The whole planet is in a recession

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
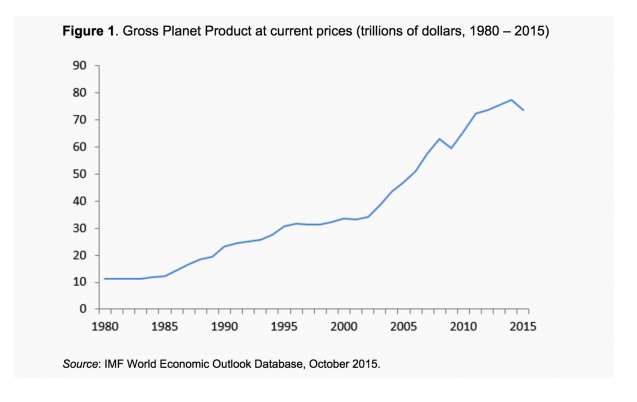
The technical definition of a recession is a time period when a country's gross domestic product (GDP) doesn't grow, and doesn't stay flat, but actually shrinks. The thing is, at this point, we can roughly measure GDP not just for individual countries, but for the whole planet as well. Call it gross planet product (GPP). And according to a new analysis of international data, GPP shrank by 4.9 percent in 2015:
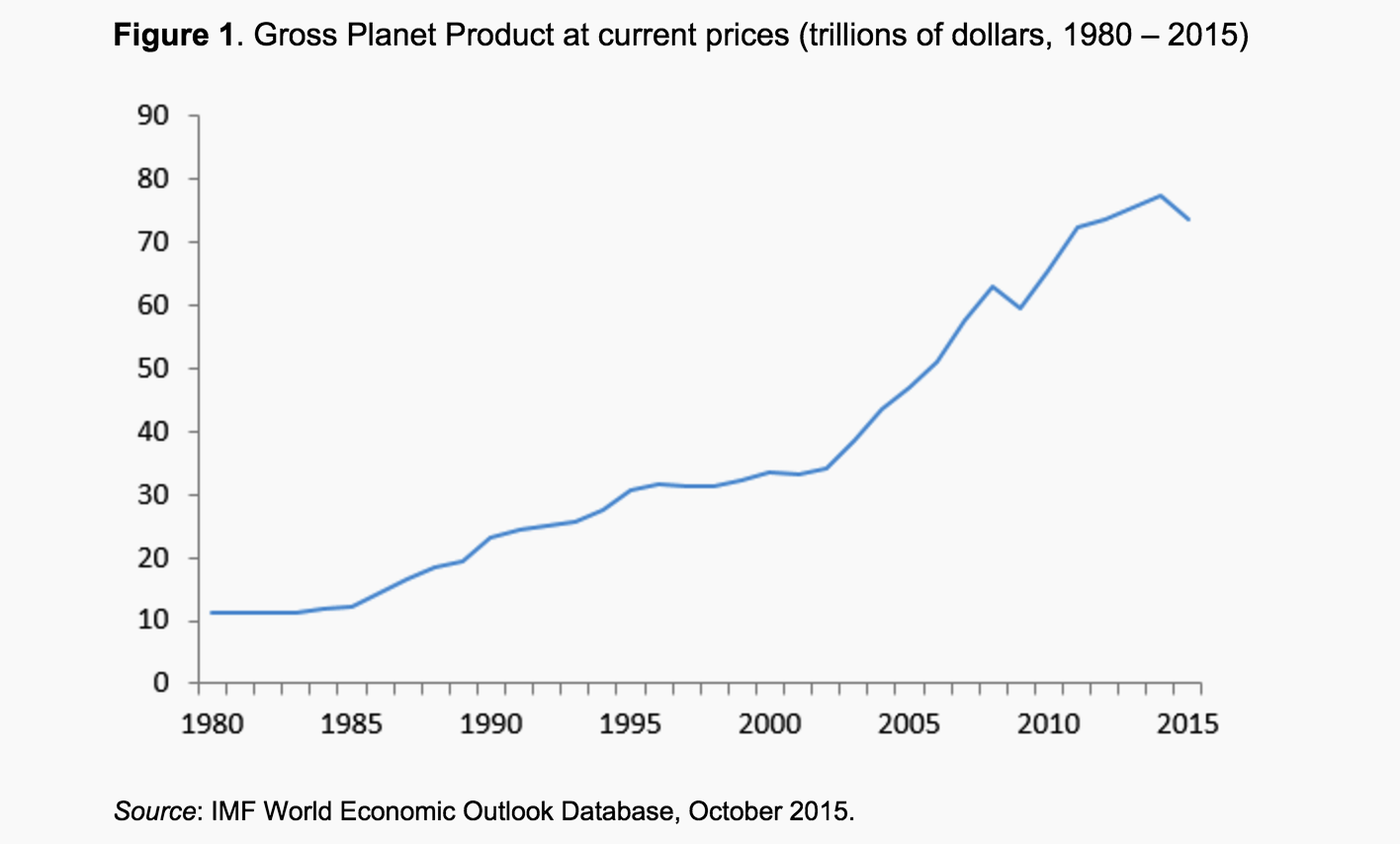
(Graph from We are shrinking! The neglected drop in Gross Planet Product by Peter A.G. van Bergeijk, VoxEU.org)
The last time we had a drop that big was with the Great Recession in 2008, when GPP contracted 5.3 percent. There have been a few other global recessions in the last 35 years, but other than a 2 percent drop in 1982, they've all been a fraction of a percent.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Arguably, a big part of the story here is that fact that the countries of the advanced world — America, Europe, and other developed nations — have been bouncing along at minimal growth, or dipping occasionally back into recession, ever since 2008. Poorer and less developed countries obviously can't take up much of the slack once the advanced world's economic engines slow down. The global downturn also adds to the possibility of a coming recession within America's borders, as well.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Jeff Spross was the economics and business correspondent at TheWeek.com. He was previously a reporter at ThinkProgress.
