The Biggest Loser doesn't actually work, according to science
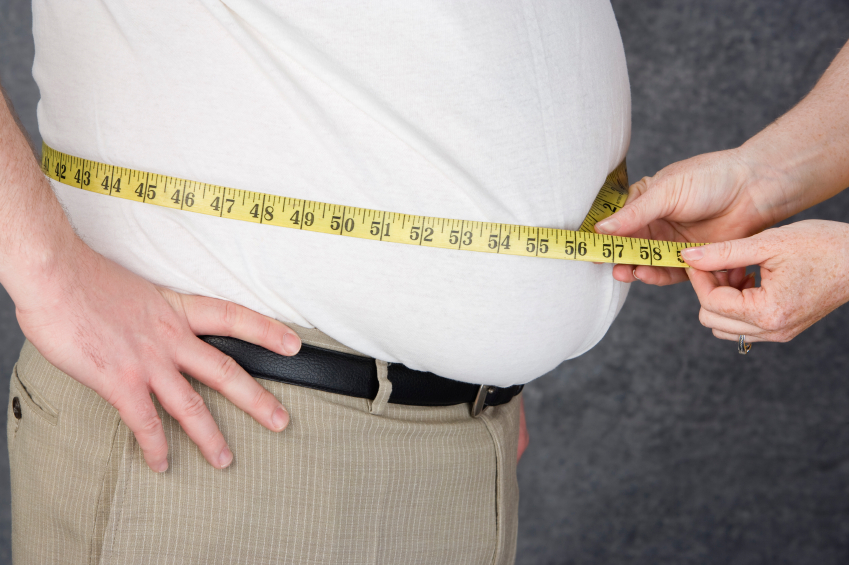


Scientists are using reality TV to crack the mysteries of the human body — specifically, why people tend to gain so much weight back after major weight losses. Following contestants from NBC's The Biggest Loser, researchers concluded that it is because bodies biologically fight tooth-and-nail to climb back to their original weight.
The problem mainly lies with metabolisms, which slow radically as the body loses weight so that they eventually don't burn enough calories to maintain the thinner body size. Former contestant Danny Cahill, 46, for example, weighed 430 pounds before The Biggest Loser, 191 at the finale of the show, and six years later now weighs 295 pounds. His body burns 800 fewer calories a day than would be expected for a man of his size.
"All my friends were drinking beer and not gaining massive amounts of weight. The moment I started drinking beer, there goes another 20 pounds. I said, 'This is not right. Something is wrong with my body,''' Cahill said.
Subscribe to The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
It turns out, he's right. "This is a subset of the most successful [dieters]," Dr. David Ludwig, who was not involved in the study, said of the Biggest Loser findings. "If they don't show a return to normal in metabolism, what hope is there for the rest of us?"
But with the problem identified, Ludwig adds researchers and people concerned about their weight shouldn't lose hope. "[It] shouldn't be interpreted to mean we are doomed to battle our biology or remain fat," Ludwig said. "It means we need to explore other approaches."
Learn more about what those approaches might be, and the science behind weight gain and loss, at The New York Times.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Jeva Lange was the executive editor at TheWeek.com. She formerly served as The Week's deputy editor and culture critic. She is also a contributor to Screen Slate, and her writing has appeared in The New York Daily News, The Awl, Vice, and Gothamist, among other publications. Jeva lives in New York City. Follow her on Twitter.
-
 The NCAA is a 'billion-dollar sports behemoth' that 'should not be a nonprofit'
The NCAA is a 'billion-dollar sports behemoth' that 'should not be a nonprofit'Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
 Trump picks conservative BLS critic to lead BLS
Trump picks conservative BLS critic to lead BLSspeed read He has nominated the Heritage Foundation's E.J. Antoni to lead the Bureau of Labor Statistics
-
 What's a pocket rescission and can Trump use one?
