Children 17 and under contract and spread COVID-19 like adults, large new study finds


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
A study of 85,000 people with COVID-19 in two southern Indian states and 575,000 people they came in contact with found that children 17 and under contract and transmit the new coronavirus at rates similar to the rest of the population. Children age 5 to 17 passed the virus on to 18 percent of close contacts their same age, a team of U.S. and Indian researchers reported Wednesday in the journal Science.
These findings are particularly important given "previous reports suggesting a minor role of children in the pandemic," Antonio Salas, a Spanish researcher who was not involved in the Indian study, told the Los Angeles Times. "National policies on how to proceed with children in schools and other social activities could change dramatically if the scientific evidence underpins the idea that children can infect as efficiently as adults, and even more, they could also behave as super-spreaders."
The two Indian states studied, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu, have robust contract tracing and other public health programs. The other major finding from the study involved super-spreaders. While 71 percent of people infected with COVID-19 did not appear to pass the virus on to anybody else, just 8 percent of infected people accounted for 60 percent of the new infections, said lead author Ramanan Laxminarayan of the Center for Disease Dynamics, Economics, and Policy in New Delhi.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
"Super-spreading events are the rule rather than the exception," Laxminarayan said. "It has lots of implications for modeling COVID, for how to keep places safe."
While children 17 and under were found to be more efficient disease transmitters than previously understood, they had the lowest death rate of any age cohort. Overall, deaths increased with age up to 65, then appeared to drop off. New York Times science reporter Apoorva Mandavilli said that might be because people who make it past India's life expectancy of 69 years told tend to be wealthy, with good heath care.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Peter has worked as a news and culture writer and editor at The Week since the site's launch in 2008. He covers politics, world affairs, religion and cultural currents. His journalism career began as a copy editor at a financial newswire and has included editorial positions at The New York Times Magazine, Facts on File, and Oregon State University.
