Moderna developing mRNA vaccine for Lyme disease


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
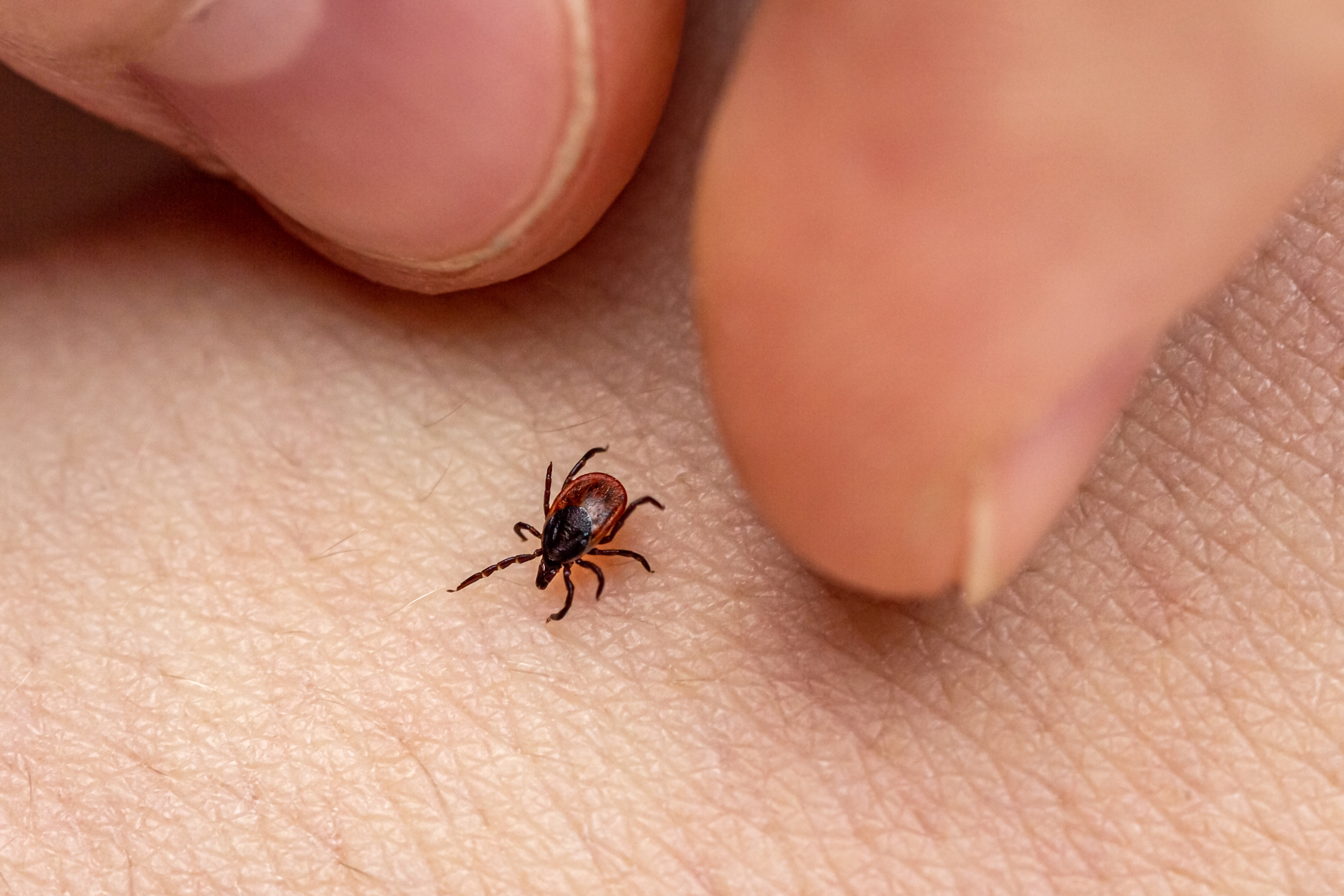
A Lyme disease vaccine could be on its way soon, according to pharmaceutical company Moderna.
The company has announced two new mRNA vaccines in development that could prevent Lyme disease, marking the "first application of its mRNA technology to bacterial pathogens." The technology was used in creating the COVID-19 vaccine. Moderna also announced vaccine development plans for norovirus and RSV, which have both been spreading rapidly.
"Untreated, Lyme disease can be very serious," emergency physician and George Washington University professor Leana Wen told Axios. "Some people develop debilitating symptoms that really impact their lives." The disease comes from tick bites and can cause fever, chills, joint pain, and rashes, according to the Centers for Disease Control. If left untreated, the symptoms can be more severe including heart palpitations, arthritis, and facial palsy.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
There has only been one human Lyme disease vaccine that was ever available on the market and it was pulled in 2002 because "negative press coverage and limited awareness of the benefits of the vaccine decreased consumer demand for the vaccine," according to a 2007 study. However, there are approximately 120,000 reported cases of Lyme reported each year in the U.S. and Europe, and that number is rising due to climate change, per Axios.
Pfizer and its partner company Valneva also have a Lyme disease vaccine in the works that has shown promise, with the company saying it could get approved as early as 2025. It is still good practice to wear long sleeves and use insect repellant to prevent tick bites in the first place, but "after years of relying on such preventive steps, an age of advanced drugs and vaccines could be nigh," Axios writes.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Devika Rao has worked as a staff writer at The Week since 2022, covering science, the environment, climate and business. She previously worked as a policy associate for a nonprofit organization advocating for environmental action from a business perspective.
-
 The Gallivant: style and charm steps from Camber Sands
The Gallivant: style and charm steps from Camber SandsThe Week Recommends Nestled behind the dunes, this luxury hotel is a great place to hunker down and get cosy
-
 The President’s Cake: ‘sweet tragedy’ about a little girl on a baking mission in Iraq
The President’s Cake: ‘sweet tragedy’ about a little girl on a baking mission in IraqThe Week Recommends Charming debut from Hasan Hadi is filled with ‘vivid characters’
-
 Kia EV4: a ‘terrifically comfy’ electric car
Kia EV4: a ‘terrifically comfy’ electric carThe Week Recommends The family-friendly vehicle has ‘plush seats’ and generous space
-
 Scientists are worried about amoebas
Scientists are worried about amoebasUnder the radar Small and very mighty
-
 Metal-based compounds may be the future of antibiotics
Metal-based compounds may be the future of antibioticsUnder the radar Robots can help develop them
-
 A Nipah virus outbreak in India has brought back Covid-era surveillance
A Nipah virus outbreak in India has brought back Covid-era surveillanceUnder the radar The disease can spread through animals and humans
-
 Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinations
Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinationsSpeed Read In a widely condemned move, the CDC will now recommend that children get vaccinated against 11 communicable diseases, not 17
-
 Deaths of children under 5 have gone up for the first time this century
Deaths of children under 5 have gone up for the first time this centuryUnder the radar Poor funding is the culprit
-
 A fentanyl vaccine may be on the horizon
A fentanyl vaccine may be on the horizonUnder the radar Taking a serious jab at the opioid epidemic
-
 Health: Will Kennedy dismantle U.S. immunization policy?
Health: Will Kennedy dismantle U.S. immunization policy?Feature ‘America’s vaccine playbook is being rewritten by people who don’t believe in them’
-
 How dangerous is the ‘K’ strain super-flu?
How dangerous is the ‘K’ strain super-flu?The Explainer Surge in cases of new variant H3N2 flu in UK and around the world