What's a pocket rescission and can Trump use one?The Explainer The White House may try to use an obscure and prohibited trick to halt more spending
-
 US, China extend trade war truce for 90 days
US, China extend trade war truce for 90 daysSpeed Read The triple-digit tariff threat is postponed for another three months
-
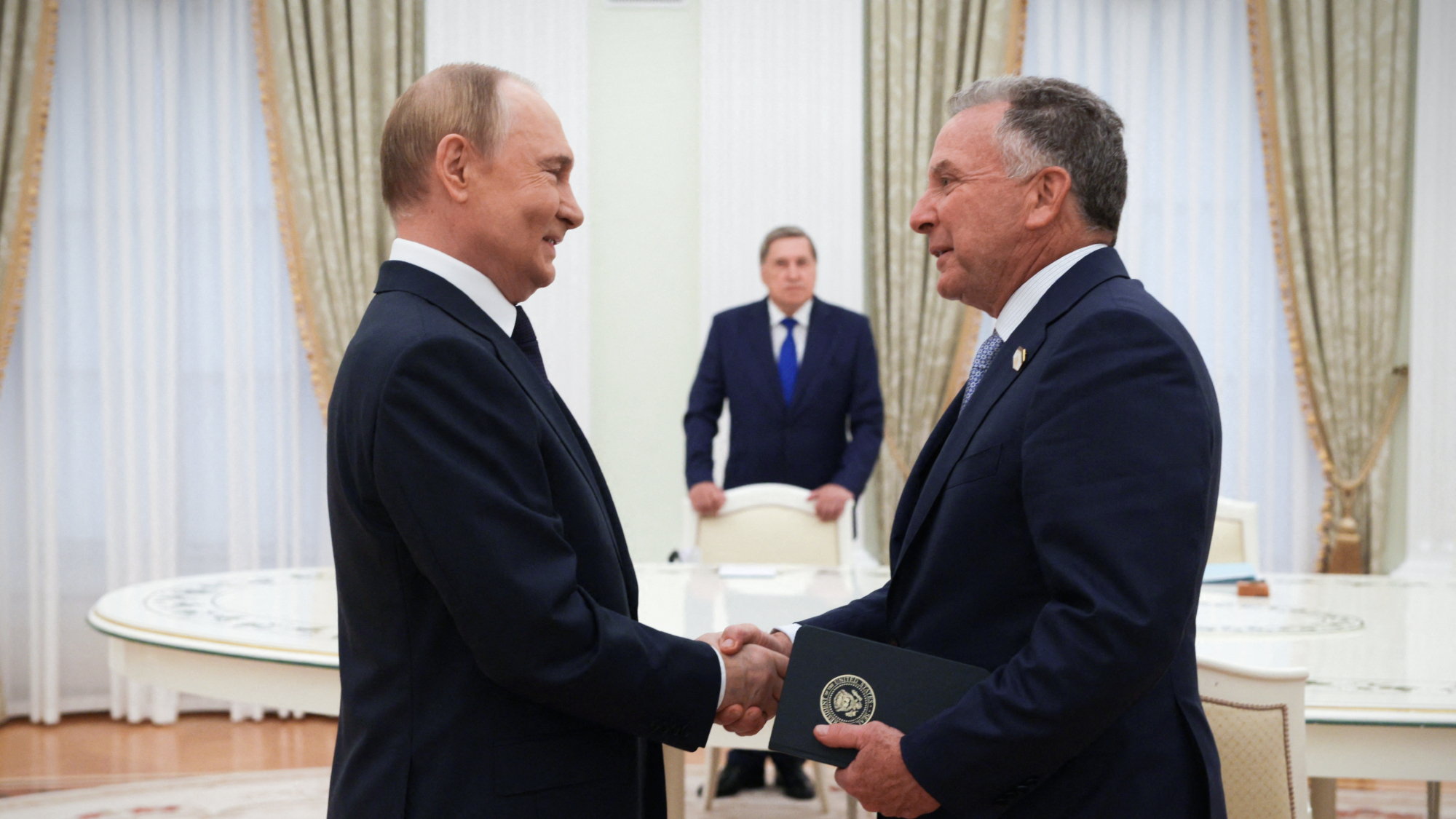 Europe counters Putin ahead of Trump summit
