The ozone will be completely healed by 2066, UN says

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
A United Nations report has shown that the hole in the ozone layer is on track to fully heal by 2066, reports The Associated Press. An assessment of the layer has been performed every four years since the world's nations agreed to stop using ozone-destroying chemicals like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
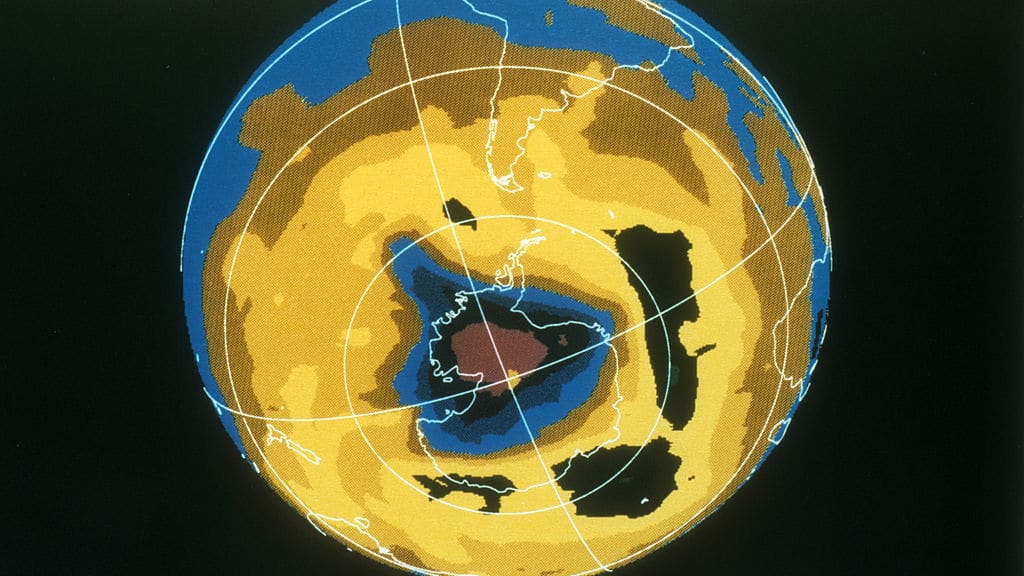
The new report says that while progress is slow, the ozone is getting better and is expected to fully heal aside from the poles by 2040. The arctic will likely heal by 2045 and Antarctica, which has the most severe damage, by 2066, reports The Guardian. The ozone layer shields the planet from harmful radiation and ultraviolet rays.
Though signs of ozone healing were also present in the report from four years ago, this latest assessment provides more conclusive evidence on the matter. "In the upper stratosphere and in the ozone hole, we see things getting better," said Paul Newman, co-chairman of the scientific assessment. "Those numbers of recovery have solidified a lot."
Article continues belowThe Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Concern about the ozone harkens back to the 1980s. In 1987, nations signed the international Montreal Protocol, which eliminated 99 percent of ozone-depleting chemicals, many of which were used as refrigerants. David Fahey, a scientist at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and a lead author of the new assessment, described the protocol as "the most successful environmental treaty in history."
However, progress has not always been easy. In 2018, a small uptick in CFC use was traced to China, which then remedied the problem. Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) also rose in popularity at one point. Though they do not destroy the ozone, HFCs are still strong greenhouse gases and many countries are working to phase them out, per The Guardian.
"Ozone action sets a precedent for climate action," said Petteri Taalas, secretary-general of the World Meteorological Organization. "Our success in phasing out ozone-eating chemicals shows us what can and must be done."
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Devika Rao has worked as a staff writer at The Week since 2022, covering science, the environment, climate and business. She previously worked as a policy associate for a nonprofit organization advocating for environmental action from a business perspective.
