How Europe put Greece on permanent life support
It's almost summer. Time for another round of Greek debt crisis talks!


If you read the news out of Europe this week, you could be forgiven for thinking you're caught in a time warp.
It's not just that the Greek government — still headed up by the Syriza party and Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras — may run out of money in June, right before it faces another round of debt payments to its creditors in July. Which is pretty much exactly what happened last summer. It's that the International Monetary Fund (IMF) is nervously trying to tell Germany and the other creditors that they're headed for another rabbit hole if this keeps up.
In July of 2015, the IMF surprised observers with a report essentially arguing that Greece's long-term fiscal position was unworkable unless the bailouts were massively increased, or Greece's debt was reduced and restructured. It was ignored. And, wouldn't you know, a year later Greece's situation is still unworkable.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
So the IMF is pressuring Germany and the creditors again, but this time with an even more dramatic position: The due dates for Greece to pay the principal on its debt need to be pushed back 30 or 40 years, and the interest it pays on that debt in the meantime needs to be fixed at 1.5 percent.
This is, of course, a sober and reasonable position, made shocking only by the absurdist Groundhog Day situation against which it stands. Germany, which is more or less the creditors' ringleader, is of course resisting.
But to get a handle on just how dumb this is, it might help to think concretely about the situation for a minute.
At the end of the day, an actual recovery for Greece looks like this: Its economy would create enough food, clothes, housing, medicine, and other goods and services to give everyone in the country a decent and at least somewhat equitable standard of living. And in the course of producing all that stuff, it would also give the vast majority of jobseekers some sort of employment. How money fits in here is equally simple: It is what is traded back and forth in exchange for all that productive work.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
What austerity does is drain the Greek economy of so much money it can't maintain that circulation. The Greek government has to hike taxes, which means taking more money out of circulation. It then has to cut spending, public investment, welfare aid programs, pensions, etc — which means putting less money into circulation. That's all so the Greek government can build up a surplus of money, which it then sends to its creditors abroad.
The problem, of course, is that the less money there is to circulate in the Greek economy, the less productive stuff people can do, and the less they can employ one another. If there's not enough money to go around, their only other option is to barter. (Which is actually happening!) Furthermore, the specific currency in this instance is the euro, which isn't just used in Greece, but throughout most of the Continent. So when the creditors get those euros, they don't necessarily invest them back into Greece. In fact, they almost certainly don't, since Greece's economy is a disaster zone and there's nothing attractive to invest in. They invest them in Germany or France or wherever.
That's why unemployment in Greece is 24.4 percent right now. That's why it was 26 percent in 2015. And why it was 26 percent, 27 percent, and 24 percent in 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively.
If fewer people are trading money for goods and services, that means the overall amount of income in the economy falls, which means there's less for the Greek government to tax. So even as it hikes taxes and cuts spending to create surplus money to give the creditors, it further damages the economy its drawing that surplus from, making it even harder to get further surpluses. This has been termed the "death spiral."
Which is why Greece, Germany and the creditors are caught in a loop of endless bailouts. With each bailout, the creditors pump euros into Greece's budget, which then go right back out again to pay the creditors for the previous bailout. And since Greece has to do another round of austerity to get each new bailout, it winds up bleeding its economy dry all over again. So instead of recovering, which economies can usually do if they're just left in peace, austerity just ensures Greece is in equally dire straits for the next round.
So this is why the IMF's idea is right: Simply slowing Greece's debt payments to a trickle is one obvious way to break the cycle.
Another option involves the European Central Bank (ECB). It actually controls the supply of currency in the eurozone, and all the national central banks — including Greece's — answer to it. If they wanted to, the Greek central bank and the ECB could inject a fresh supply of euros into Greece on their own. The most obvious way would be to promise to create new euros to buy up any new debt Greece issues, so it can start deficit spending again and rebuild public investments and welfare state aid and the like.
Eurozone elites, especially in Germany, seem to think that would lead to inflation. But there's so much slack in the Greek economy that inflation is the least of Greece's worries. Of course, it's not riskless: You could overheat the economy, at which point you really would need austerity to cool it down. But by definition, that would only happens if you've already gotten unemployment down about as low as it can go.
The point is, no one's even trying this route. The ECB itself is playing nice with Germany and the other creditors. So it's also only giving Greece fresh supplies of euros in exchange for fresh rounds of austerity.
None of this is economically necessary, even though Germany and the creditors tend to act like it is. It's a purely political choice. The eurozone has put Greece on permanent life support, draining it and then infusing it with new blood, only to drain it again, and doing enormous damage to countless Greek lives in the process.
