Is post-election violence inevitable, win or lose?
As Election Day draws near so does the prospect of a violent response, no matter the eventual outcome


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
There's an argument to be made that the defining moment of Donald Trump's presidency, if not the past decade of politics at large, was Jan. 6, 2021, when a violent mob of MAGA protesters stormed the U.S. Capitol building to disrupt Congress' certification of Joe Biden as the winner of the 2020 election. The images from that day — lawmakers cowering behind security forces with their guns drawn, a mock gallows erected outside the Capitol rotunda, a braying "QAnon Shaman" stalking the Senate chambers — have become an indelible reminder that America is just as susceptible to political violence as anywhere else. It is perhaps even more so, given Trump's penchant for actively stoking the flames of resentment and frustration across his already fervent base.
Now, as the 2024 presidential election kicks into high gear with just three months to go before polls close in November, the specter of violence once again looms large over an electorate still grappling with the legal and political fallout of Jan. 6. In a Reuters/Ipsos poll taken this spring, more than two-thirds of respondents — Democrats and Republicans alike — said they were "concerned that extremists will resort to violence if they are unhappy with the election outcome." A more recent Deseret News/HarrisX poll saw three-fourths of the country "concerned about more political violence occurring before Election Day."
It's clear that fears of political violence, to say nothing of its actual likelihood, have a hold on the national psyche. Whether those fears will be realized one way or another remains to be seen.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
What did the commentators say?
"Almost no one considered the U.S. a serious candidate for post-election violence until recently," political scientist Barbara Walter said at The New Yorker. But in the past decade, it's become "impossible to ignore that America has all the characteristics of a country at risk" including the "exact type of political system — presidential, winner-takes-all — that is most vulnerable."
"Many of the same sources of instability and grievances that precipitated" the Jan. 6, attack, "along with other challenges to the outcome of the last election, remain present today," agreed The Counsel on Foreign Relations. Even though the most acute threats are largely confined to the right wing, the "possibility of far-left extremist violence cannot be dismissed." The threat — an "urgent national security imperative" — isn't simply domestic, either. The prospect of violence could "undermine the United States' international standing and foreign policy goals, in a year where at least eighty elections will take place around the world."
If Donald Trump wins in November, there are "two components" of potential violence to watch out for, said right-wing extremism expert David Neiwert at The American Prospect. "One is the immigrant front" as has been previously seen in border states, where militia members are "rounding people up and serving them up to the Border Patrol" but on a national scale. The other is "Three Percenters, militias, the Proud Boys, who have all been gearing up" to attack protesters gathering to demonstrate against a Trump electoral victory. Conversely, if Kamala Harris wins, the risk of violence comes when bad actors "show up at ballot-counting centers, as well as at any other sort of body involved in counting and certifying the votes."
If this seems familiar, there's a reason for that. Many of the people involved in previous efforts to delegitimize American elections are the same ones agitating for — or at least anticipating — future violence and think that either "a lot" or a "great deal" of political violence will occur after the 2024 election. A study last month from Johns Hopkins University found more than 30% of conservatives who believe Joe Biden did not legally win the 2020 election "think that either 'a lot' or 'a great deal' of political violence will occur after the 2024 election." Perhaps more alarmingly, 65% of that group also "believe that the United States is 'very likely' or 'somewhat likely' to lapse into a civil war."
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
What next?
While a Republican victory in November is "likely to yield a more peaceful transition," the long-term effect means "we'll probably see more violence under a Trump presidency," said Walter at The New Yorker.
With the possibility of violence looming no matter the electoral outcome, "people should be getting ready; they should be talking to local and statewide law enforcement," said Neiwert. Stakeholders in the upcoming election, "including government, the private sector, and civil society," should begin exploring "countermeasures at the motive, means, and opportunity levels" to help diffuse the threat of, and perhaps even mitigate any outbreaks of, political violence, agreed CFR.
Rafi Schwartz has worked as a politics writer at The Week since 2022, where he covers elections, Congress and the White House. He was previously a contributing writer with Mic focusing largely on politics, a senior writer with Splinter News, a staff writer for Fusion's news lab, and the managing editor of Heeb Magazine, a Jewish life and culture publication. Rafi's work has appeared in Rolling Stone, GOOD and The Forward, among others.