Europe counters Putin ahead of Trump summitSpeed Read President Trump will meet with Russian President Vladimir Putin in Alaska this week for Ukraine peace talks
-
 Israeli security cabinet OKs Gaza City takeover
Israeli security cabinet OKs Gaza City takeoverSpeed Read Netanyahu approved a proposal for Israeli Defense Forces to take over the largest population center in the Gaza Strip
-
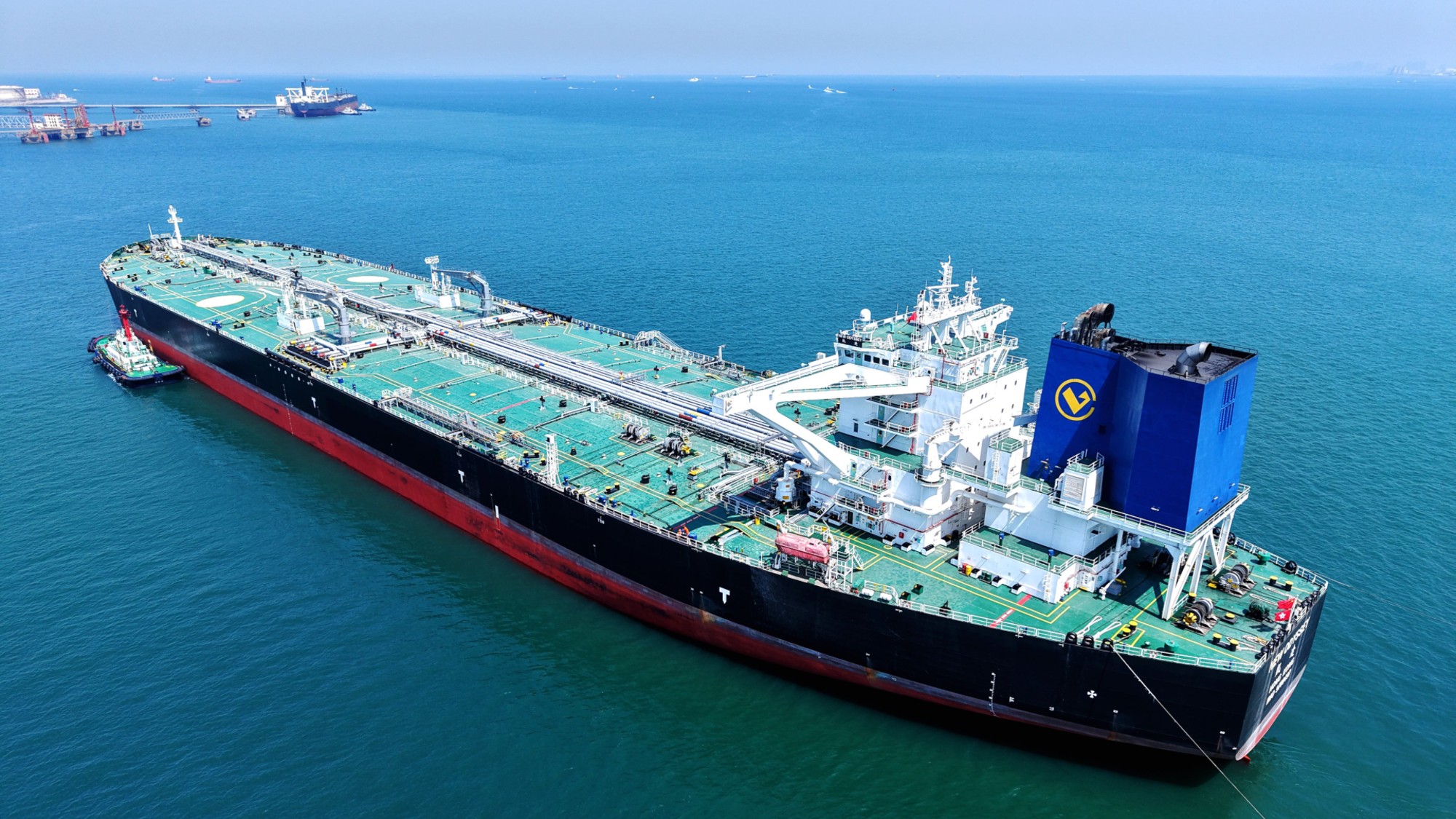 How China uses 'dark fleets' to circumvent trade sanctions