And they've done it simply because they lack the economic literacy, the political imagination, or the simple decency to do otherwise.
Jeff Spross was the economics and business correspondent at TheWeek.com. He was previously a reporter at ThinkProgress.
-
 31 political cartoons for January 2026
31 political cartoons for January 2026Cartoons Editorial cartoonists take on Donald Trump, ICE, the World Economic Forum in Davos, Greenland and more
-
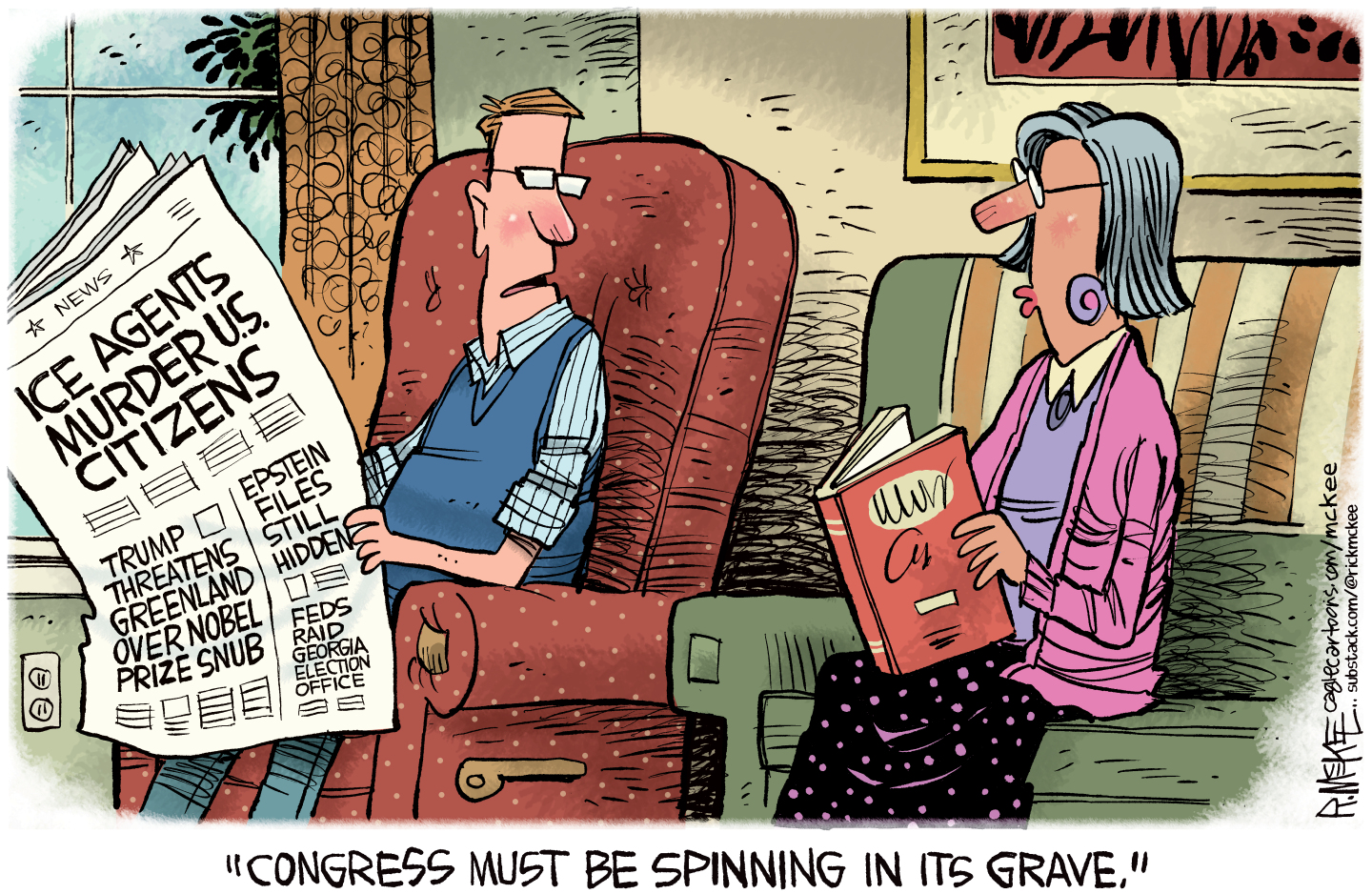 Political cartoons for January 31
Political cartoons for January 31Cartoons Saturday's political cartoons include congressional spin, Obamacare subsidies, and more