-
 Bad Bunny’s Super Bowl: A win for unity
Bad Bunny’s Super Bowl: A win for unityFeature The global superstar's halftime show was a celebration for everyone to enjoy
-
 Book reviews: ‘Bonfire of the Murdochs’ and ‘The Typewriter and the Guillotine’
Book reviews: ‘Bonfire of the Murdochs’ and ‘The Typewriter and the Guillotine’Feature New insights into the Murdoch family’s turmoil and a renowned journalist’s time in pre-World War II Paris
-
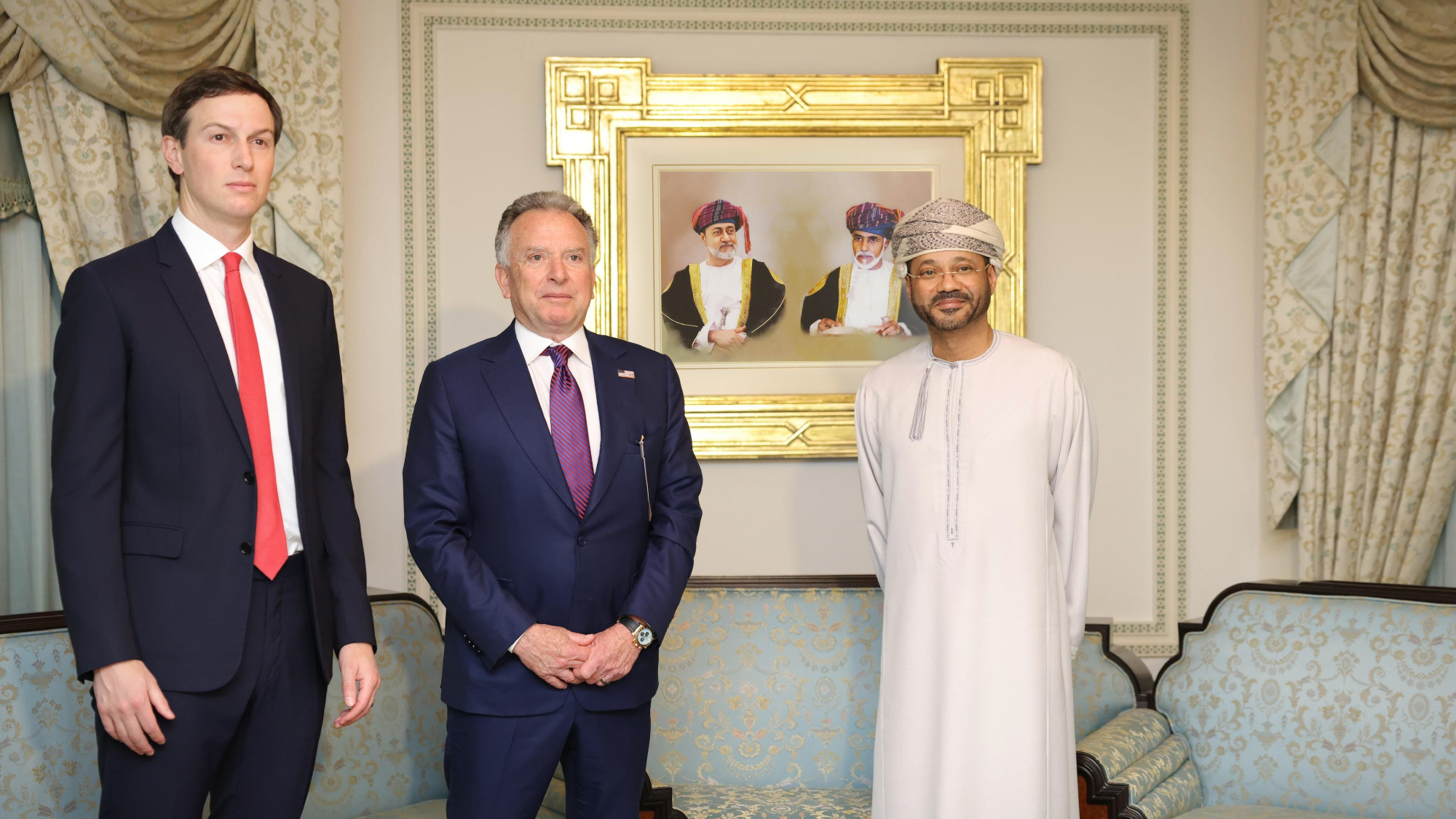 Witkoff and Kushner tackle Ukraine, Iran in Geneva
