Why China and America are barrelling towards war
In the South China Sea, the People's Republic is playing with fire
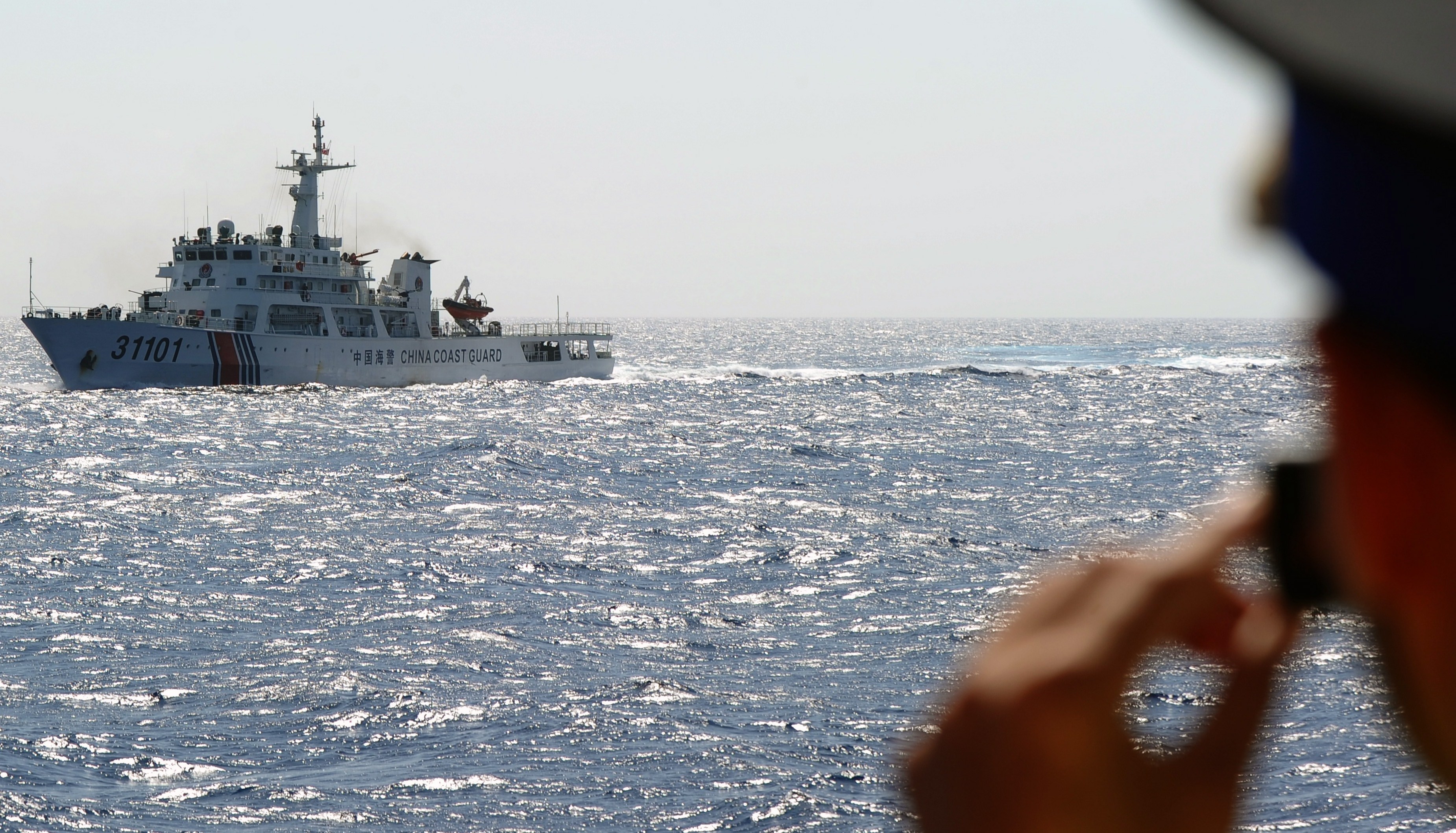

The People's Republic of China has stationed advanced, long-range surface-to-air missiles on an artificial island in the South China Sea, breaking its own promise to use the islands for peaceful purposes. The stationing of HQ-9 missiles on Woody Island is just the latest provocation in China's gradual takeover of the South China Sea.