How China uses 'dark fleets' to circumvent trade sanctionsThe Explainer The fleets are used to smuggle goods like oil and fish
-
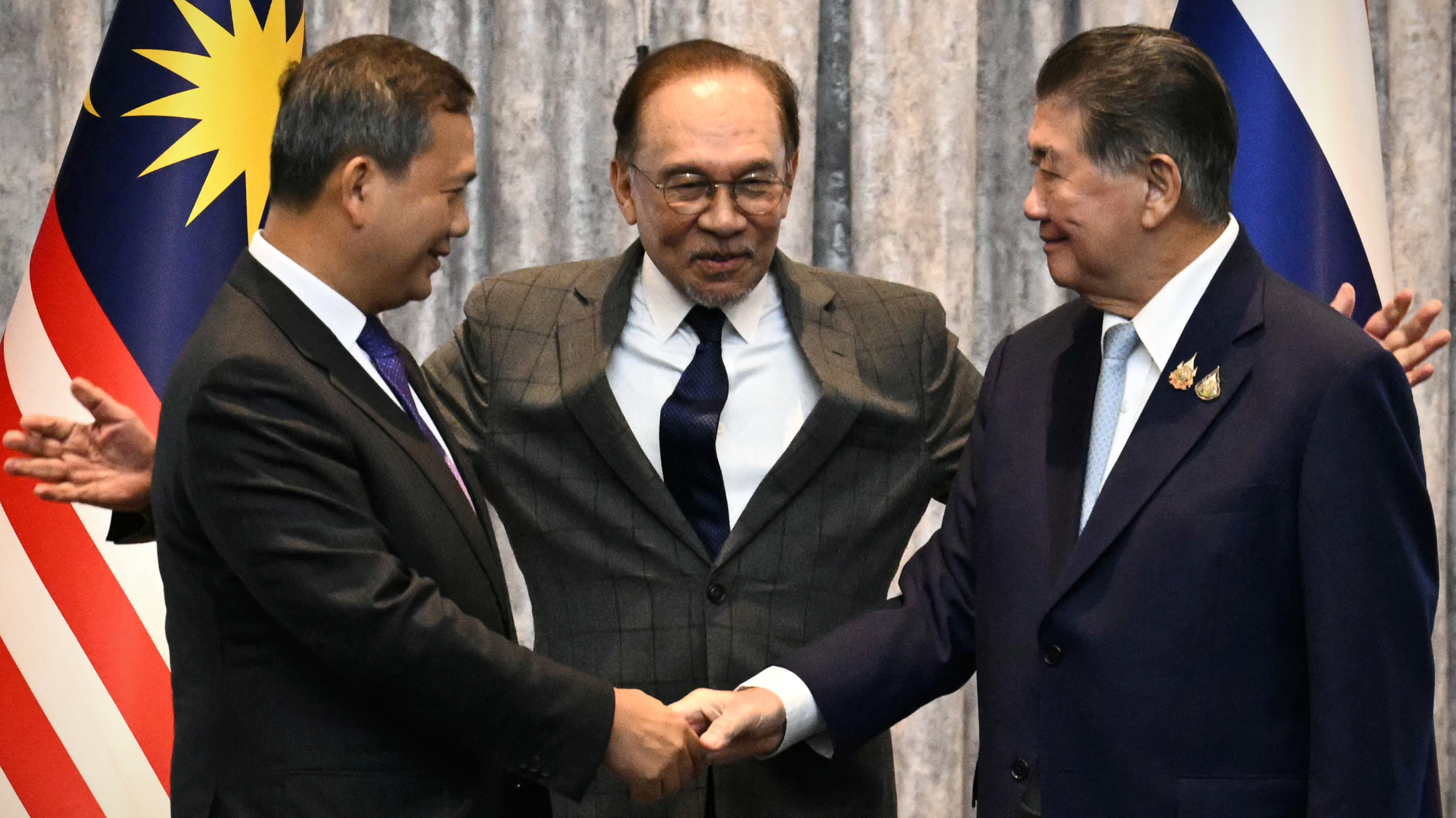 Thailand, Cambodia agree to ceasefire in border fight
Thailand, Cambodia agree to ceasefire in border fightSpeed Read At least 38 people were killed and more than 300,000 displaced in the recent violence
-
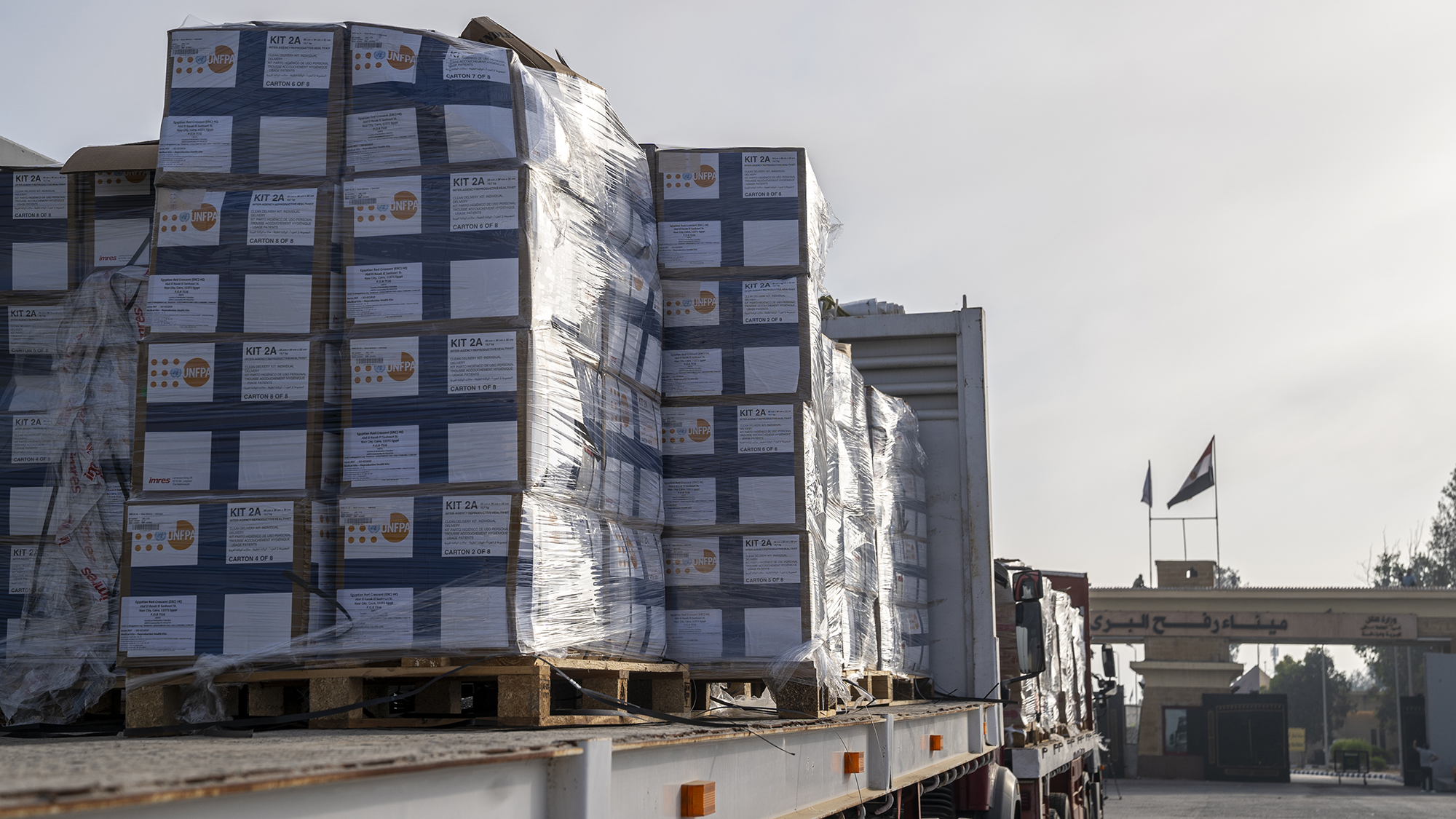 Israel 'pauses' Gaza military activity as aid outcry grows
Israel 'pauses' Gaza military activity as aid outcry growsSpeed Read The World Health Organization said malnutrition has reached 'alarming levels' in Gaza
-
 US and EU reach trade deal
US and EU reach trade dealSpeed Read Trump's meeting with European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen resulted in a tariff agreement that will avert a transatlantic trade war
-
 At least 12 dead in Thai-Cambodian clashes
At least 12 dead in Thai-Cambodian clashesSpeed Read Both countries accused the other of firing first