Witkoff and Kushner tackle Ukraine, Iran in GenevaSpeed Read Steve Witkoff and Jared Kushner held negotiations aimed at securing a nuclear deal with Iran and an end to Russia’s war in Ukraine
-
 Witkoff and Kushner tackle Ukraine, Iran in Geneva
Witkoff and Kushner tackle Ukraine, Iran in GenevaSpeed Read Steve Witkoff and Jared Kushner held negotiations aimed at securing a nuclear deal with Iran and an end to Russia’s war in Ukraine
-
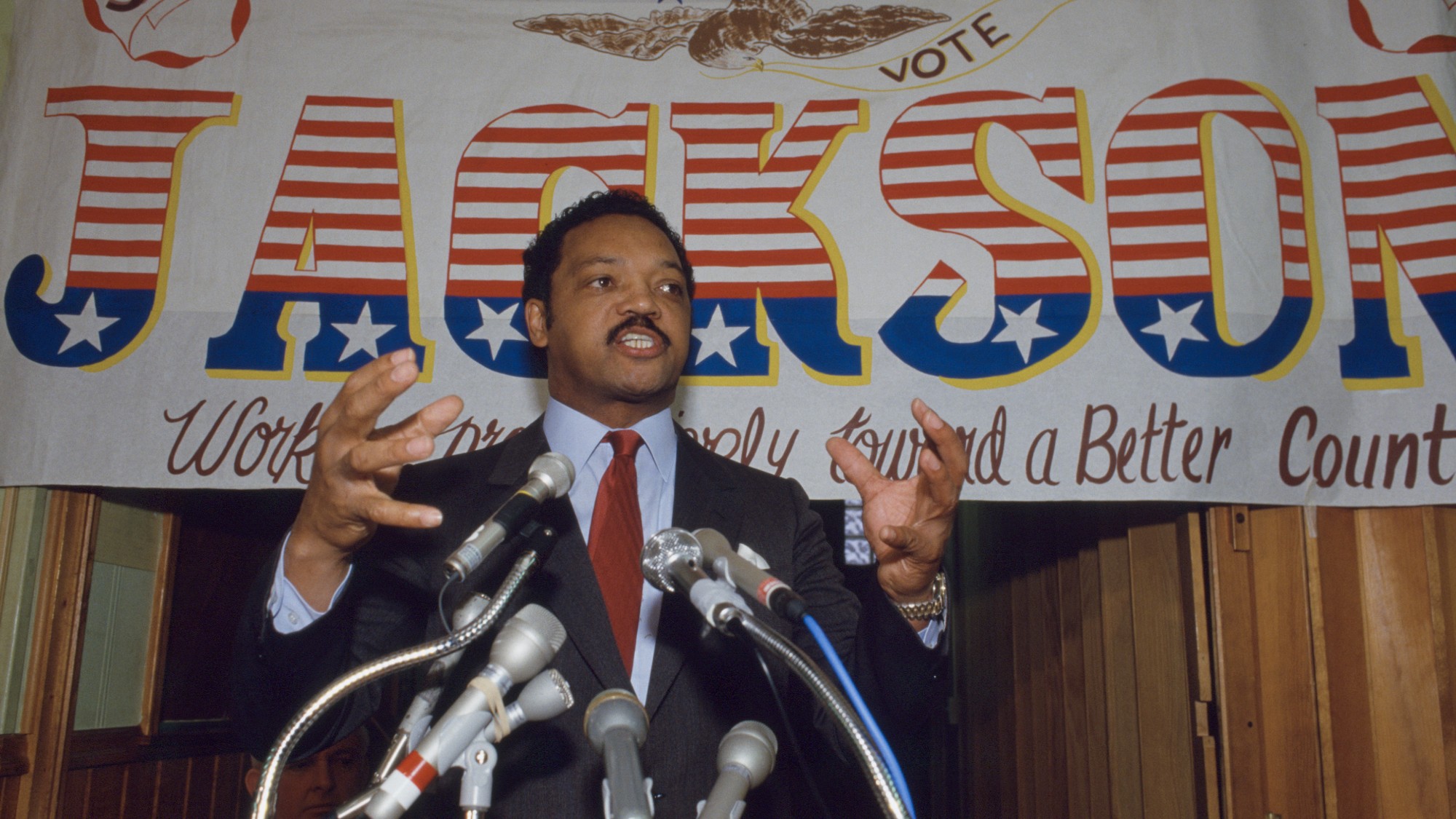 ‘The forces he united still shape the Democratic Party’
‘The forces he united still shape the Democratic Party’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
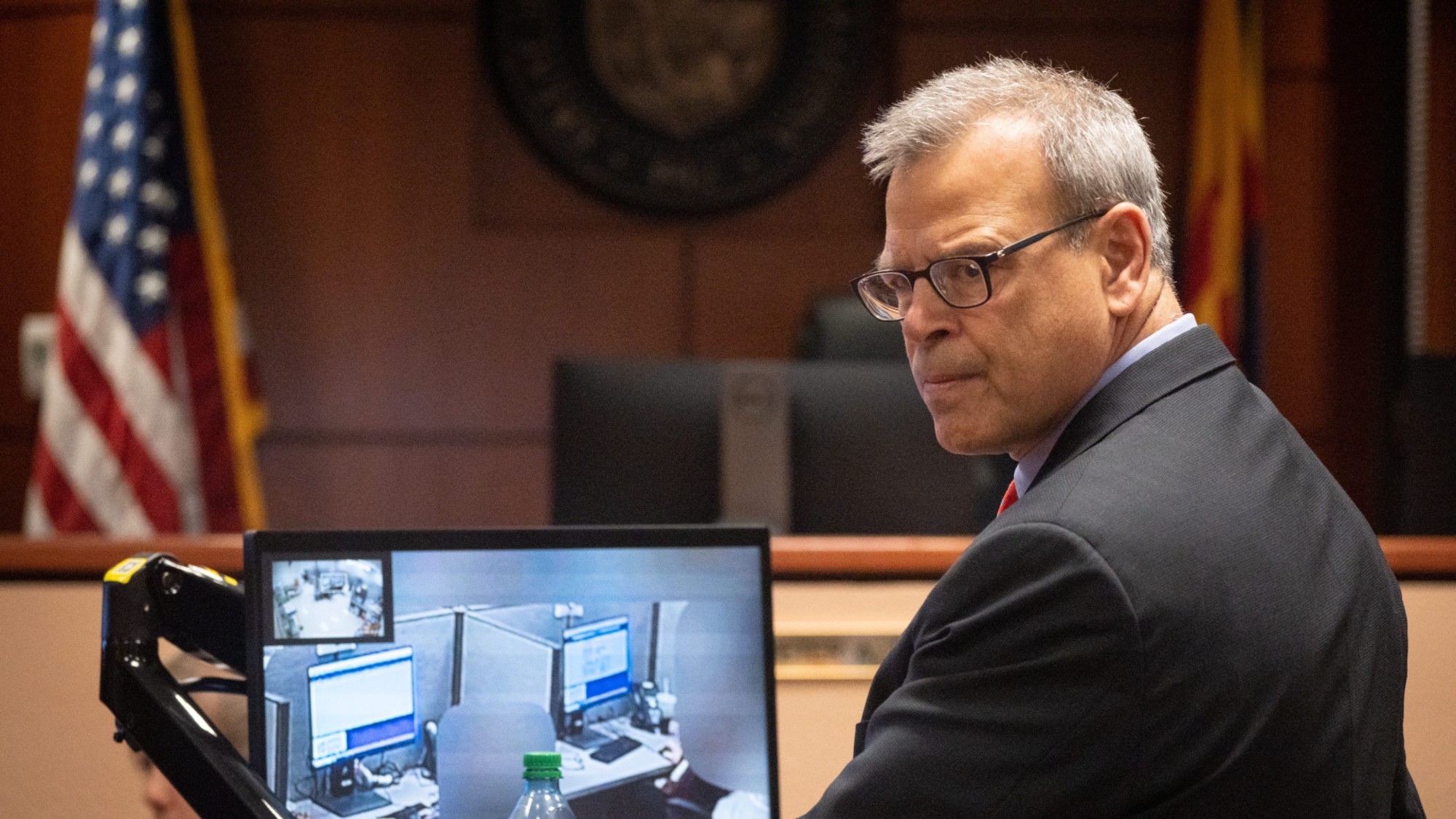 Kurt Olsen: Trump’s ‘Stop the Steal’ lawyer playing a major White House role
Kurt Olsen: Trump’s ‘Stop the Steal’ lawyer playing a major White House roleIn the Spotlight Olsen reportedly has access to significant US intelligence
-
 How are Democrats turning DOJ lemons into partisan lemonade?