The rest of the world — particularly China's neighbors and the United States — have few good options for reversing the takeover. China's neighbors in the South China Sea region are unable to agree on a common policy for opposing her, and the United States has to tread a tricky line between peace and war with the second largest economy in the world.
Over the past four years, an increasingly aggressive Beijing has sought to claim territory it has regarded as historically part of China. This includes up to 90 percent of the South China Sea, a body of water that Vietnam, Brunei, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Taiwan all claim part of.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
While many countries claim part of the South China Sea, none have claimed — and seized — as much as China. To support it's claim, China has taken several shoals and reefs and expanded them dramatically with sand dredged from the sea floor. Legally, China believes this transforms them from nothing more than navigational hazards to full sovereign territory, complete with a 12 mile territorial boundary and a 200 mile exclusive right to economic development.
China has claimed this island development is entirely peaceful, and undertaken to create tourist destinations, to protect the local environment, and to help in weather prediction.
Meanwhile, China's actions have demonstrated the exact opposite. Tiny, insignificant islands incapable of supporting tourism have seen airstrips and harbors enlarged for what may only be military purposes. The dredging has been an environmental catastrophe, and Chinese fishermen have been observed intentionally destroying coral reefs.
The deployment of HQ-9 anti-aircraft missiles, similar to the American Patriot missile, comes after a Royal Australian Air Force maritime patrol plane flew near China's artificial islands, and a Chinese communist party newspaper later opined it would be a "shame" if in the future an Australian plane "fell out of the sky".
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
China's strategy has been called "salami-slicing" — in order to take a salami, cut yourself a thin slice at a time, until you have the whole thing. The idea is to take just a small enough portion to make it not worthwhile for anyone to stop you. Eventually, you have the whole salami.
How can China's neighbors — and the United States — stop this territorial grab? There's a lot of potential solutions but no simple answer.
One course of action is simply taking China to court. The Philippines has sued China in international court, claiming the latter is violating its rights under the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea.
That sounds like a great solution that promises to peacefully resolve things — except that China has simply ignored the legal proceedings completely. It takes two sides to agree that there's a dispute to solve — China simply doesn't believe there's a dispute.
A second option is to physically challenge China's new territorial boundaries. These so-called Freedom of Navigation Operations (FONOPs) typically send air and naval forces to breach — or coming pointedly close to — the 12-mile limit the offending country imposes. The United States and Australia have conducted such operations in the South China Sea.
Though this tactic sounds confrontational, there's less to it than meets the eye. Airplanes visit the area for minutes at a time, and ships for hours or days at the most. Although China has been unhappy with the FONOPs, it knows planes and ships are only temporary visitors. Eventually they go home, and China is still there.
Yet another solution might be a diplomatic one. Roundly condemning China for this aggression at the United Nations and imposing economic sanctions would be a powerful signal. Unfortunately, there is no chance of this happening: China is a permanent member of the UN Security Council, and would obviously veto any resolution against it. Economic sanctions are also dead on arrival for another reason: China's neighbors are economically intertwined with Beijing, meaning that sanctions would harm their own economies.
There's one sure fire way to get China out of the South China Sea: sailing a fleet up to the islands, bombarding them with naval guns and missiles, and then landing marines to capture any survivors. This is the 21st Century, and one would hope that civilized nations are beyond using force to settle disputes. And yet as we examine the options that Vietnam, the Philippines, Taiwan, Brunei, Malaysia, and the United States all have, there is no sure-fire solution except that ancient one. Unless the diplomats can reach some sort of equitable agreement on who owns the South China Sea, we may see the rocks flying sooner than we think.
Kyle Mizokami is a freelance writer whose work has appeared in The Daily Beast, TheAtlantic.com, The Diplomat, and The National Interest. He lives in San Francisco.
