Global coronavirus responses ‘have made other diseases worse’
From mental health to cancer, a medical history expert explains the hidden damage caused by Covid-19
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Agnes Arnold-Forster, research fellow in history of medicine and healthcare at the University of Bristol, on the unseen legacy of Covid-19.
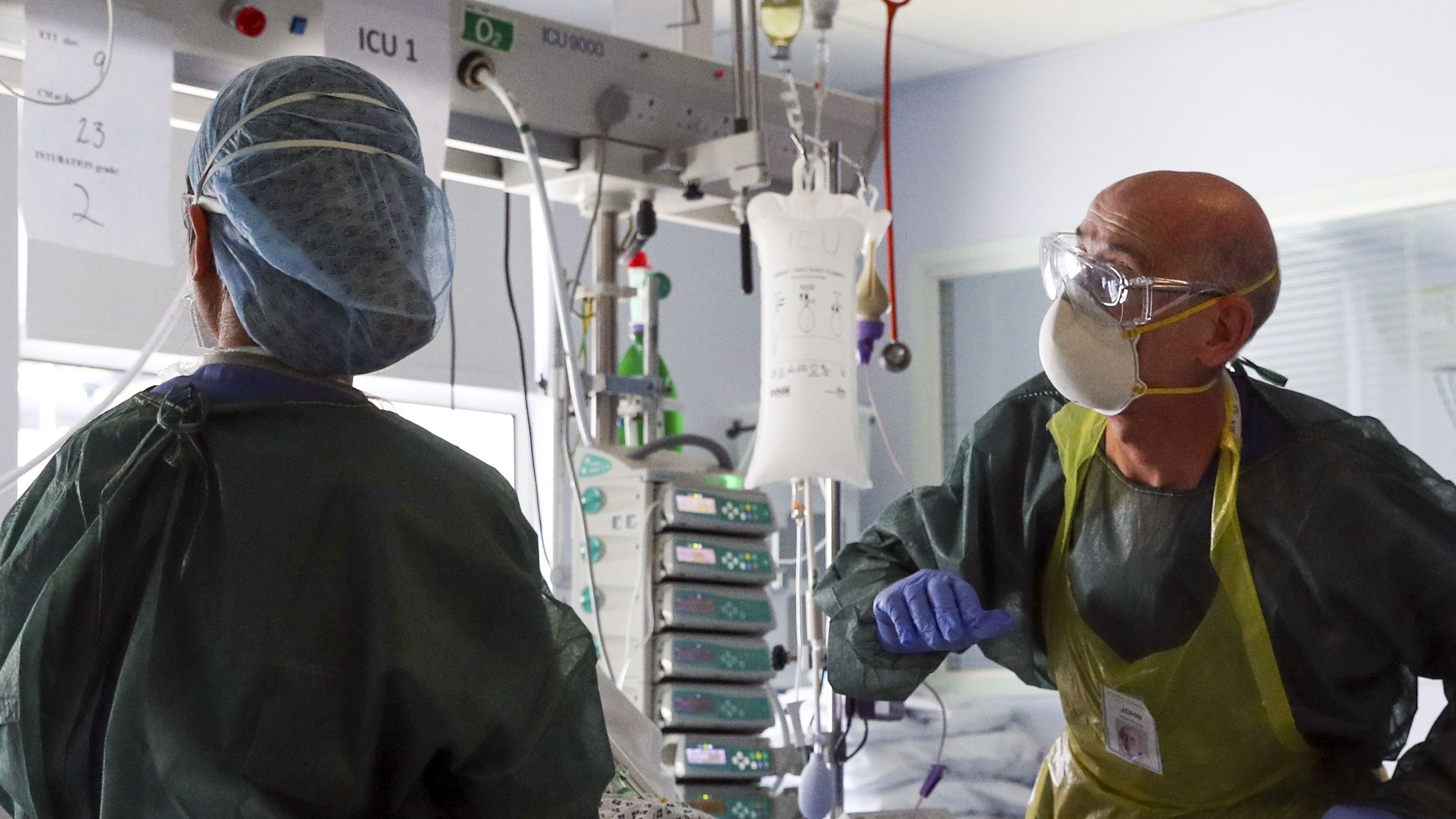
We are living through an age of untold suffering. Over 500,000 people have died from coronavirus in the US alone, over 120,000 in the UK, and over two million worldwide. With Covid-19 dominating the news cycle, you would be forgiven for forgetting that other diseases still exist. And yet we know full well that diseases don’t stop just because one is hogging all the limelight.
