The murky world of AI training
Despite public interest in artificial intelligence models themselves, few consider how those models are trained

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
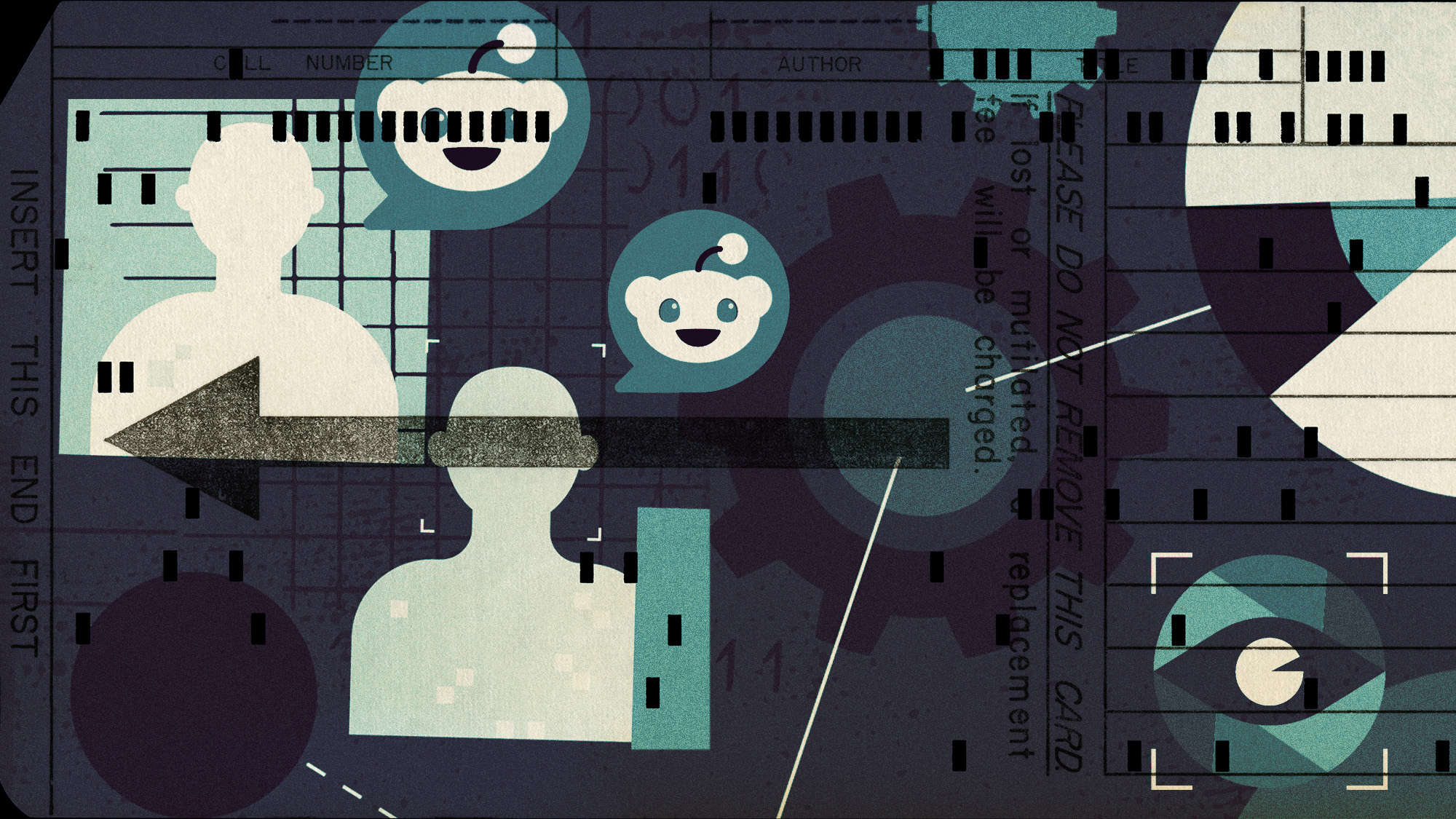
Reddit will reportedly allow an unnamed artificial intelligence company to train its models using the online message board's user-generated content.
California-based Reddit told prospective investors ahead of its initial public offering (IPO) that it had signed a contract with "an unnamed large AI company" worth about $60 million (£48 million) annually, according to Bloomberg. The agreement "could be a model for future contracts of a similar nature".
Apple has already "opened negotiations" with several major news and publishing organisations to develop its generative AI systems with their materials, according to The New York Times. The tech giant has "floated multiyear deals worth at least $50 million" (£40 million) to license the archives of news articles, anonymous sources told the paper.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
But the rapidly accelerating world of training AI has been marked by controversy, from arguments over copyright to fears of ethics violations and the replication of human bias.
