Microplastics accumulating in human brains, study finds
The amount of tiny plastic particles found in human brains increased dramatically from 2016 to 2024


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
What happened
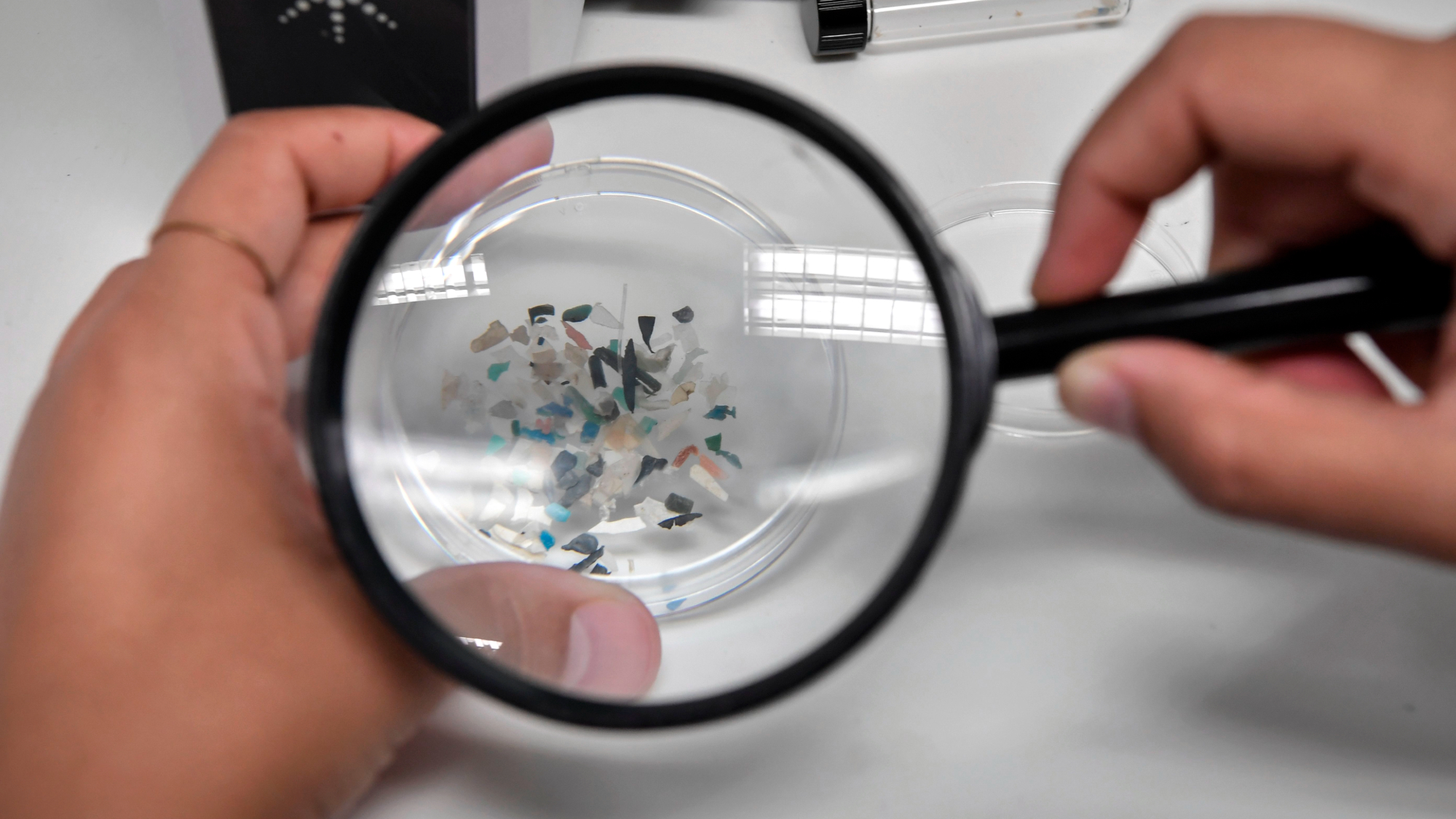
Microplastics are amassing in the human brain, with the amount increasing over time, according to a study published Monday in the journal Nature Medicine.
Who said what
The researchers examined samples of 52 autopsied brains from 2016 and 2024 and found a 50% increase in the tiny plastic particles in those eight years. They also studied liver and kidney samples from the same patients and found only a slight increase in the relatively small amounts of microplastics. Previous studies have found microplastics in the human placenta, blood, testicles and coronary arteries, but the large amounts in the brain were a "surprise because of the blood-brain barrier," USA Today said.
Dr. Matthew Campen, a University of New Mexico toxicology professor and a lead author of the study, said the 7 grams of microplastics found in the 2024 brains was roughly equivalent to a plastic spoon. The levels were three to five times higher in 12 brains from people who had been diagnosed with dementia, but the researchers made "no claims to causation — just correlation," the Los Angeles Times said.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
What next?
The long-term effects of microplastics on humans are unknown, but studies of mice brains "found troubling signs," The Washington Post said. "I certainly don't feel comfortable with this much plastic in my brain, and I don't need to wait around 30 more years to find out what happens if the concentrations quadruple," Campen said. But "there are no control groups" with microplastics, he added. "Everyone is exposed."
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Peter has worked as a news and culture writer and editor at The Week since the site's launch in 2008. He covers politics, world affairs, religion and cultural currents. His journalism career began as a copy editor at a financial newswire and has included editorial positions at The New York Times Magazine, Facts on File, and Oregon State University.
-
 ‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’
‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
 Earth is rapidly approaching a ‘hothouse’ trajectory of warming
Earth is rapidly approaching a ‘hothouse’ trajectory of warmingThe explainer It may become impossible to fix
-
 Health insurance: Premiums soar as ACA subsidies end
Health insurance: Premiums soar as ACA subsidies endFeature 1.4 million people have dropped coverage
-
 Scientists are worried about amoebas
Scientists are worried about amoebasUnder the radar Small and very mighty
-
 Metal-based compounds may be the future of antibiotics
Metal-based compounds may be the future of antibioticsUnder the radar Robots can help develop them
-
 How space travel changes your brain
How space travel changes your brainUnder the Radar Space shifts the position of the brain in the skull, causing orientation problems that could complicate plans to live on the Moon or Mars
-
 Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinations
Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinationsSpeed Read In a widely condemned move, the CDC will now recommend that children get vaccinated against 11 communicable diseases, not 17
-
 Stopping GLP-1s raises complicated questions for pregnancy
Stopping GLP-1s raises complicated questions for pregnancyThe Explainer Stopping the medication could be risky during pregnancy, but there is more to the story to be uncovered
-
 Choline: the ‘under-appreciated’ nutrient
Choline: the ‘under-appreciated’ nutrientThe Explainer Studies link choline levels to accelerated ageing, anxiety, memory function and more
-
 Tips for surviving loneliness during the holiday season — with or without people
Tips for surviving loneliness during the holiday season — with or without peoplethe week recommends Solitude is different from loneliness
-
 More women are using more testosterone despite limited research
More women are using more testosterone despite limited researchThe explainer There is no FDA-approved testosterone product for women
