords are nonbinding, 55 countries have signed on as of last month. Russia and China, two of the most proactive countries trying to reach the moon, have not signed on.
Exploration economics
A monetary incentive for reaching the moon could change space exploration as we know it. Astronomy is "done to satiate our curiosity," said Jayanth Chennamangalam, an astrophysicist and the lead author of the study, to New Scientist. It has "very few practical applications" and is "mostly paid for by taxpayer money." If we can "monetize space resources, be it on the moon or on asteroids, private enterprises will invest in the exploration of the solar system."
While that could lead to wider research being done, it could also lead to the exploitation of the moon. It was recently listed as a threatened historic site for this very reason. "Take one last good look at the moon tonight," Luis Prada said at Vice. "There might be a time when the moon is not so innocent and pretty anymore and you only see cynical corporate greed."
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Devika Rao has worked as a staff writer at The Week since 2022, covering science, the environment, climate and business. She previously worked as a policy associate for a nonprofit organization advocating for environmental action from a business perspective.
-
 How to Get to Heaven from Belfast: a ‘highly entertaining ride’
How to Get to Heaven from Belfast: a ‘highly entertaining ride’The Week Recommends Mystery-comedy from the creator of Derry Girls should be ‘your new binge-watch’
-
 The 8 best TV shows of the 1960s
The 8 best TV shows of the 1960sThe standout shows of this decade take viewers from outer space to the Wild West
-
 Microdramas are booming
Microdramas are boomingUnder the radar Scroll to watch a whole movie
-
 AI surgical tools might be injuring patients
AI surgical tools might be injuring patientsUnder the Radar More than 1,300 AI-assisted medical devices have FDA approval
-
 How roadkill is a surprising boon to scientific research
How roadkill is a surprising boon to scientific researchUnder the radar We can learn from animals without trapping and capturing them
-
 NASA’s lunar rocket is surrounded by safety concerns
NASA’s lunar rocket is surrounded by safety concernsThe Explainer The agency hopes to launch a new mission to the moon in the coming months
-
 Nasa’s new dark matter map
Nasa’s new dark matter mapUnder the Radar High-resolution images may help scientists understand the ‘gravitational scaffolding into which everything else falls and is built into galaxies’
-
 The world’s oldest rock art paints a picture of human migration
The world’s oldest rock art paints a picture of human migrationUnder the Radar The art is believed to be over 67,000 years old
-
 Moon dust has earthly elements thanks to a magnetic bridge
Moon dust has earthly elements thanks to a magnetic bridgeUnder the radar The substances could help supply a lunar base
-
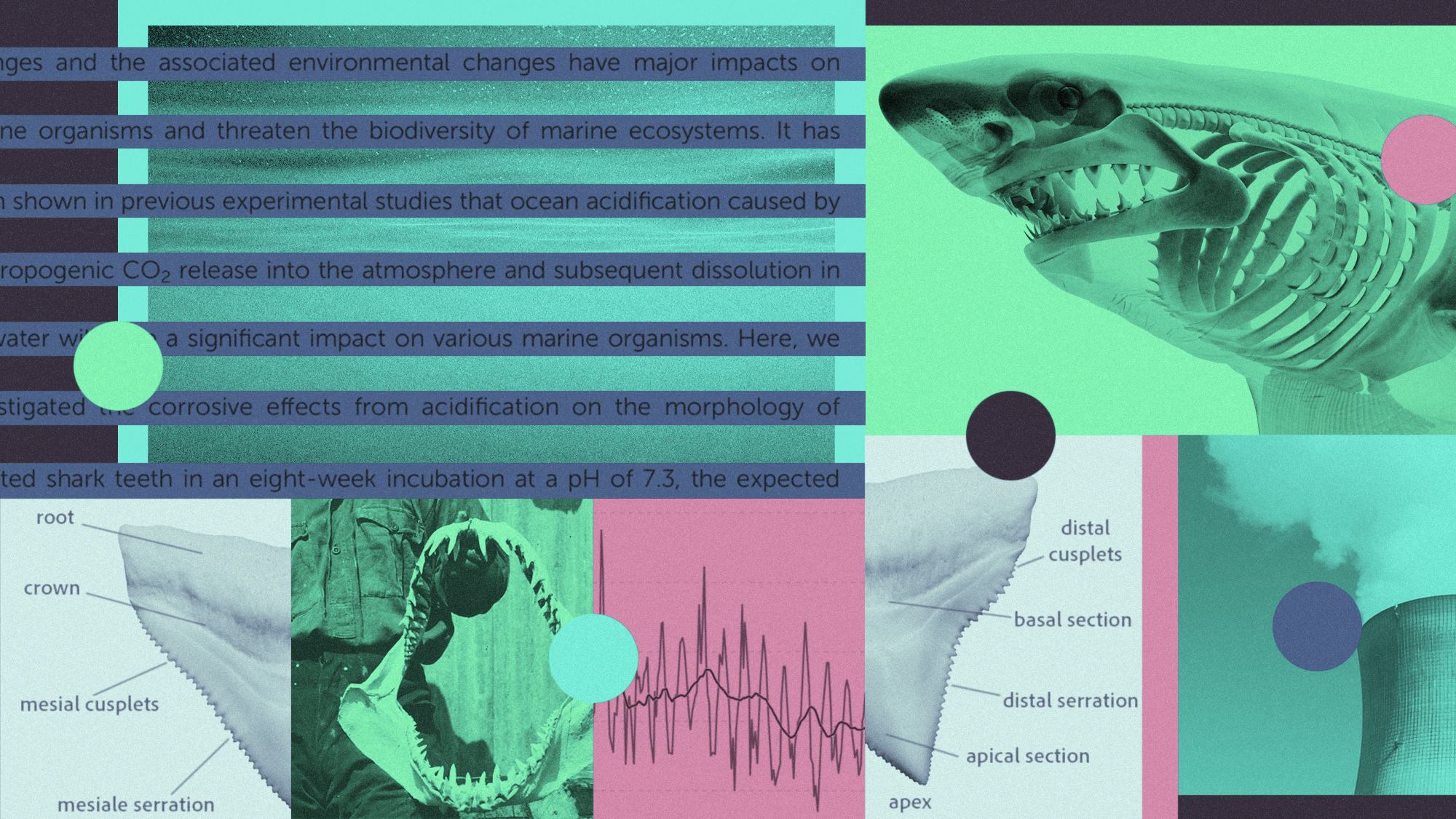 The ocean is getting more acidic — and harming sharks’ teeth
The ocean is getting more acidic — and harming sharks’ teethUnder the Radar ‘There is a corrosion effect on sharks’ teeth,’ the study’s author said
-
 How Mars influences Earth’s climate
How Mars influences Earth’s climateThe explainer A pull in the right direction