-
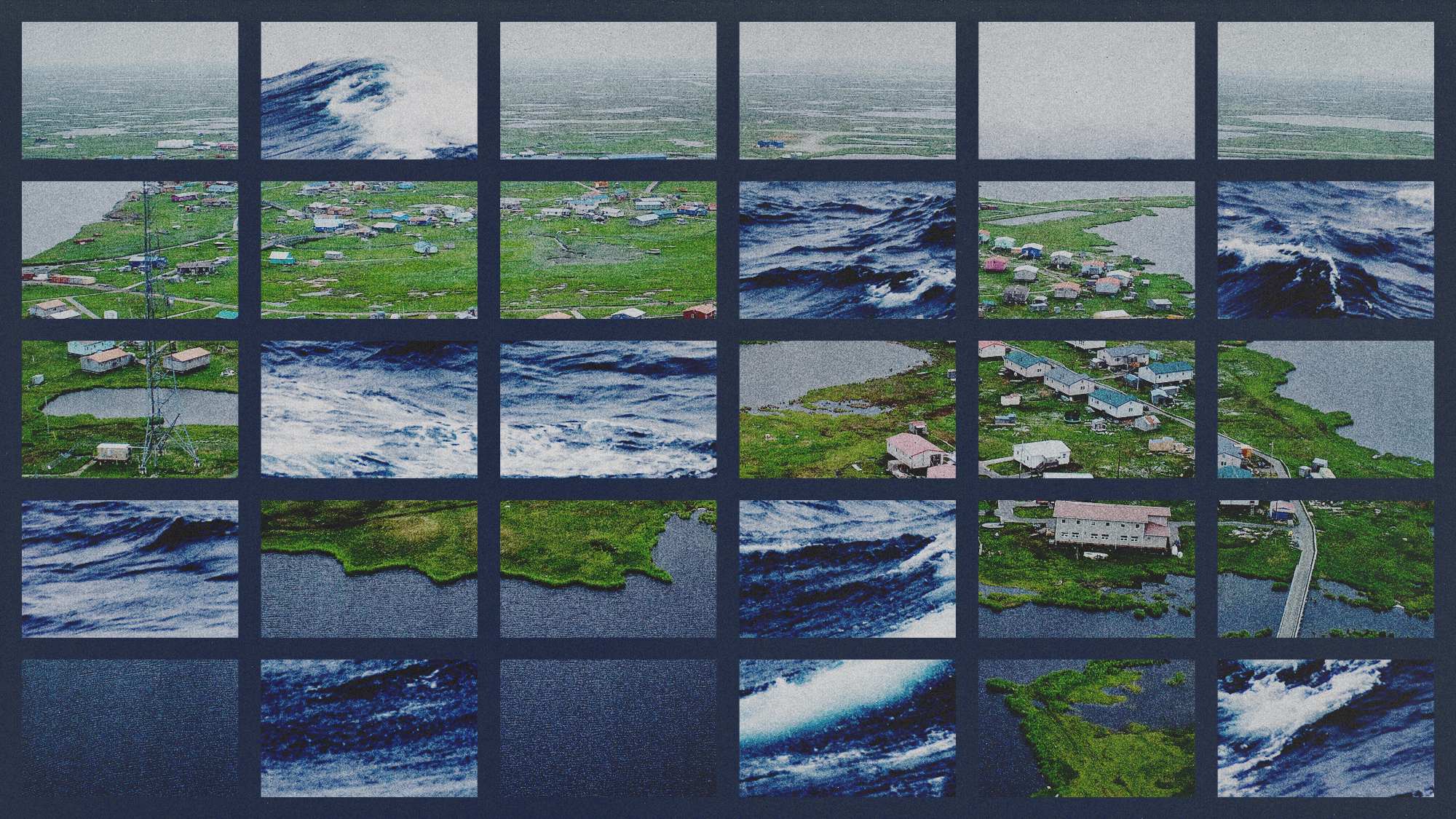 Western Alaska reels as storm aftermath prompts mass evacuations
Western Alaska reels as storm aftermath prompts mass evacuationsUNDER THE RADAR Alaskan lawmakers point to climate change as airlifts relocate hundreds from coastal communities devastated by the remnants of Typhoon Halong
-
 Crossword: October 17, 2025
Crossword: October 17, 2025The Week's daily crossword
-
 Codeword: October 17, 2025
Codeword: October 17, 2025The Week's daily codeword puzzle
-
 Sanae Takaichi: Japan’s Iron Lady set to be the country’s first woman prime minister
Sanae Takaichi: Japan’s Iron Lady set to be the country’s first woman prime ministerIn the Spotlight Takaichi is a member of Japan’s conservative, nationalist Liberal Democratic Party
-
 Russia is ‘helping China’ prepare for an invasion of Taiwan