How are Democrats turning DOJ lemons into partisan lemonade?TODAY’S BIG QUESTION As the Trump administration continues to try — and fail — at indicting its political enemies, Democratic lawmakers have begun seizing the moment for themselves
-
 Trump’s EPA kills legal basis for federal climate policy
Trump’s EPA kills legal basis for federal climate policySpeed Read The government’s authority to regulate several planet-warming pollutants has been repealed
-
 House votes to end Trump’s Canada tariffs
House votes to end Trump’s Canada tariffsSpeed Read Six Republicans joined with Democrats to repeal the president’s tariffs
-
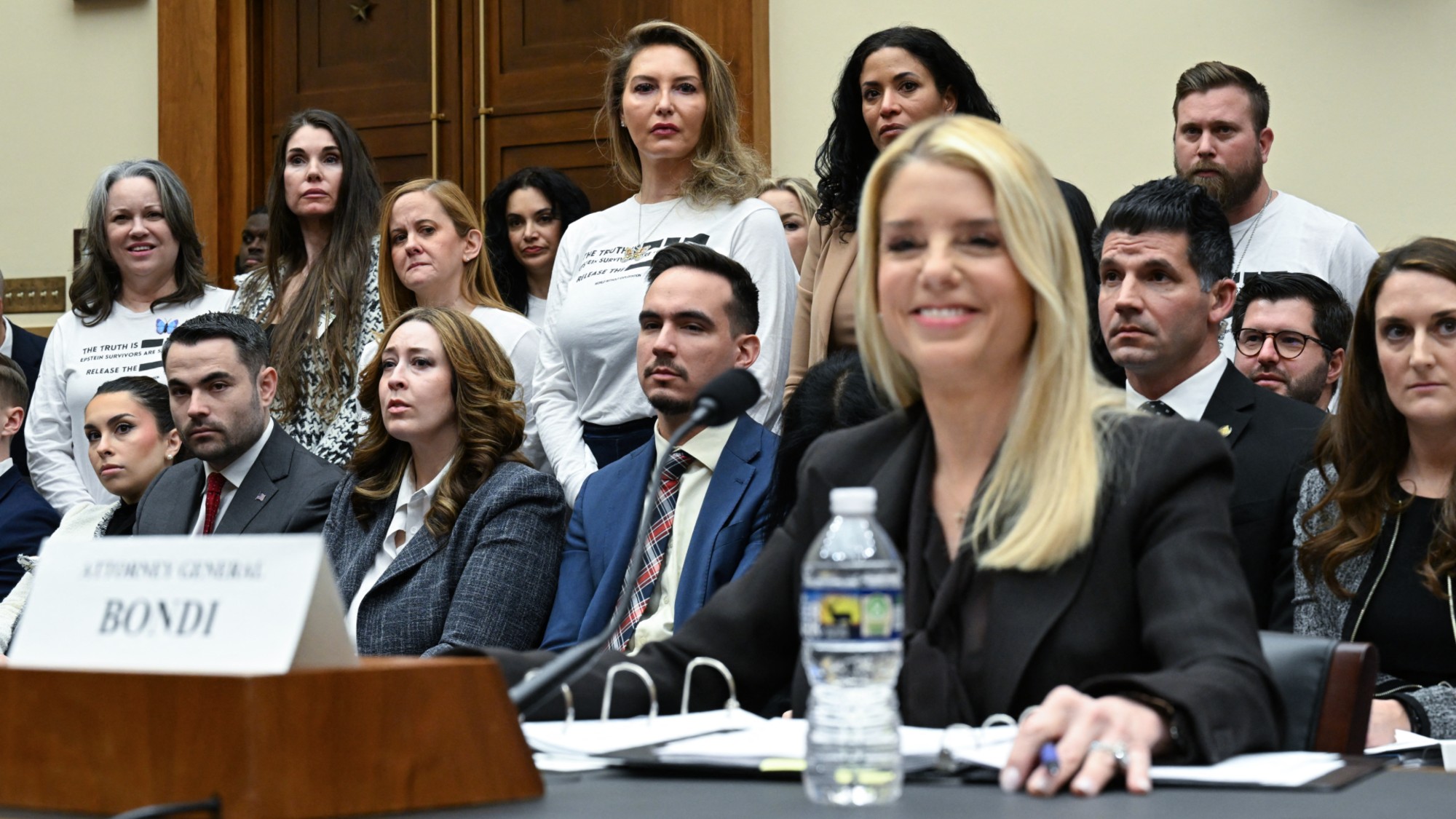 Bondi, Democrats clash over Epstein in hearing
Bondi, Democrats clash over Epstein in hearingSpeed Read Attorney General Pam Bondi ignored survivors of convicted sex offender Jeffrey Epstein and demanded that Democrats apologize to Trump
-
 How did ‘wine moms’ become the face of anti-ICE protests?
How did ‘wine moms’ become the face of anti-ICE protests?Today’s Big Question Women lead the resistance to Trump’s deportations
