What the fall of Margaret Thatcher can teach Boris Johnson
The 1990 sacking of Iron Lady offers lessons for embattled current Tory leader

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Politics experts Paul Whiteley of University of Essex and Harold D. Clarke of University of Texas at Dallas on the implications of the polling parallels between the two prime ministers
It has been a bad few weeks for Boris Johnson and the Conservative government. It began with allegations that Christmas parties had been held in Downing Street during the lockdown of 2020 and has escalated into open conflict between the prime minister and his backbenchers.
A series of votes on new Covid-19 regulations saw around 100 Conservative MPs rebel against the government line in what was a major blow to the prime minister’s authority.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Days later, the Conservatives lost the North Shropshire constituency in a by-election triggered by the resignation of Owen Patterson MP, who was caught up in a lobbying scandal. The Liberal Democrats overturned a Conservative majority of nearly 23,000 to take the seat. Prominent backbencher Roger Gale described the result as a referendum on Johnson’s performance and warned, “one more strike and he’s out”.
But have enough Conservative backbenchers reached the conclusion that Johnson should be removed as party leader? There is a historical precedent which throws light on the present situation. This was when Margaret Thatcher was sacked as leader of her party – and consequently lost her job as prime minister – in 1990. She had a loyal following in the party and had won three elections in a row, but even that couldn’t save her when polling showed that the Conservatives were heading for a serious defeat under her leadership.
A key factor in her downfall was her decision to introduce the poll tax, which replaced the old system for local government finance. The tax meant that everyone paid the same regardless of their income, which prompted a serious backlash and widespread protests. Many people refused to pay and a few serious riots broke out. It precipitated a rapid drop in Conservative support in the polls.
When you look at the trends in voting intentions in the polls from Thatcher’s third successful election contest in 1987 up to the point that she resigned as prime minister in November 1990, you can see that Conservative support took a nosedive from the middle of 1989. By April 1990, Labour led the Conservatives by 23% in terms of voting intentions.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
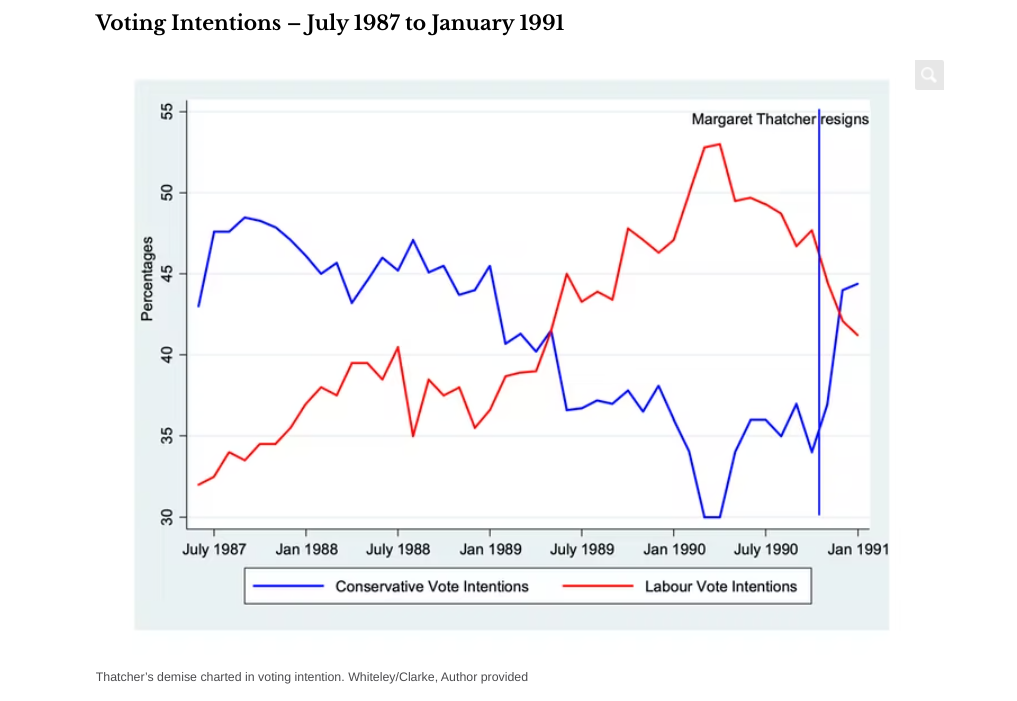
Backbench Conservative MPs grew increasingly alarmed for their prospects in a future election. Michael Heseltine was thereby encouraged to challenge her leadership and her failure to win in the first round of voting meant that she had to resign. She was subsequently succeeded by John Major, a change which rapidly shifted the party’s standing in the polls. He went on to win the general election of 1992.