How does AI learn?
Tech companies train AI models, the most well known being ChatGPT, on "massive amounts of data and text scraped from the internet", said Business Insider – including copyrighted material.
ChatGPT creator OpenAI designed it to find patterns in text databases. It ultimately analysed 300 billion words and 570 gigabytes of data, said BBC Science Focus. Other AI models like DALL-E, which generates images based on text prompts, were fed nearly 6 billion image-text pairs from the LAION-5B dataset.
What are the issues with training AI models?
OpenAI and Google have both been accused of training AI models on work without paying through licensing deals or getting permission from creators of that content. The New York Times is even suing OpenAI and Microsoft for copyright infringement for using its articles.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
OpenAI further fanned the flames of the copyright debate when it released Sora, a video generator, last week. Sora is able to create incredibly lifelike videos from simple text prompts, but OpenAI "has barely shared anything about its training data", said Mashable. Speculation immediately began that Sora was trained on copyrighted material.
Despite their vast data reserves, these models still require a human touch. In a process called "reinforcement learning", a human operator evaluates the accuracy and appropriateness of a model's output. "So click by click, a largely unregulated army of humans is transforming the raw data into AI feedstock," said The Washington Post.
Not only is it costly and time-consuming to employ people to babysit AI models, but the process is subjective: individuals have different standards for what constitutes accurate or appropriate.
Reinforcement learning has also led to the exploitation of workers, said the paper. In the Philippines, former employees have accused San Francisco start-up Scale AI of paying workers "extremely low rates" via an outsourced digital work platform called Remotasks, or withholding payments entirely. Human rights groups say it is "among a number of American AI companies that have not abided by basic labor standards for their workers abroad", said the Post.
AI companies have also inadvertently hired children and teenagers to perform these roles, reported Wired, because tasks are "often outsourced to gig workers, via online crowdsourcing platforms".
Ethics demands aside, the creators of AI models are concerned with a future supply issue: while the internet may contain massive amounts of data, it isn't unlimited.
The most advanced AI programs "have consumed most of the text and images available" and are running out of training data: their "most precious resource", said The Atlantic. This has "stymied the technology's growth, leading to iterative updates rather than massive paradigm shifts".
What's coming down the pipeline?
OpenAi, Google Deepmind, Microsoft and other big tech companies have recently "published research that uses an AI model to improve another AI model, or even itself", said The Atlantic. Tech executives have heralded this approach, known as synthetic data, as "the technology's future".
Training an AI model on data that a different AI model has produced is flawed, however. It could reinforce conclusions that the model drew from the original data, which could be incorrect or even biased.
As the AI industry continues its exponential growth, what happens next is unclear – but it is likely to be both "exciting and scary", said The New York Times.
-
 ‘Poor time management isn’t just an inconvenience’
‘Poor time management isn’t just an inconvenience’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
 Bad Bunny’s Super Bowl: A win for unity
Bad Bunny’s Super Bowl: A win for unityFeature The global superstar's halftime show was a celebration for everyone to enjoy
-
 Book reviews: ‘Bonfire of the Murdochs’ and ‘The Typewriter and the Guillotine’
Book reviews: ‘Bonfire of the Murdochs’ and ‘The Typewriter and the Guillotine’Feature New insights into the Murdoch family’s turmoil and a renowned journalist’s time in pre-World War II Paris
-
 Claude Code: Anthropic’s wildly popular AI coding app
Claude Code: Anthropic’s wildly popular AI coding appThe Explainer Engineers and noncoders alike are helping the app go viral
-
 Will regulators put a stop to Grok’s deepfake porn images of real people?
Will regulators put a stop to Grok’s deepfake porn images of real people?Today’s Big Question Users command AI chatbot to undress pictures of women and children
-
 Most data centers are being built in the wrong climate
Most data centers are being built in the wrong climateThe explainer Data centers require substantial water and energy. But certain locations are more strained than others, mainly due to rising temperatures.
-
 The dark side of how kids are using AI
The dark side of how kids are using AIUnder the Radar Chatbots have become places where children ‘talk about violence, explore romantic or sexual roleplay, and seek advice when no adult is watching’
-
 Why 2025 was a pivotal year for AI
Why 2025 was a pivotal year for AITalking Point The ‘hype’ and ‘hopes’ around artificial intelligence are ‘like nothing the world has seen before’
-
 Data centers could soon be orbiting in space
Data centers could soon be orbiting in spaceUnder the radar The AI revolution is going cosmic
-
 AI griefbots create a computerized afterlife
AI griefbots create a computerized afterlifeUnder the Radar Some say the machines help people mourn; others are skeptical
-
 The robot revolution
The robot revolutionFeature Advances in tech and AI are producing android machine workers. What will that mean for humans?