We could be living in a black hole
And our universe may not be the only one

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Could our galaxy actually be inside a black hole? New research seems to suggest this possibility. NASA's James Webb Telescope discovered that the rotation of the galaxies goes against what scientists previously thought about the universe. The findings have revealed new insights about deep space.
Not so random
Data from NASA's James Webb Space Telescope Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey found that the majority of galaxies rotate in the same direction, according to a journal article in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. After analyzing 263 galaxies, two-thirds were found to rotate clockwise, while approximately one-third of them rotated counterclockwise.
The Milky Way rotates counterclockwise, putting it in the minority. These findings are surprising because if the universe is random, as previously thought, "there should be an approximately equal amount of galaxies rotating in both direction[s]," said Popular Mechanics.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
One explanation for this phenomenon is that the "universe was born rotating," Lior Shamir, a computer science professor at Kansas State University and the author of the study, said in a statement. This explanation "agrees with theories such as black hole cosmology, which postulates that the entire universe is the interior of a black hole." However, if the universe was born rotating, "it means that the existing theories about the cosmos are incomplete."
Black hole cosmology "suggests that the Milky Way and every other observable galaxy in our universe is contained within a black hole that formed in another, much larger, universe," said The Independent. The theory "challenges many fundamental models of the cosmos, including the idea that the Big Bang was the beginning of the universe." The study's data also opens the door to the idea that each black hole is a door to another universe and that we exist in a multiverse.
Black hole in the wall
The idea that the universe is in the interior of a black hole is decades old. The theory posits that the "'event horizon' (the boundary from within which nothing can escape a black hole, not even light) is also the horizon of the visible universe," said Space.com (a sister site of The Week). In turn, "each and every black hole in our universe could be the doorway to another 'baby universe,'" and "these universes would be unobservable to us because they are also behind an event horizon."
This would also explain why there seem to be more rotations in one direction. "It would be fascinating if our universe had a preferred axis," Nikodem Poplawski, a theoretical physicist at the University of New Haven, said to Space.com. "Such an axis could be naturally explained by the theory that our universe was born on the other side of the event horizon of a black hole existing in some parent universe."