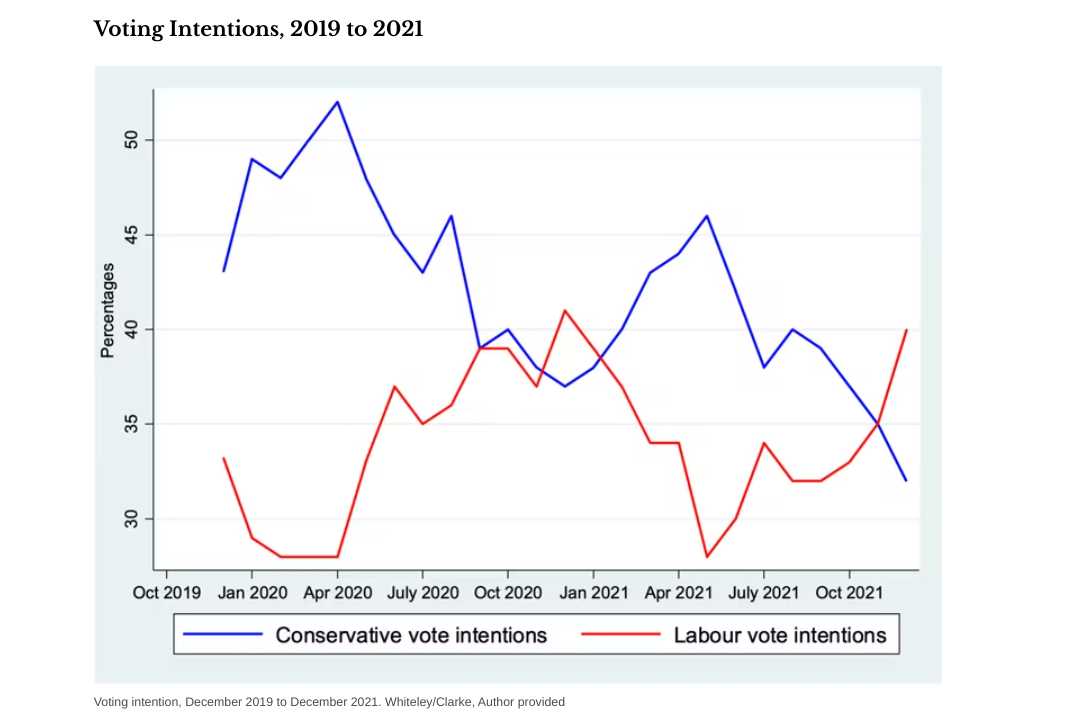
Fast forward 30 years and you can see Johnson’s own shifting fortunes. After winning the 2019 election, he experienced a brief honeymoon, but then his party started to lose support after Keir Starmer became the new Labour leader in April 2020. The new Labour leader also had a honeymoon, although it must be said that it did not produce a decisive lead over the Conservatives for a long time, and then only fairly briefly.
The main problem for Johnson was the government’s floundering response to the emerging pandemic. The early messaging was confusing and accompanied by numerous policy U-turns and a generally slow reaction to the crisis. There was also a scramble to acquire the protective equipment for the NHS to deal with the upsurge in hospital admissions. This has subsequently returned to haunt the government as ministers are questioned over pandemic-related contracts, such as for healthcare supplies, some of which appear to have been awarded to personal contacts.
But by early 2021 the successful rollout of Covid vaccines was serving to restore public confidence. The result was a surge in support for the Conservatives in the early part of 2021. But the recent series of scandals, particularly over accusations that government staff were holding Christmas parties when the rest of Britain was locked down, have put Labour in the lead again. A YouGov poll published on 10 December put Labour on 40% in voting intentions, with the Conservatives trailing on 32%.
That said, if Thatcher’s experience is anything to go by, at present the Conservatives are not going to sack Johnson. It took 18 months of seriously deteriorating polling for a revolt over Thatcher’s leadership to finally succeed – and she almost survived the leadership challenge. The present hope among Conservative backbenchers will be that the party can recover next year.
The loss of North Shropshire is reminiscent of the Ribble Valley by-election in rural Lancashire which took place in March 1991 after Margaret Thatcher had left office. The Liberal Democrats captured this traditional Conservative seat with a 25% swing, but this did not prevent Major winning the general election the following year.
Given the volatility in the polls which has grown significantly since the 1990s, things could turn around rapidly. On the other hand, if the fallout for the economy from the Covid pandemic is more enduring than the government expects, and inflation returns to haunt the British economy next year at some point, Johnson’s sojourn in Downing Street could be shortened.
Paul Whiteley, Professor, Department of Government, University of Essex, and Harold D. Clarke, Ashbel Smith professor, School of Economic, Political and Policy Sciences, University of Texas at Dallas.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons licence. Read the original article.