-
 Elon Musk’s pivot from Mars to the moon
Elon Musk’s pivot from Mars to the moonIn the Spotlight SpaceX shifts focus with IPO approaching
-
 ‘Hong Kong is stable because it has been muzzled’
‘Hong Kong is stable because it has been muzzled’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
 Magazine solutions - February 20, 2026
Magazine solutions - February 20, 2026Puzzle and Quizzes Magazine solutions - February 20, 2026
-
 Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinations
Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinationsSpeed Read In a widely condemned move, the CDC will now recommend that children get vaccinated against 11 communicable diseases, not 17
-
 FDA OKs generic abortion pill, riling the right
FDA OKs generic abortion pill, riling the rightSpeed Read The drug in question is a generic version of mifepristone, used to carry out two-thirds of US abortions
-
 RFK Jr. vaccine panel advises restricting MMRV shot
RFK Jr. vaccine panel advises restricting MMRV shotSpeed Read The committee voted to restrict access to a childhood vaccine against chickenpox
-
 Texas declares end to measles outbreak
Texas declares end to measles outbreakSpeed Read The vaccine-preventable disease is still spreading in neighboring states, Mexico and Canada
-
 RFK Jr. shuts down mRNA vaccine funding at agency
RFK Jr. shuts down mRNA vaccine funding at agencySpeed Read The decision canceled or modified 22 projects, primarily for work on vaccines and therapeutics for respiratory viruses
-
 Measles cases surge to 33-year high
Measles cases surge to 33-year highSpeed Read The infection was declared eliminated from the US in 2000 but has seen a resurgence amid vaccine hesitancy
-
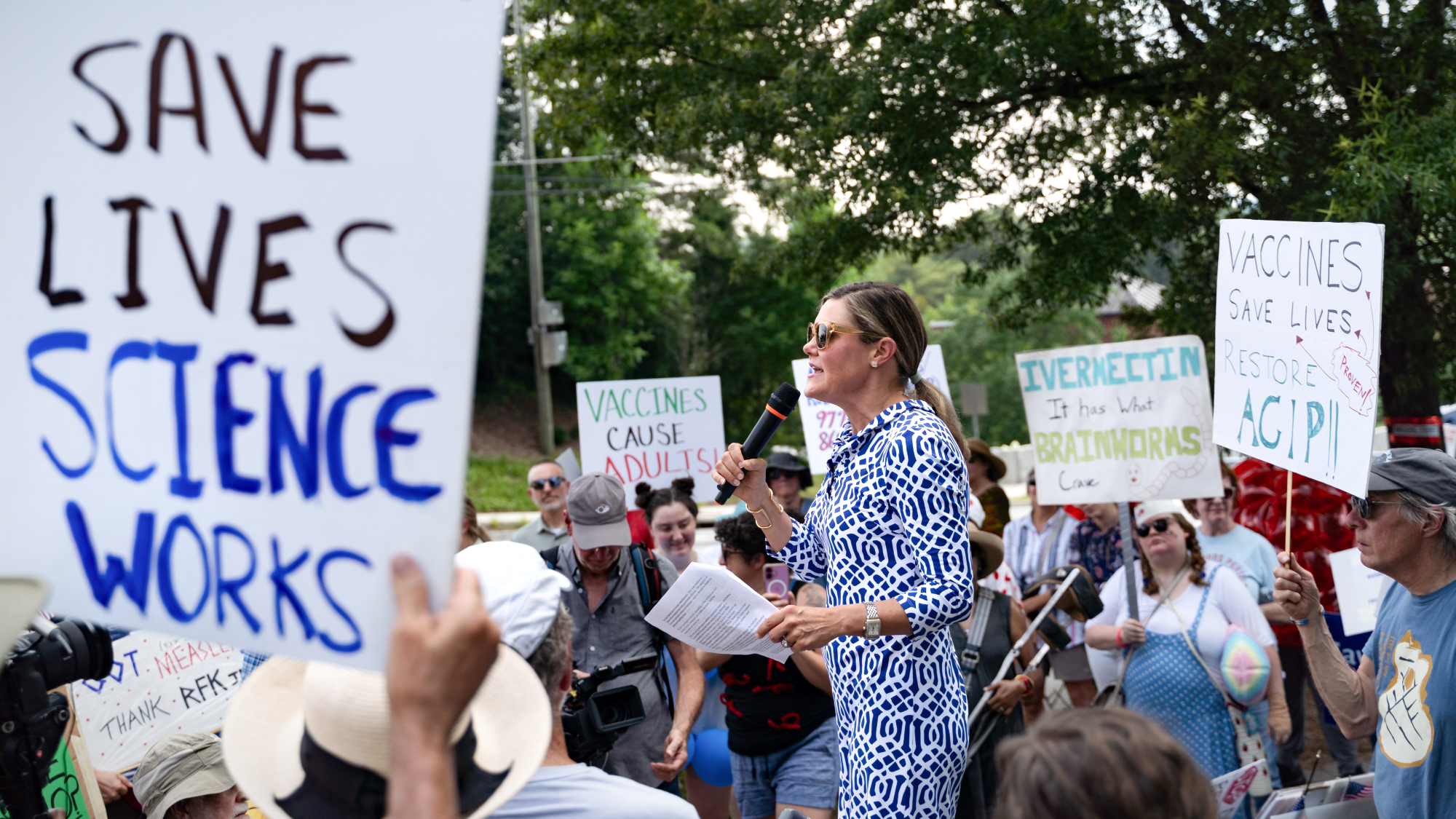 Kennedy's vaccine panel signals skepticism, change
Kennedy's vaccine panel signals skepticism, changeSpeed Read RFK Jr.'s new vaccine advisory board intends to make changes to the decades-old US immunization system
-
 Kennedy ousts entire CDC vaccine advisory panel
Kennedy ousts entire CDC vaccine advisory panelspeed read Health Secretary RFK Jr. is a longtime anti-vaccine activist who has criticized the panel of experts