Russia is ‘helping China’ prepare for an invasion of TaiwanIn the Spotlight Russia is reportedly allowing China access to military training
-
 Interpol arrests hundreds in Africa-wide sextortion crackdown
Interpol arrests hundreds in Africa-wide sextortion crackdownIN THE SPOTLIGHT A series of stings disrupts major cybercrime operations as law enforcement estimates millions in losses from schemes designed to prey on lonely users
-
 China is silently expanding its influence in American cities
China is silently expanding its influence in American citiesUnder the Radar New York City and San Francisco, among others, have reportedly been targeted
-
 How China uses 'dark fleets' to circumvent trade sanctions
How China uses 'dark fleets' to circumvent trade sanctionsThe Explainer The fleets are used to smuggle goods like oil and fish
-
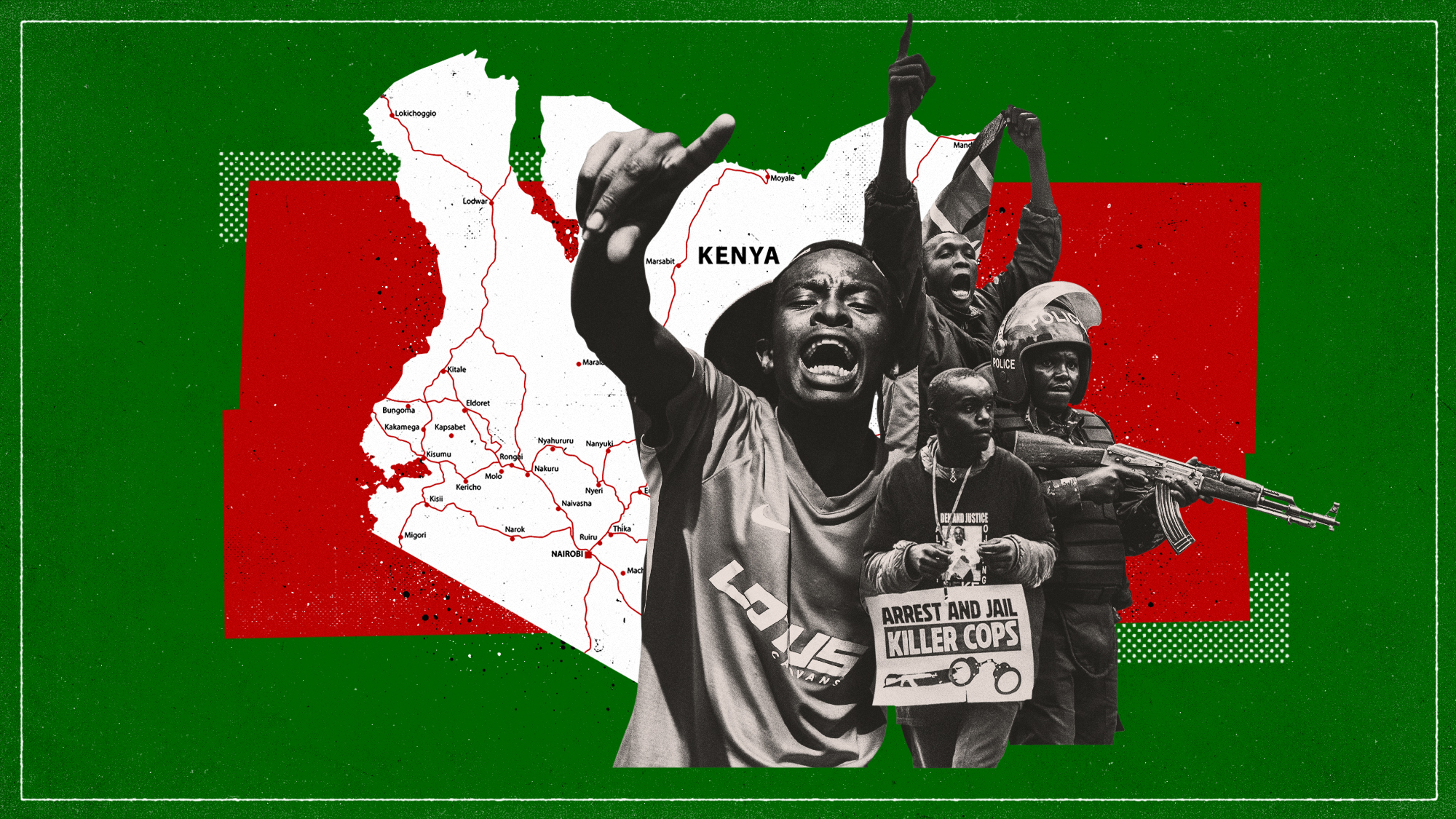 One year after mass protests, why are Kenyans taking to the streets again?