There have been plenty of reports on the troubling cost of the pandemic and associated lockdowns or shelter-in-place orders on people’s mental health. For example, it has had a profound effect on those living with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Studies from Europe show that between a third and half of those suffering from OCD had their symptoms worsen during the pandemic.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Young adults seem to have been particularly affected by the emotional burdens of isolation and insecurity. In a recent survey, conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in the US, 63% of 18-to-24-year-olds reported symptoms of anxiety or depression, with 25% reporting increased substance use to deal with stress, and 25% saying they’d seriously considered suicide.
Crucially, these issues won’t abate as soon as the pandemic is over. Even when the crisis recedes, Dr Shekar Saxena of the Harvard School of Public Health suggests that 10% of these young people will have to live with the long-lasting effects of the mental illnesses they are currently enduring.
The damage done by the pandemic to mental health has already attracted well-deserved attention. It has highlighted the importance of looking beyond coronavirus deaths to assess the success of global pandemic responses. Cancer tells a similar, and equally distressing, story.
Cancer care in the pandemic
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Throughout 2020, hospitals across the UK, US and Europe cancelled or postponed urgent cancer operations because they could not cope with the rising number of desperately ill coronavirus patients. Determining cancer prognosis is complex, but early evidence suggests that even a four-week delay in treatment can raise the risk of death by up to 10%.
The danger is not just physical, but psychological too. Despite these distressing figures of cancellations and waiting times, we don’t yet know much about the emotional toll these delays will have on people living with cancer today. Stories are, however, starting to emerge. One man, diagnosed with stage four bowel cancer in June 2020, had his December surgery postponed, and then “cancelled indefinitely”.
Even in the 19th century, doctors and patients alike were acutely aware of the importance of timely treatment.
As I argue in my book, The Cancer Problem, the “do not delay” principle in cancer treatment has its origins in the early 1800s. Surgeons implored cancer sufferers to seek their advice as soon as they had identified any unexpected lumps or bumps. And in their writings, patients expressed extreme distress at waiting for a diagnosis or cure.
Doctors lamented the patients who, “because of their praiseworthy modesty”, consulted too late for effective treatment. Medical textbooks designed to be read by patients told their readers that “were proper means used in due time, a cancer might often be prevented; but after the disorder has arrived at a certain height it generally sets all medicine at defiance”.
Looking at this longer history of cancer reminds us of the emotional and physical costs of any delays. After all, even if these waits have only minimal effects on patients’ survival or long-term health, we must also think about the psychological trauma of living in limbo.
