Hubble Space Telescope captures 'spokes' moving across Saturn's rings

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has captured "spokes" moving across Saturn's rings, a phenomenon that indicates the start of the planet's autumnal equinox in its northern hemisphere, CNN reports. The equinox will occur on May 6, 2025.
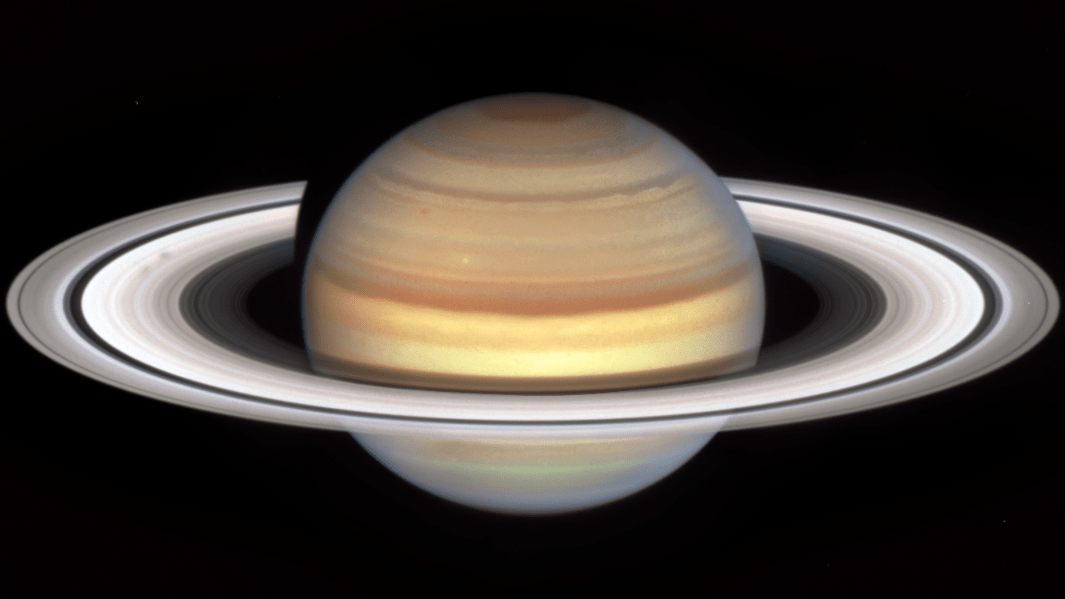
The reason for the spokes has yet to be discovered, however the "suspected culprit for the spokes is the planet's variable magnetic field," according to NASA. "Planetary magnetic fields interact with the solar wind, creating an electrically charged environment." The space agency compares the phenomenon to the northern lights on Earth.
NASA is hoping that Hubble's new data will either confirm or deny this theory based on the previous data from Voyager and Cassini, which was a designated Saturn probe. "Despite years of excellent observations by the Cassini mission, the precise beginning and duration of the spoke season is still unpredictable, rather like predicting the first storm during hurricane season," explained Amy Simon, a senior planetary scientist at NASA.
Article continues belowThe Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
The spokes were last seen in the 2000s. Like Earth, Saturn also experiences seasons, however since Saturn's orbit is much longer than Earth's, each season lasts around seven years. The spokes appear as the planet gets close to its equinox where the rings are tilted toward the sun. The spokes disappear near Saturn's summer or winter solstice.
NASA also explains that while the phenomenon could also occur on other ringed planets like Uranus and Neptune, it has only been observed on Saturn so far. "It's a fascinating magic trick of nature we only see on Saturn — for now at least," remarked Simon.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Devika Rao has worked as a staff writer at The Week since 2022, covering science, the environment, climate and business. She previously worked as a policy associate for a nonprofit organization advocating for environmental action from a business perspective.