One year after mass protests, why are Kenyans taking to the streets again?today's big question More than 60 protesters died during demonstrations in 2024
-
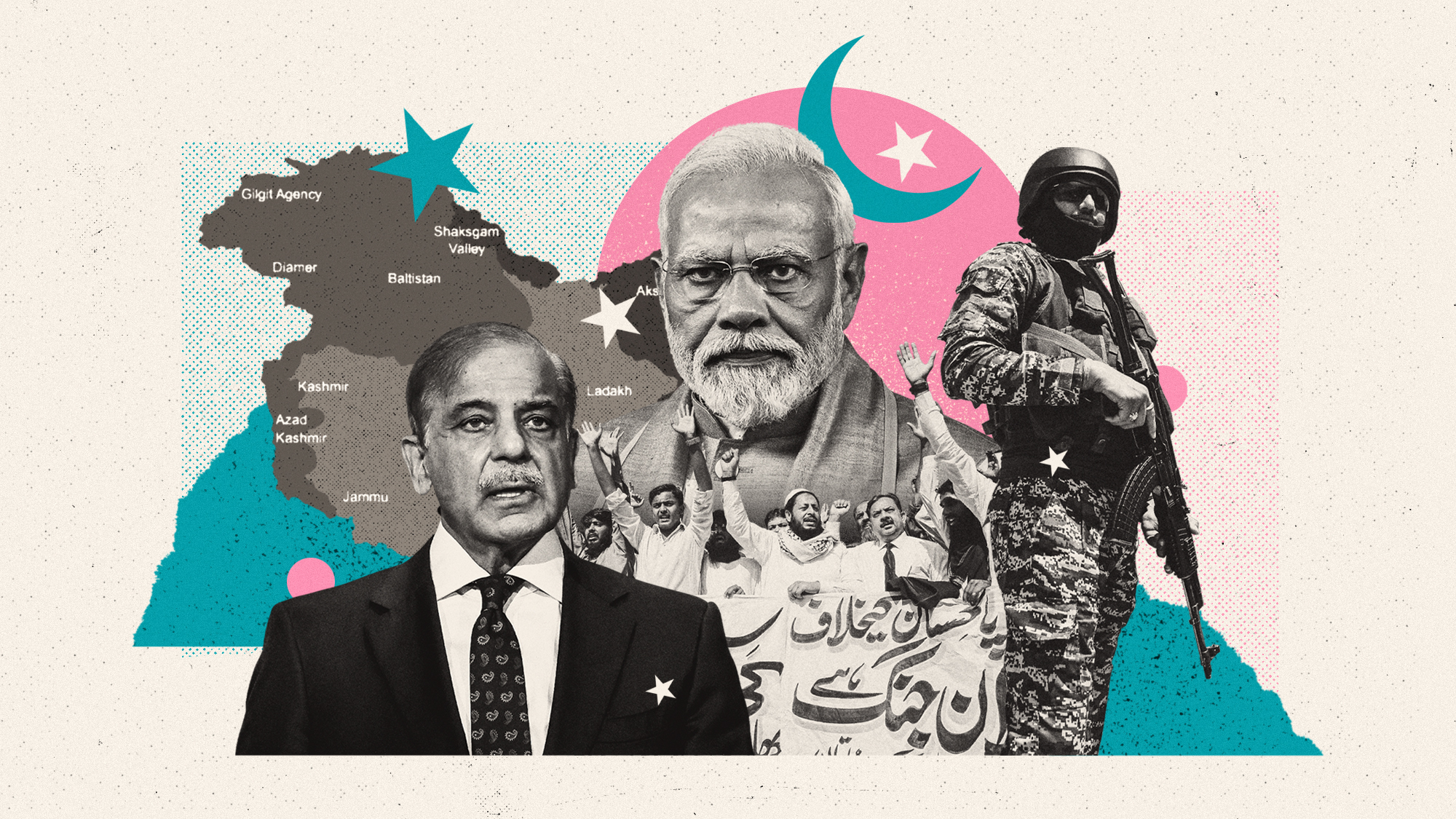 What happens if tensions between India and Pakistan boil over?