Particularly when that limbo is associated with cancer, a disease that has long carried with it a sense of profound anxiety, so much so that in the 19th century it was often termed “the dread disease”. It is often understood as an alien invader, now very much outstaying its welcome.
As the Covid-19 crisis slowly abates, we must not just look back with regret at the number of people killed by the virus or celebrate the success of vaccines. We must instead assess the pandemic’s impact in the round and consider the physical as well as emotional costs of a disease that turned our world upside down.
When the next pandemic comes, we must be prepared to not only treat the victims of epidemic disease but to continue to provide the fundamental healthcare services we need to stay both healthy and happy.
Agnes Arnold-Forster, research fellow in history of medicine and healthcare at the University of Bristol.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons licence. Read the original article.
-
 Political cartoons for February 21
Political cartoons for February 21Cartoons Saturday’s political cartoons include consequences, secrets, and more
-
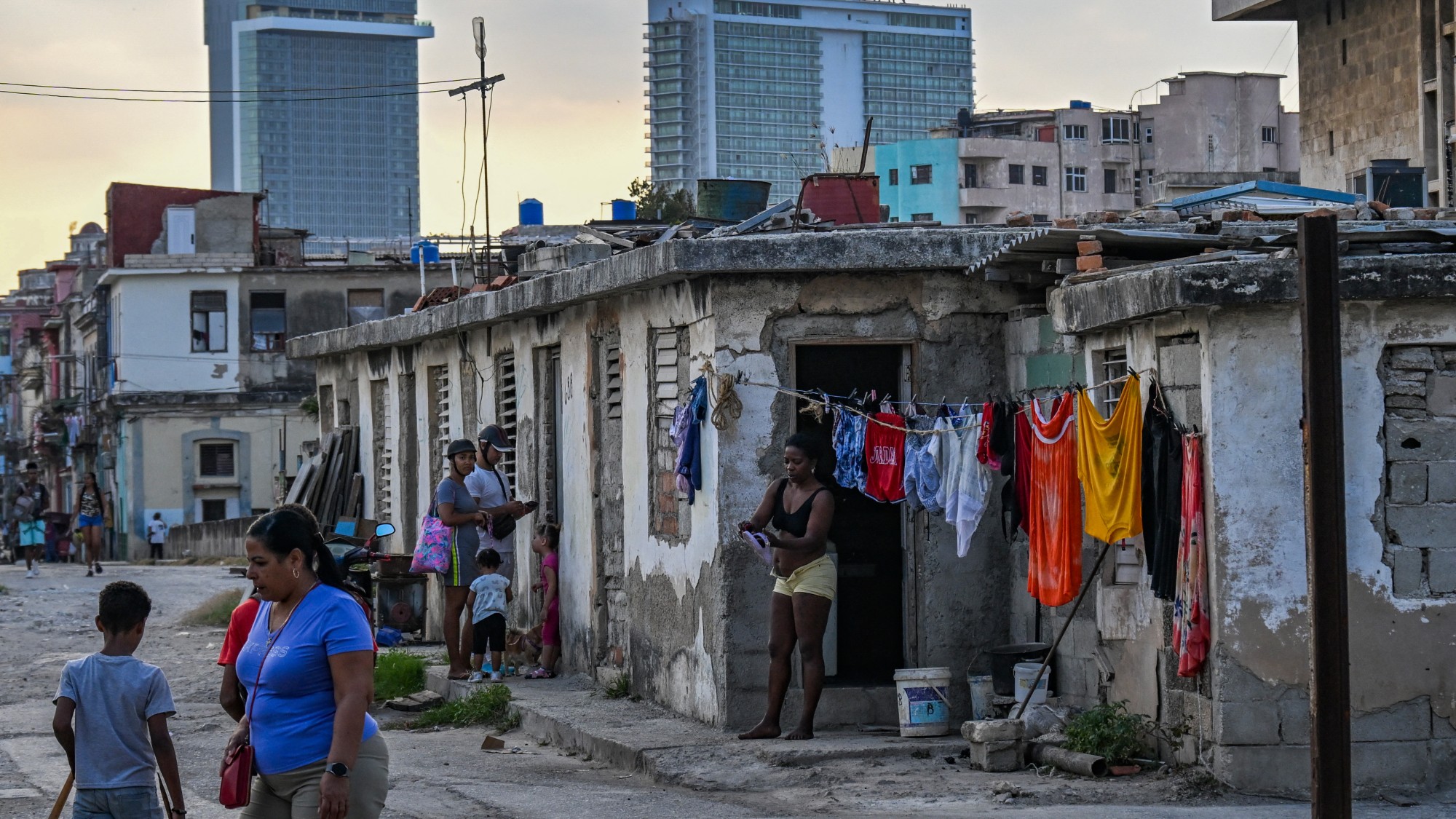 Crisis in Cuba: a ‘golden opportunity’ for Washington?
Crisis in Cuba: a ‘golden opportunity’ for Washington?Talking Point The Trump administration is applying the pressure, and with Latin America swinging to the right, Havana is becoming more ‘politically isolated’
-
 5 thoroughly redacted cartoons about Pam Bondi protecting predators
5 thoroughly redacted cartoons about Pam Bondi protecting predatorsCartoons Artists take on the real victim, types of protection, and more
-
 ‘Longevity fixation syndrome’: the allure of eternal youth
‘Longevity fixation syndrome’: the allure of eternal youthIn The Spotlight Obsession with beating biological clock identified as damaging new addiction
-
 A Nipah virus outbreak in India has brought back Covid-era surveillance
A Nipah virus outbreak in India has brought back Covid-era surveillanceUnder the radar The disease can spread through animals and humans
-
 The truth about vitamin supplements
The truth about vitamin supplementsThe Explainer UK industry worth £559 million but scientific evidence of health benefits is ‘complicated’
-
 RFK Jr. sets his sights on linking antidepressants to mass violence
RFK Jr. sets his sights on linking antidepressants to mass violenceThe Explainer The health secretary’s crusade to Make America Healthy Again has vital mental health medications on the agenda
-
 Covid-19 mRNA vaccines could help fight cancer
Covid-19 mRNA vaccines could help fight cancerUnder the radar They boost the immune system
-
 The new Stratus Covid strain – and why it’s on the rise
The new Stratus Covid strain – and why it’s on the riseThe Explainer ‘No evidence’ new variant is more dangerous or that vaccines won’t work against it, say UK health experts
-
 RFK Jr. vaccine panel advises restricting MMRV shot
RFK Jr. vaccine panel advises restricting MMRV shotSpeed Read The committee voted to restrict access to a childhood vaccine against chickenpox
-
 The app tackling porn addiction
The app tackling porn addictionUnder the Radar Blending behavioural science with cutting-edge technology, Quittr is part of a growing abstinence movement among men focused on self-improvement