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
The black hole theory is only one potential explanation for why most galaxies appear to rotate clockwise. The other is that the Milky Way's rotational velocity is affecting the measurements. "If that is indeed the case, we will need to recalibrate our distance measurements for the deep universe," said Shamir. The "recalibration of distance measurements can also explain several other unsolved questions in cosmology."
Devika Rao has worked as a staff writer at The Week since 2022, covering science, the environment, climate and business. She previously worked as a policy associate for a nonprofit organization advocating for environmental action from a business perspective.
-
 How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule works
How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule worksIn the Spotlight The law is at the heart of the Colbert-CBS conflict
-
 What is the endgame in the DHS shutdown?
What is the endgame in the DHS shutdown?Today’s Big Question Democrats want to rein in ICE’s immigration crackdown
-
 ‘Poor time management isn’t just an inconvenience’
‘Poor time management isn’t just an inconvenience’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
 AI surgical tools might be injuring patients
AI surgical tools might be injuring patientsUnder the Radar More than 1,300 AI-assisted medical devices have FDA approval
-
 How roadkill is a surprising boon to scientific research
How roadkill is a surprising boon to scientific researchUnder the radar We can learn from animals without trapping and capturing them
-
 NASA’s lunar rocket is surrounded by safety concerns
NASA’s lunar rocket is surrounded by safety concernsThe Explainer The agency hopes to launch a new mission to the moon in the coming months
-
 Nasa’s new dark matter map
Nasa’s new dark matter mapUnder the Radar High-resolution images may help scientists understand the ‘gravitational scaffolding into which everything else falls and is built into galaxies’
-
 The world’s oldest rock art paints a picture of human migration
The world’s oldest rock art paints a picture of human migrationUnder the Radar The art is believed to be over 67,000 years old
-
 Moon dust has earthly elements thanks to a magnetic bridge
Moon dust has earthly elements thanks to a magnetic bridgeUnder the radar The substances could help supply a lunar base
-
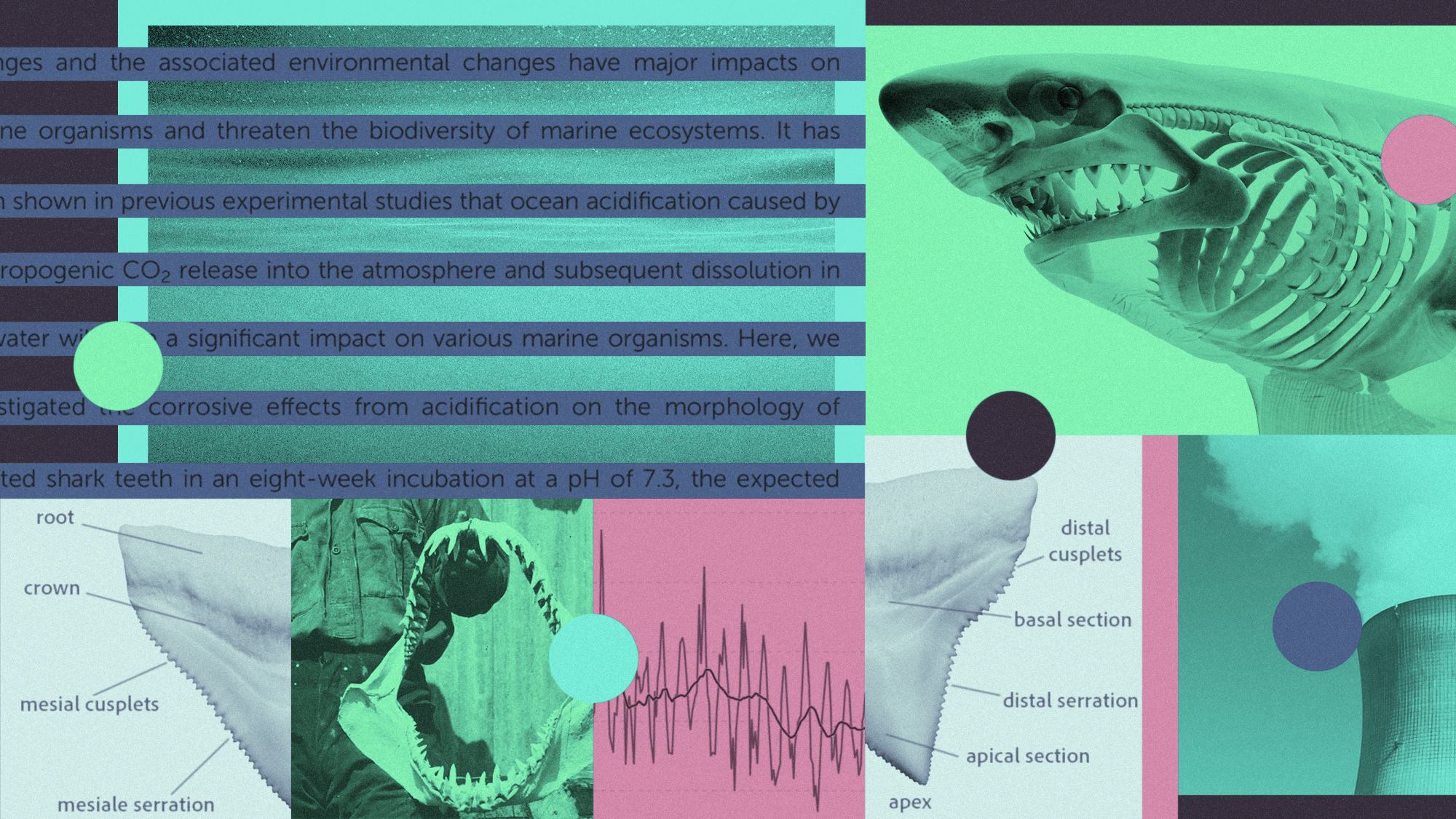 The ocean is getting more acidic — and harming sharks’ teeth
The ocean is getting more acidic — and harming sharks’ teethUnder the Radar ‘There is a corrosion effect on sharks’ teeth,’ the study’s author said
-
 How Mars influences Earth’s climate
How Mars influences Earth’s climateThe explainer A pull in the right direction