-
 Syria’s Kurds: abandoned by their US ally
Syria’s Kurds: abandoned by their US allyTalking Point Ahmed al-Sharaa’s lightning offensive against Syrian Kurdistan belies his promise to respect the country’s ethnic minorities
-
 Israel retrieves final hostage’s body from Gaza
Israel retrieves final hostage’s body from GazaSpeed Read The 24-year-old police officer was killed during the initial Hamas attack
-
 China’s Xi targets top general in growing purge
China’s Xi targets top general in growing purgeSpeed Read Zhang Youxia is being investigated over ‘grave violations’ of the law
-
 Panama and Canada are negotiating over a crucial copper mine
Panama and Canada are negotiating over a crucial copper mineIn the Spotlight Panama is set to make a final decision on the mine this summer
-
 Why Greenland’s natural resources are nearly impossible to mine
Why Greenland’s natural resources are nearly impossible to mineThe Explainer The country’s natural landscape makes the task extremely difficult
-
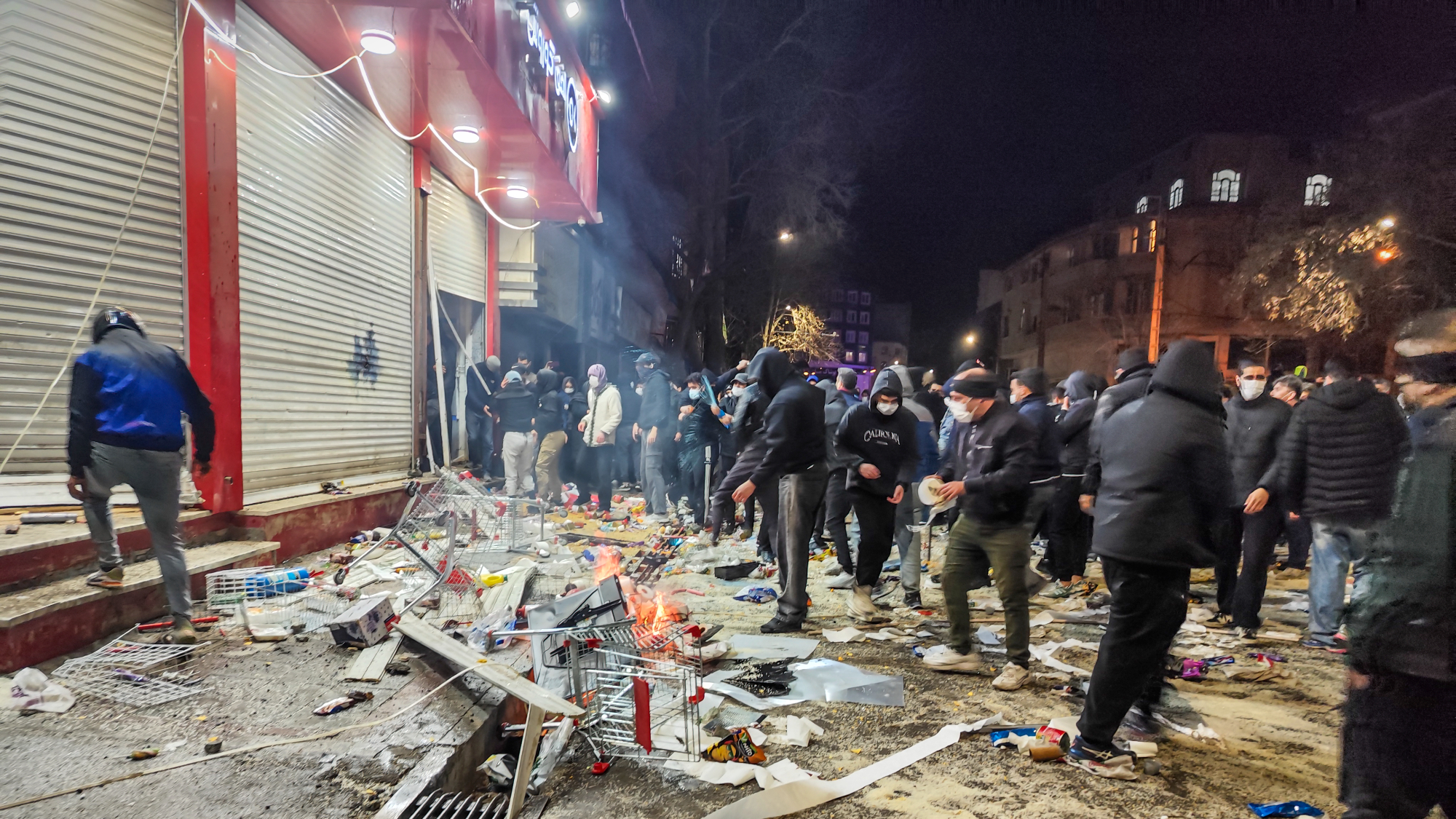 Iran cuts internet as protests escalate
Iran cuts internet as protests escalateSpeed Reada Government buildings across the country have been set on fire
-