What happens if tensions between India and Pakistan boil over?TODAY'S BIG QUESTION As the two nuclear-armed neighbors rattle their sabers in the wake of a terrorist attack on the contested Kashmir region, experts worry that the worst might be yet to come
-
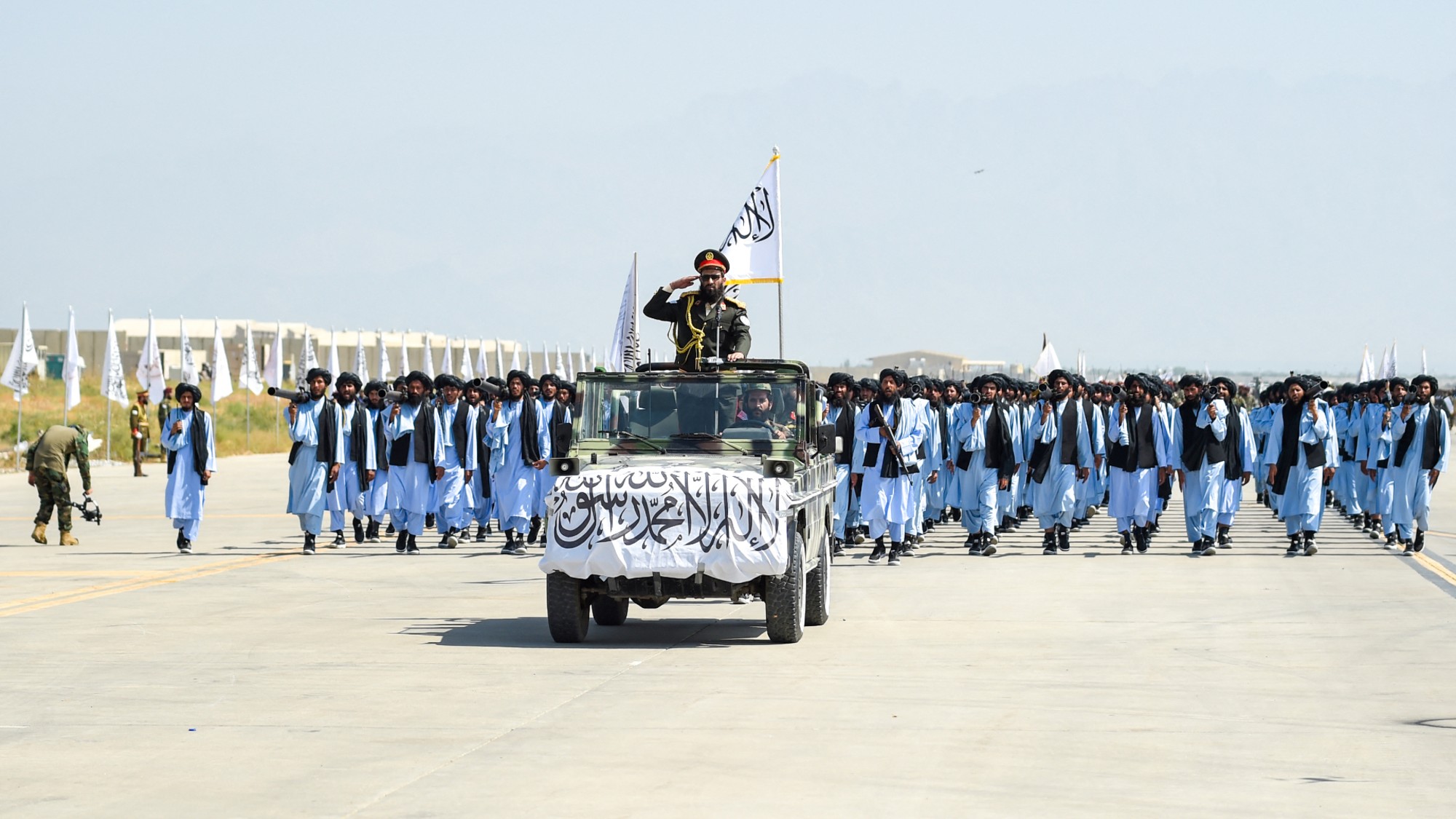 Why Russia removed the Taliban's terrorist designation
Why Russia removed the Taliban's terrorist designationThe Explainer Russia had designated the Taliban as a terrorist group over 20 years ago