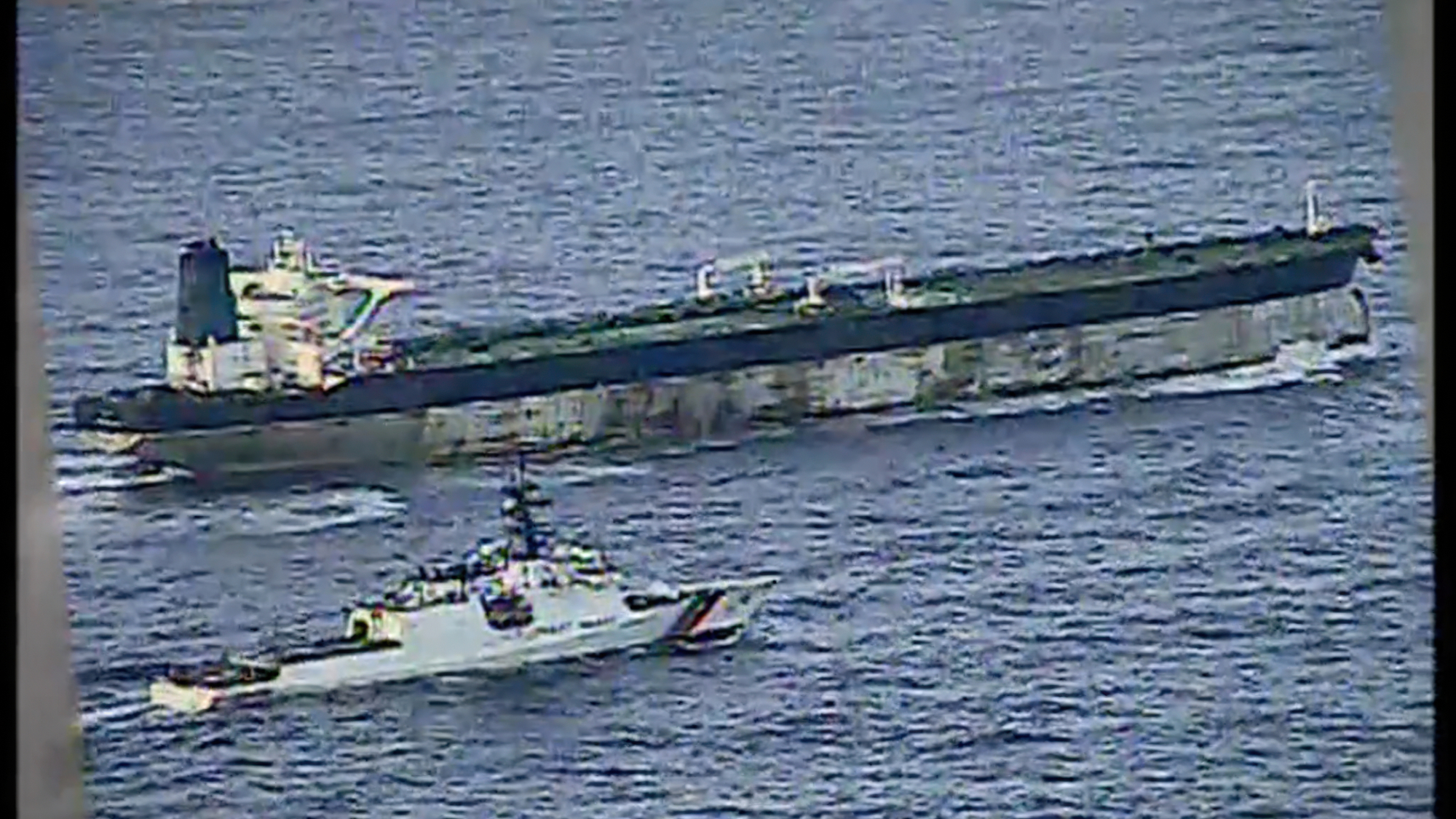 US nabs ‘shadow’ tanker claimed by Russia
US nabs ‘shadow’ tanker claimed by RussiaSpeed Read The ship was one of two vessels seized by the US military
-
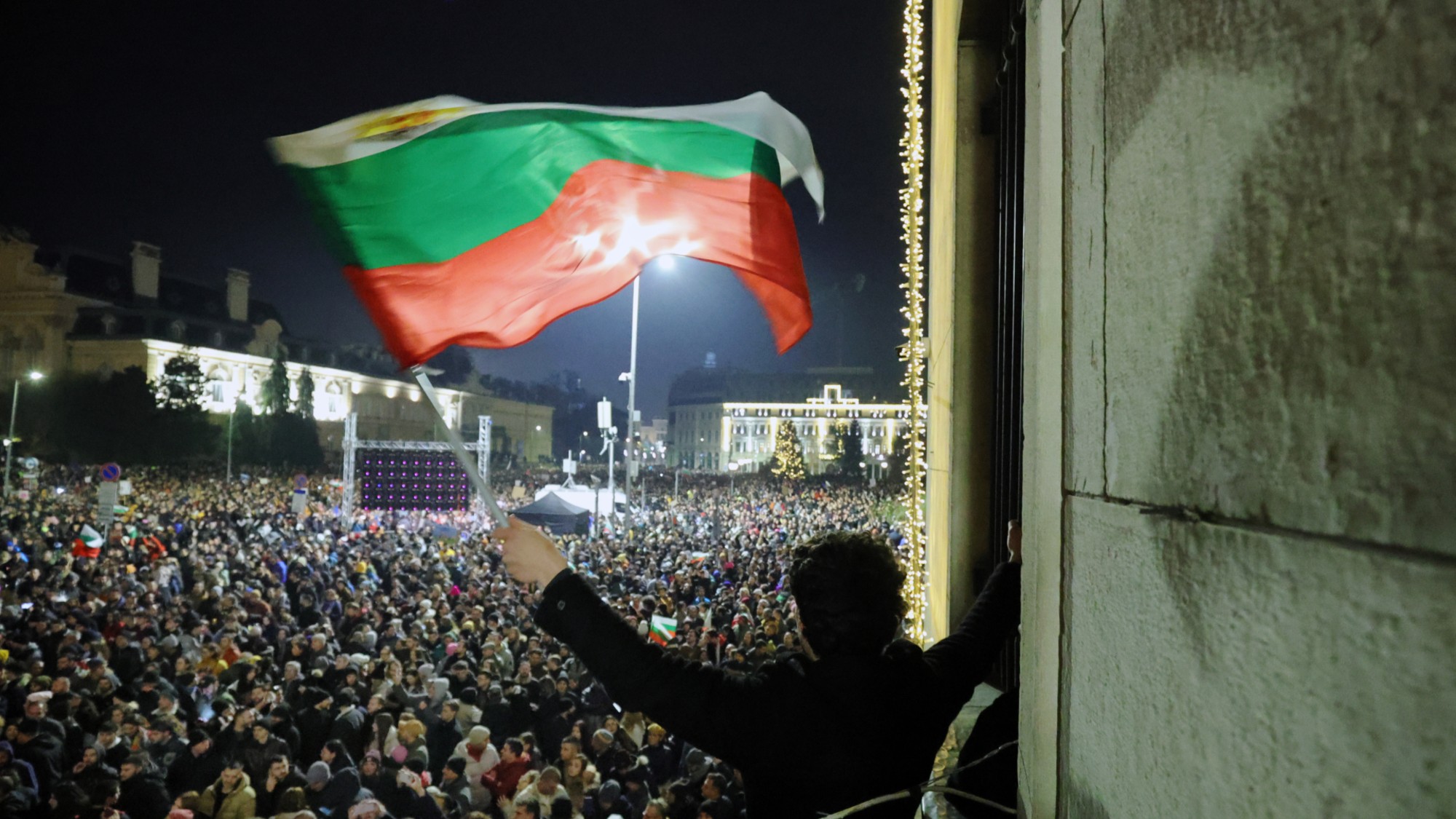 How Bulgaria’s government fell amid mass protests
How Bulgaria’s government fell amid mass protestsThe Explainer The country’s prime minister resigned as part of the fallout
-
 Femicide: Italy’s newest crime
Femicide: Italy’s newest crimeThe Explainer Landmark law to criminalise murder of a woman as an ‘act of hatred’ or ‘subjugation’ but critics say Italy is still deeply patriarchal
